Lactobacillus acidophilus
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | |
|---|---|
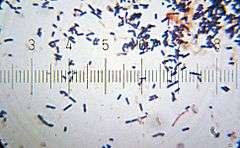 | |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus Numbered ticks are 11 µm (micrometers) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Firmicutes |
| Class: | Bacilli |
| Order: | Lactobacillales |
| Family: | Lactobacillaceae |
| Genus: | Lactobacillus |
| Species: | L. acidophilus |
| Binomial name | |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus (Moro 1900) Hansen & Mocquot 1970 | |
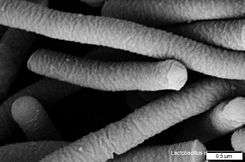
Lactobacillus acidophilus (New Latin 'acid-loving milk-bacillus') is a species of gram positive bacteria in the genus Lactobacillus. L. acidophilus is a homofermentative, microaerophilic species, fermenting sugars into lactic acid, and grows readily at rather low pH values (below pH 5.0) and has an optimum growth temperature of around 37 °C (99 °F).[1] L. acidophilus occurs naturally in the human and animal gastrointestinal tract and mouth.[2] Some strains of L. acidophilus may be considered to have probiotic characteristics.[3] These strains are commercially used in many dairy products, sometimes together with Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus in the production of acidophilus-type yogurt. Its genome has been sequenced.[4]
Health effects
Some strains of L. acidophilus have been studied extensively for health effects. The Mayo Clinic publishes a list of disorders for which L. acidophilus has been tested, grading the evidence for each use from strong evidence of effectiveness, through unclear, down to strong evidence of ineffectiveness.[5] According to the list there is good (rather than strong) evidence supporting the use of L. acidophilus or yogurt enriched with it for the treatment of some vaginal infections; effectiveness for other conditions ranges from unclear to fair negative evidence.
A blend of bacterial strains including L. acidophilus NCFM decreased the incidence of pediatric diarrhea. L. acidophilus led to a significant decrease in levels of toxic amines in the blood of dialysis patients with small bowel bacterial overgrowth. At adequate daily feeding levels, L. acidophilus may facilitate lactose digestion in lactose-intolerant subjects.[6]
The Mayo Clinic lists use of L. acidophilus for heart disease among those "based on tradition or scientific theories" that "often have not been thoroughly tested in humans, and safety and effectiveness have not always been proven."[5]
Uses for lactose intolerance
There are many fermented dairy products that use L. acidophilus including yogurt and some types of cheese. Sweet acidophilus milk is consumed by individuals who suffer from lactose intolerance or maldigestion, which occurs when enzymes (lactase) cannot break down lactose (milk sugar) in the intestine. Failure to digest lactose results in discomfort, cramps and diarrhea.[7] Some bacteria have been shown to improve lactose digestion by providing β-galactosidase, while some L. acidophilus strains have been linked to improvement in symptoms and indicators of lactose indigestion.[8]
Vaginal microbiota
Lactobacillus acidophilus is part of the vaginal microbiota along with other species in the genus including Lactobacillus crispatus, Lactobacillus gasseri, Lactobacillus jensenii, and Lactobacillus iners.[4][9][10][11] In lab experiments, L. acidophilus seemed to decrease Candida albicans’ ability to adhere to vaginal epithelial cells; however, L. acidophilus’ role in preventing yeast infections is unclear because this species of Lactobacilli has also been found not to have a very strong ability to adhere to (and thereby colonize) the vaginal cells.[12]
Side effects
Although probiotics are generally safe, when they are used by oral administration there is a small risk of passage of viable bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the blood stream (bacteremia), which can cause adverse health consequences.[13] Some people, such as those with a compromised immune system, short bowel syndrome, central venous catheters, cardiac valve disease and premature infants, may be at higher risk for adverse events.[14] In children with lowered immune systems or who are already critically ill, consumption of probiotics may rarely cause bacteremia or fungemia, leading to sepsis, which is a potentially fatal disease.[15] Scant complaints of mild gastrointestinal discomfort or gas have been noted.[16]
Therapeutic applications
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a constituent in VSL#3. This proprietary, standardized, formulation of live bacteria may be used in combination with conventional therapies to treat ulcerative colitis.[17]
See also
References
- ↑ Bâati, L. ̈L.; Fabre-Gea, C.; Auriol, D.; Blanc, P. J. (2000). "Study of the cryotolerance of Lactobacillus acidophilus: Effect of culture and freezing conditions on the viability and cellular protein levels". International Journal of Food Microbiology. 59 (3): 241–247. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00361-5. PMID 11020044.
- ↑ "Bacteria Genomes – Lactobacillus acidophilus". European Bioinformatics Institute. Retrieved 2007-08-22.
- ↑ Ljungh A, Wadström T (2006). "Lactic acid bacteria as probiotics". Curr Issues Intest Microbiol. 7 (2): 73–89. PMID 16875422.
- 1 2 Fijan, Sabina (2014). "Microorganisms with Claimed Probiotic Properties: An Overview of Recent Literature". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 11 (5): 4745–4767. doi:10.3390/ijerph110504745. ISSN 1660-4601. PMC 4053917
 . PMID 24859749.
. PMID 24859749. - 1 2 "Mayo Clinic: Evidence – Lactobacillus acidophilus". Retrieved May 25, 2010.
- ↑ Sanders ME, Klaenhammer TR (2001). "Invited review: the scientific basis of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM functionality as a probiotic". J Dairy Sci. 84 (2): 319–331. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(01)74481-5. PMID 11233016.
- ↑ de Roos N, Katan M (1 February 2000). "Effects of probiotic bacteria on diarrhea, lipid metabolism, and carcinogenesis: a review of papers published between 1988 and 1998". Am J Clin Nutr. 71 (2): 405–11. PMID 10648252.
- ↑ Yuan-Kun Lee (2009). Handbook of Probiotics (2nd ed.). Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 441–443. ISBN 978-0-470-13544-0.
- ↑ Ratner, Adam J.; Aagaard, Kjersti; Riehle, Kevin; Ma, Jun; Segata, Nicola; Mistretta, Toni-Ann; Coarfa, Cristian; Raza, Sabeen; Rosenbaum, Sean; Van den Veyver, Ignatia; Milosavljevic, Aleksandar; Gevers, Dirk; Huttenhower, Curtis; Petrosino, Joseph; Versalovic, James (2012). "A Metagenomic Approach to Characterization of the Vaginal Microbiome Signature in Pregnancy". PLoS ONE. 7 (6): e36466. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036466. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 22719832.
- ↑ Senok, Abiola C; Verstraelen, Hans; Temmerman, Marleen; Botta, Giuseppe A; Senok, Abiola C (2009). "Probiotics for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD006289. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006289.pub2. PMID 19821358.
- ↑ Nardis, C.; Mastromarino, P.; Mosca, L. (September–October 2013). "Vaginal microbiota and viral sexually transmitted diseases". Annali di Igiene. 25 (5): 443–56. doi:10.7416/ai.2013.1946 (inactive 2016-10-14). PMID 24048183.
- ↑ Can Yogurt Prevent Yeast Infections?. Planned Parenthood Advocates of Arizona. 28 February 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ↑ Durchschein F, Petritsch W, Hammer HF (2016). "Diet therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases: The established and the new". World J Gastroenterol (Review). 22 (7): 2179–94. doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2179 (inactive 2016-10-14). PMC 4734995
 . PMID 26900283.
. PMID 26900283. - ↑ Doron S, Snydman DR (2015). "Risk and safety of probiotics.". Clin Infect Dis (Review). 60 Suppl 2: S129–34. doi:10.1093/cid/civ085. PMC 4490230
 . PMID 25922398.
. PMID 25922398. - ↑ Singhi SC, Kumar S (2016). "Probiotics in critically ill children". F1000Res (Review). 5: 407. doi:10.12688/f1000research.7630.1. PMC 4813632
 . PMID 27081478.
. PMID 27081478. - ↑ "Lactobacillus acidophilus". Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database, Consumer Version. Medline Plus. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
- ↑ Ghouri, Yezaz A; Richards, David M; Rahimi, Erik F; Krill, Joseph T; Jelinek, Katherine A; DuPont, Andrew W (9 December 2014). "Systematic review of randomized controlled trials of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in inflammatory bowel disease". Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 7: 473–487. doi:10.2147/CEG.S27530. PMC 4266241
 . PMID 25525379.
. PMID 25525379.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lactobacillus acidophilus. |
- Lactobacillus at MedlinePlus
- Lactobacillus acidophilus at University of Maryland Medical Center
- Lactobacillus acidophilus from the U. of Wisconsin
- Global analysis of carbohydrate utilization by Lactobacillus acidophilus using cDNA microarrays
- Safety and protective effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus casei used as probiotic agent in vivo
- Pictures and research on Lactobacillus acidophilus
- Type strain of Lactobacillus acidophilus at BacDive – the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase