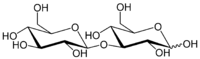
Laminaribiose
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-[(3R,4S,5R,6R)-2,3,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-4-yl]oxyoxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Other names
3-beta-D-Glucosyl-D-glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
| 34980-39-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 388710 |
| PubChem | 439637 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g/mol |
| Density | 1.768 g/mL |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Laminaribiose is a disaccharide which is used notably in the agricultural field and as an antiseptic. It is in general obtained by hydrolysis or by acetolysis of natural polysaccharides of plant origin. [1] It is also a product of the caramelization of glucose. [2]
References
- ↑ US 6632940
- ↑ Sugisawa, Hirqshi; Edo, Hiroshi (1966). "The Thermal Degradation of Sugars I. Thermal Polymerization of Glucose". Journal of Food Science. 31 (4): 561. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1966.tb01905.x.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.