List of software palettes
Computer systems that use a 4-bit or 8-bit pixel depth can display up to 16 or 256 colors simultaneously. Many personal computers in the early 1990s displayed at most 256 different colors, freely selected by software (either by the user or by a program) from their wider hardware's RGB color palette.
Usual selections of colors in limited subsets (generally 16 or 256) of the full palette includes some RGB level arrangements commomly used with the 8-bit palettes as master palettes or universal palettes (i.e., palettes for multipurpose uses).
These are some representative software palettes, but any selection can be made in such type of systems.
For specific hardware color palettes, see the List of monochrome and RGB palettes, List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes, the List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes and the List of videogame consoles palettes articles.
Each palette is represented by an array of color patches. A one-pixel size version appears below each palette, to make it easy to compare palette sizes.
For each unique palette, an image color test chart and sample image (truecolor original follows) rendered with that palette (without dithering) are given. The test chart shows the full 8-bit, 256 levels of the red, green, and blue (RGB) primary colors and cyan, magenta, and yellow complementary colors, along with a full 8-bit, 256 levels grayscale. Gradients of RGB intermediate colors (orange, lime green, sea green, sky blue, violet and fuchsia), and a full hue spectrum are also present. Color charts are not gamma corrected.
These elements illustrate the color depth and distribution of the colors of any given palette, and the sample image indicates how the color selection of such palettes could represent real-life images.
System specifics
These are selections of colors officially employed as system palettes in some popular operating systems for personal computers that support 8-bit displays.
Microsoft Windows default 16-color palette
Used by this platform as a roughly backward compatible palette for the CGA, EGA and VGA text modes, but with colors arranged in a different order. Also is the default palette for 16 color icons.
The corresponding indices into this palette are:
0 — black 8 — gray 1 — maroon 9 — red 2 — green 10 — lime 3 — olive 11 — yellow 4 — navy 12 — blue 5 — purple 13 — fuchsia 6 — teal 14 — aqua 7 — silver 15 — white
Microsoft Windows default 20-color palette
In 256-color mode, there are four additional standard Windows colors, twenty system reserved colors in total;[1] thus the system leaves 236 palette indexes free for applications to use. The system color entries inside a 256-color palette table are the first ten plus the last ten. In any case, the additional system colors do not seem to add a sharp color richness: they are only some intermediate shades of grayish colors.
The complete 20-color Windows' system palette is:
0 — black 246 — cream 1 — dark red 247 — medium grey 2 — dark green 248 — dark grey 3 — dark yellow 249 — red 4 — dark blue 250 — green 5 — dark magenta 251 — yellow 6 — dark cyan 252 — blue 7 — light grey 253 — magenta 8 — money green 254 — cyan 9 — sky blue 255 — white
Apple Macintosh default 16-color palette
When Apple Computer introduced the Macintosh II in 1987, this 16-color palette was included in System 4.1.
0 — white 8 — green 1 — yellow 9 — dark green 2 — orange 10 — brown 3 — red 11 — tan 4 — magenta 12 — light grey 5 — purple 13 — medium grey 6 — blue 14 — dark grey 7 — cyan 15 — black
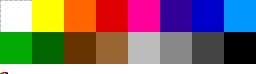
RISC OS default palette
Acorn RISC OS 2.x and 3.x provided this 16-color palette:[2]
0 — white 8 — dark blue 1 9 — yellow 2 10 — green 3 11 — red 4 12 — beige 5 13 — dark green 6 14 — orange 7 — black 15 — light blue
RGB arrangements
These are selections of colors based in evenly ordered RGB levels which provide complete RGB combinations, mainly used as master palettes to display any kind of image within the limitations of the 8-bit pixel depth.
6 level RGB
Having six levels for every primary, with 63 = 216 combinations. The index can be addressed by (36×R)+(6×G)+B, with all R, G and B values in a range from 0 to 5. Intended as homogeneous RGB cube, it gives six true grays. Also there is room for another sorts of 40 colors, so this disposition wastes many places in the 8-bit palette.
Systems that use this software palette are:
- Web palette
- Apple Macintosh 256 color default palette, it also contains four gradients of ten shades each for gray, red, green and blue.
6-7-6 levels RGB
This palette is constructed with six levels for red and blue primaries and seven levels for the green primary, giving 6×7×6 = 252 combinations. The index can be addressed by (42×R)+(6×G)+B, with R and B values in a range from 0 to 5 and G in a range from 0 to 6. The same case as the former, but with an added level of green due to the greater sensibility of the normal human eye to this frequency.
It does not provide true grays, but remaining indexes can be filled with four intermediate grays. In any case, there is little room for any other color.
6-8-5 levels RGB
This palette is constructed with six levels for red, eight levels for green and five levels for the blue primaries, giving 6×8×5 = 240 combinations. The index can be addressed by (40×R)+(5×G)+B, with R ranging from 0 to 5, G from 0 to 7 and B from 0 to 4. Levels are chosen in function of sensibility of the normal human eye to every primary color.
Also, it does not provide true grays. Remaining indexes can be filled with sixteen intermediate grays or other fixed colors. In fact, this is the best balanced RGB master software palette, in a compromise between the RGB arrangement based in the human eye's sensibility and a sufficient remaining palette entries for another purposes.
8-8-4 levels RGB
The 8-8-4 level RGB use eight levels for each of the red and green color components (3+3 high order bits), and four levels (2 low order bits) for the blue component, due to the lesser sensitivity of the normal human eye to this primary color. This results in an 8×8×4 = 256-color palette as follows:
This RGB software palette occupies the full 8-bit range of possible palette entries, so there is no room for other fixed colors. Software using this palette must draw their user interface elements with the same colors used to show pictures. Also again, it does not provide true grays.
Other common uses of software palettes
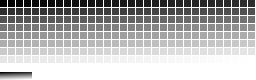
Grayscale palettes
Simple palette made doing every triplet RGB primaries having equal values as a continuous gradient from black to white through the full available palette entries. Here is the 8-bit, 256 levels palette:
Used to display pure grayscale TIFF or JPEG images, for example.
Color gradient palettes
Palettes made of a continuous color gradient from darkest to lightest arbitrary hues. The pixel data is treated as if it were grayscale, but the color table plays with RGB color combinations, not only gray. The relationship between the original luminance and the mapped one can vary, but the lighting scale is preserved along all the palette entries.
One very common case of such palettes is the sepia tone palette, which gives an image an old fashioned and aged look (left). Another gradient example, based on blue hues, is presented here (right), but any hue or mixing of hues can be used. Many cell phones with built-in cameras have options to take colorized photos using this technique.
Adaptive palettes
Those whose whole number of available indexes are filled with RGB combinations selected from the statistical order of appearance (usually balanced) of a concrete full true color original image. There exist many algorithms to pick the colors through color quantization; one well known is the Heckbert's median-cut algorithm. Here is the 8-bit, 256 color palette used with the color test chart and the image sample above:
Adaptive palettes only work well with a unique image. Trying to display different images with adaptive palettes over an 8-bit display usually results in only one image with correct colors, because the images have different palettes and only one can be displayed at a time. Here is an example of what happens when an indexed color image is displayed with any color palette that is not its own adaptive palette:
False color palettes
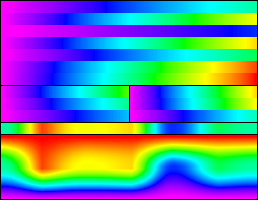
Arbitrary gradient color scales, usually 256 shades, with no relationship with real colors of a given image. They are employed to artificially colorize a grayscale image to reveal details and/or to map the pixel level values to amounts of some physical magnitude (potential, temperature, altitude, etc.)
Note, in the example above, that new details can be seen as blue over magenta in the background's dark areas of the original photograph.
Here is the 8-bit, 256 color gradient palette used with the color test chart and the image sample above:
There exist many false color palettes, some of them standardized, used mainly in scientific applications: astronomy and radioastronomy, satellite land imaging, thermography, study of materials, tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in medicine, etc.
Notes
- ↑ The Palette Manager: How and Why It Does What It Does, the article is in Windows Write file inside self-extracting archive.
- ↑ House of Mabel: RISC OS 2







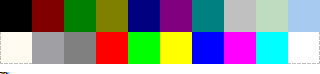



















_palette_sample_image.png)
_palette_sample_image.png)
_palette.png)
_palette.png)