LitPol Link
| LitPol Link | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Lithuania; Poland |
| Coordinates |
54°47′56″N 24°15′19″E / 54.79889°N 24.25528°E 54°26′34″N 23°58′32″E / 54.44278°N 23.97556°E 54°26′19″N 23°58′02″E / 54.43861°N 23.96722°E 53°46′25″N 22°19′20″E / 53.77361°N 22.32222°E 53°01′38″N 23°02′43″E / 53.02722°N 23.04528°E 53°49′39″N 20°20′51″E / 53.82750°N 20.34750°E |
| General direction | east–west–east |
| From | Kruonis |
| Passes through |
Alytus Ełk |
| To |
Narew Matki |
| Ownership information | |
| Owner | LitPol Link |
| Partners |
PSE-Operator Litgrid |
| Construction information | |
| Construction started | 5 May 2014 |
| Construction cost | € 340 mill.[1] |
| Technical information | |
| Type | overhead transmission line |
| Type of current | HVDC ( back-to-back) |
| Total length | 341 km (212 mi) |
| Power rating |
500 MW (current) 1,000 MW (planned) |
| AC Voltage |
330& kV in Lithuania 400 kV in Poland |
| DC Voltage | ±70 kV |
| Number of circuits | 2 |
The Lithuania–Poland interconnection LitPol Link represents electricity link between the Baltic transmission system (part of the IPS/UPS system) and the synchronous grid of Continental Europe. Currently the first stage of the project has been completed that has a capacity of 500 MW.
History
In 2000, European Commission and the EBRD agreed to finance a feasibility study on the Poland–Lithuania transmission interconnection. The study was completed in September 2002.[2] The connection is expected to increase Poland's electricity interconnection level from 2% to 4%.[3] Parts of LitPol are on the EU "Projects of Common Interest" list in November 2015.[4]
On 29 September 2006 Polish President Lech Kaczyński and Lithuanian President Valdas Adamkus signed joint declaration on the joint power grid project during their meeting in Warsaw.[5] The memorandum of understanding to establish a joint interconnection operator was signed between Lietuvos Energija and Polish PSE-Operator in Vilnius on 8 December 2006. Project Company Shareholding Agreement signed on 12 February 2008 in Warsaw.[6] The joint project company LitPol Link was founded on 19 May 2008.[7]
Aiming to build a 400 kV overhead line between Ełk and Łomża PSE-Operator signed a contract with the Polish construction company PBE ELBUD Group on 12 September 2011.[8] During start of 2013 Lithuanian transmission system operator Litgrid awarded ABB Group a $110 million contract to supply and install the first HVDC converter station in proximity of Alytus, Lithuania.[9]
Construction of the link commenced in the Alytus district on 5 May 2014.[10] LitPol electricity link started operations on 9 December 2015 the same day transmitting up to 200 MW power from Poland to Lithuania.[11]
The second part of project (another 500 MW capacity link) is planned to have a different route through Marijampolė. The full plan of second part is scheduled to be reviewed at the end of 2016.[12]
Technical features
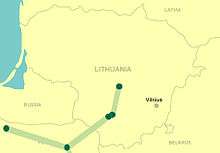
The interconnection represents 53-kilometre (33 mi) double circuit 330 kV line Kruonis–Alytus, 1000 MW back-to-back converter in Alytus and 48-kilometre (30 mi) double circuit 400 kV line from Alytus to the Lithuania–Poland border on Lithuanian side and 106-kilometre (66 mi) double circuit 400 kV line border–Ełk on Polish side.[13]
According to the pre-feasibility study cost of the interconnection estimated €237 million. With intention to enhance existing energy infrastructure including Poland–Germany and Poland–Czech Republic upgrades in addition Polish TSO invested €650 million and Lithuanian TSO €262 million.[7] Lithuania–Poland interconnection has been listed as a EU Trans-European Networks project. The interconnection initial capacity is 500 MW with transmission capacity upgrade up to 1000 MW possible after completion of second HVDC back-to-back station.[14][15]
HVDC Back-to-back station
The Alytus HVDC back-to-back station is located 600 metres (2,000 ft) southwest of the existing 330 kV-substation which has been extended as well. It consists of two converters each rated for 500 MW transmission power. The facility is 200 metres (660 ft) long and 170 metres (560 ft) wide.[16]
Project company
LitPol Link was founded by PSE-Operator and Litgrid with equal stakes. The company is based in Warsaw.[14] Acting Managing Director of LitPol Link Mr.Artūras Vilimas.[17]
See also
- Energy in Lithuania
- Estlink (between Estonia and Finland)
- NordBalt (between Lithuania and Sweden)
- SwePol (between Poland and Sweden)
- Lithuania-Poland pipeline (proposed natural gas interconnection between Lithuania and Poland)
References
- ↑ Lithuania's Litgrid secures EUR 50 million from NIB to fund LitPol Link
- ↑ Mozer, Zygmunt (23 October 2007). "Current status of the LitPol project" (PPT). PSE SA. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- ↑ "Achieving the 10% electricity interconnection target" page 5+8. European Commission, 25 February 2015.
- ↑ "Union list of projects of common interest" page 10. European Commission, 18 November 2015.
- ↑ "Poland, Lithuania agree to hook up power grids". Deutsche Presse-Agentur. 29 September 2006. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- ↑ "Poland, Lithuania clinch power link deal". Power Engineering International. PennWell Corporation. 13 February 2008. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- 1 2 "Polish, Lithuanians in energy venture". The Associated Press. 19 May 2008. Archived from the original on 14 February 2010. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- ↑ "Poland picks contractor to build power link with Lithuania". Polish News Bulletin. 14 September 2011. (subscription required). Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- ↑ "ABB to install 500 MW high-voltage converter station in Lithuania". The Lithuania Tribune. 18 February 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- ↑ "Pradedama "LitPol Link" statyba" [Construction of LitPol Link starts]. Verslo žinios (in Lithuanian). 2014-05-05. Retrieved 2015-12-10.
- ↑ "Russia's Power Grip Over Baltics Ending With Billion-Euro Cables". Bloomberg. 9 December 2015. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- ↑ Šiaurės rytų Lenkija įvertino „LitPol Link“ naudą
- ↑ Paškevičius, Vladas (26 January 2006). "Lithuanian power system and integration into European Union electricity market" (PPT). Lietuvos Energija. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- 1 2 "Lithuania, Poland sign power deal, spurring nuclear plan". Forbes. 12 February 2008. Archived from the original on 23 May 2011. Retrieved 16 February 2008.
- ↑ "Phase I: present status of the electricity sector in the EU Member States surrounding the Baltic Sea, including Norway, Belarus, Kaliningrad region and Ukraine; main gaps and bottlenecks, qualitative assessment of new interconnection projects" (PDF). Centro Elettrotecnico Sperimentale Italiano Giacinto Motta SpA. European Commission. June 2009. Retrieved 15 May 2010.
- ↑ "Back-to-back station". Litpol Link. Retrieved 23 February 2012.
- ↑ ""Power bridge" deal finalised". The Baltic Times. 24 May 2008. Retrieved 24 May 2008.