Liver sinusoid
| Liver sinusoid | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Basic liver structure | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vas sinusoideum |
| TH | H3.04.05.0.00014 |
| FMA | 17543 |
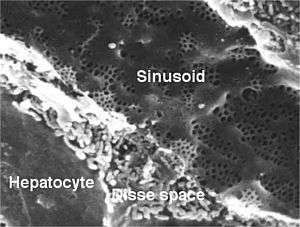
A liver sinusoid is a type of sinusoidal blood vessel (with fenestrated, discontinuous endothelium) that serves as a location for mixing of the oxygen-rich blood from the hepatic artery and the nutrient-rich blood from the portal vein.[1]
Hepatocytes are separated from the sinusoids by the space of Disse. Kupffer cells are located inside the sinusoids and can take up and destroy foreign material such as bacteria.
Endothelium
The sinusoidal endothelial cells are cultured for a variety of research purposes. The utility of these cells are of particular interest. One problem to overcome is the reversing of cellular differentiation that has made these cells highly specialized phenotypically in vitro.[2]
Additional images
- Human liver sinusoid
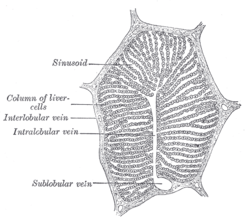 A single lobule of the liver of a pig. X 60.
A single lobule of the liver of a pig. X 60.
References
- ↑ SIU SOM Histology GI
- ↑ Sellaro TL, Ravindra AK, Stolz DB, Badylak SF. (September 2007). "Maintenance of hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype in vitro using organ-specific extracellular matrix scaffolds". Tissue Eng. 13 (9): 2301–2310. doi:10.1089/ten.2006.0437. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
External links
- UIUC Histology Subject 589
- Histology image: 15504loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Liver, Gall Bladder, and Pancreas: liver, classic lobule"
- Histology image: 22103loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Ultrastructure of the Cell: hepatocytes and sinusoids, sinusoid and space of Disse"
- Histology at anhb.uwa.edu.au
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.