Long Cecil
| Long Cecil | |
|---|---|
  | |
| Type | Howitzer |
| Place of origin | Kimberley |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1900-01-23[1] to 1900-02-15 |
| Used by | British Empire |
| Wars | Second Boer War |
| Production history | |
| Designer | George Labram |
| Designed | 1899 |
| Manufacturer | De Beers |
| Produced | January 1900 |
| Number built | 1 |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 1,625 kilograms (3,583 lb)[2] |
|
| |
| Shell | 13.5 kilograms (29.8 lb)[2] |
| Calibre | 104 millimetres (4.1 in)[2] |
| Carriage | Custom |
| Elevation | 0° to +26° |
| Traverse | nil |
| Muzzle velocity | 512 metres per second (1,680 ft/s)[2] |
| Effective firing range | 7,300 metres (8,000 yd)[2] |
Long Cecil is a unique one-off gun, designed by George Labram, a United States citizen, and built in the workshops of the De Beers mining company in Kimberley for use by the British during the Siege of Kimberley in the Second Boer War.
In 1902, during Cecil Rhodes' funeral procession in Cape Town, his coffin was carried on top of the Long Cecil carriage.[3] Today the gun is located on the stylobate (facing the Free State) of the Honoured Dead Memorial in Kimberley.
At some time before 1915 Pratt & Whitney built a model of this gun as a gift to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers.[4]
Construction
The defenders at Kimberley had only the relatively small RML 2.5 inch Mountain Gun at their disposal and therefore lacked a weapon that could effectively match those fielded by the surrounding Boers.[5]

Labram and Edward Goffe, Chief Draughtsman at the mine, reviewed the limited number of textbooks and publications on gunmaking that were available in Kimberley. From this and calculations on what it would require to build a gun capable of firing a shell over 7,600 metres (24,900 ft), they decided that it was feasible to build the gun with the materials at hand.[2]
Construction of the gun began on 26 December 1899 with rough-turning of the barrel,[1] but some of the tools required for rifling the barrel were not available and first had to be manufactured on site.[2]
The barrel was constructed from a 10-foot-long (3.0 m), 10.5-inch-diameter (270 mm) billet of mild steel.[6] The steel billet was originally ordered as a shaft for one of the De Beers workshop machines.[2]
Impact on the siege
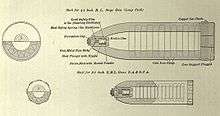
As with all the components, custom ammunition for the gun had to be manufactured in the De Beers workshops. The first proving shot was fired a little over three weeks later on 19 January 1900 at a Boer encampment near Kamfers Dam, north of the city.[1] Contemporary accounts state that the Boers were initially surprised by range of the new gun, which was able to land projectiles very accurately on their previously safe position.[5]
The gun fired a total of 255 shells onto Boer positions from the time of its manufacture until the end of the siege about a month later.[1] The gun did not change the balance of power for long, because the Boers brought a larger 100-pound "Long Tom" gun to bear within two weeks of Long Cecil's deployment. The shelling of the besieged residents thereby escalated and soon became more lethal than before. The shelling ended only with arrival of Major-General French's 8,000-strong cavalry on 15 February 1900.
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 Williams, Gardner Fred (1902). The diamond mines of South Africa; some account of their rise and development. Macmillan. p. 649. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Peddle, D. E. (1 June 1977). "LONG CECIL – The Gun made in Kimberley during the Siege". Military History Journal. The South African Military History Society. 4 (1). ISSN 0026-4016. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ↑ "Funeral of Cecil Rhodes". The Norfolk weekly news. 4 April 1902. Retrieved 4 September 2009.
- ↑ Hutton, Frederick Remsen (1915). A history of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers from 1880 to 1915. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. p. 305. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- 1 2 Lewis Childs (2001). Battleground South Africa - Kimberley. Barnsley, South Yorkshire: LEO COOPER / Pen and Sword Books Ltd. p. 134. ISBN 0-85052-766-X.
- ↑ Cassell's History of the Boer War, 1899–1902 by Richard Danes (1903), p. 557 (n573) on the Internet Archive
Further reading
- Goffe, Edward (June 1900). "Notes on the construction of "Long Cecil", a 4.1 inch rifled breachloading gun, in Kimberley, during the siege 1899-1900". Institute of Mechanical Engineers. Proceedings: 359.
External links
![]() Media related to Long Cecil at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Long Cecil at Wikimedia Commons
Coordinates: 28°45′4″S 24°46′10″E / 28.75111°S 24.76944°E