Maltodextrin
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 9050-36-6 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.934 |
| PubChem | 62698 |
| UNII | 7CVR7L4A2D |
| Properties | |
| C6nH(10n+2)O(5n+1) | |
| Molar mass | variable |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Free soluble or readily dispersible in water[1] | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble to insoluble in anhydrous alcohol[1] |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide that is used as a food additive. It is produced from starch by partial hydrolysis and is usually found as a white hygroscopic spray-dried powder.[1] Maltodextrin is easily digestible, being absorbed as rapidly as glucose and might be either moderately sweet or almost flavorless. It is commonly used for the production of soft drinks and candy. It can also be found as an ingredient in a variety of other processed foods.
Structure
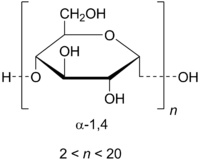
Maltodextrin consists of D-flutype units connected in chains of variable length. The glucose units are primarily linked with α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. Maltodextrin is typically composed of a mixture of chains that vary from three to 17 glucose units long.[2]
Maltodextrins are classified by DE (dextrose equivalent) and have a DE between 3 and 20. The higher the DE value, the shorter the glucose chains, the higher the sweetness, the higher the solubility, corn syrup|glucose syrup, at DE 10 or lower the customs CN code nomenclature classifies maltodextrins as dextrins.
Production
Maltodextrin can be enzymatically derived from any starch. In the US, this starch is usually corn; in Europe, it is commonly wheat. Some individuals suffering from gluten-related disorders may be concerned by the presence of wheat derived maltodextrin but it is highly unlikely to contain significant (20 mg/kg or 20ppm) amounts of gluten. Maltodextrin derived from wheat is exempt from labeling, as set out in Annex II of EC Directive No 1169/2011.[3]
Food uses
Maltodextrin is sometimes used in beer brewing to increase the specific gravity of the final product.[4] This improves the mouthfeel of the beer, increases head retention and reduces the dryness of the drink. Maltodextrin is not fermented by yeast, so it does not increase the alcohol content of the brew. It is also used in some snacks such as potato chips and jerky. It is used in "light" peanut butter to reduce the fat content, but keep the texture. Maltodextrin is also sometimes taken as a supplement by bodybuilders and other athletes in powder form or in gel packets.
Maltodextrin is used as an inexpensive additive to thicken food products such as infant formula. It is also used as a filler in sugar substitutes and other products.[5]
Maltodextrin has a glycemic index ranging from 85 to 105.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Reference Tables: Description and Solubility - M". pharmacopeia.cn.
- ↑ "Other Caloric Sweeteners", Sugar Association website
- ↑ Annex II, REGULATION (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL, Directive No. 1169/2011 of 25 October 2011. Retrieved on 4 Apr 2016.
- ↑ "How to Brew" at Black Rock, a beer brewing supplier in New Zealand
- ↑ "What is Maltodextrin? (with pictures)". wisegeek.org.
