Methylenecyclopropane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
methylenecyclopropane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 6142-73-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 72487 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.584 |
| PubChem | 80245 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6 | |
| Molar mass | 54.09 |
| Density | 0.8 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 9 to 12 °C (48 to 54 °F; 282 to 285 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
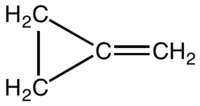
Methylenecyclopropane is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)2CCH2. It is a colourless easily condensed gas that is used as a reagent in organic synthesis.
Synthesis
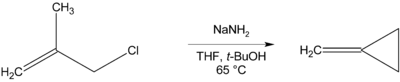
Methylenecyclopropane can be synthesised via an intramolecular cyclisation reaction, using β-halo alkenes and a strong base such as sodium amide.[1]
Reactions
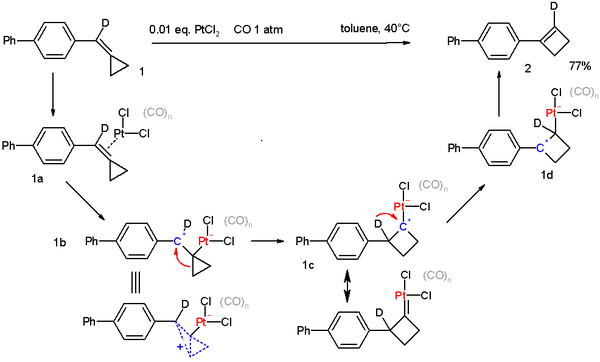
Being a strained and unsaturated molecule methylenecyclopropane undergoes many reactions, especially in the presence of metal catalysts.[2] For example, methylenecyclopropanes can be converted to cyclobutenes in the presence of a Platinum catalyst.[3] This can be considered similar to the ring expansion seen in vinylcyclopropane rearrangements
Substituted methylenecyclopropanes can also be involved in trimethylenemethane cycloaddition reactions.
See also
References
- ↑ Salaun, J. R.; Champion, J.; Conia, J. M. (1977). "Cyclobutanone from methylenecyclopropane via oxaspiropentane". Org. Synth. 57: 36.; Coll. Vol., 6, p. 320
- ↑ Nakamura, I.; Yamamoto, Y. (2002). "Transition Metal-Catalyzed Reactions of Methylenecyclopropanes". Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis. 344 (2): 111–129. doi:10.1002/1615-4169(200202)344:2<111::AID-ADSC111>3.0.CO;2-0.
- ↑ PtCl2-Catalyzed Rearrangement of Methylenecyclopropanes Alois Fürstner and Christophe Aïssa J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 2006; 128(19) pp 6306 -6307; Abstract