Motion sensing in vision
Motion sensing in vision allows for an organism to detect motion across its visual field. This is crucial for detecting a potential mate, prey, or predator, and thus it is found both in vertebrates and invertebrates vision throughout a wide variety of species although it is not universally found in all species. In vertebrates, the process takes place in retina and more specifically in retinal ganglion cells, which are neurons that receive input from bipolar cells and amacrine cells on visual information and process output to higher regions of the brain including, thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon.
The study of directionally selective units began with a discovery of such cells in the cerebral cortex of cats by David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel in 1959. Following the initial report, an attempt to understand the mechanism of directionally selective cells was pursued by Horace B. Barlow and William R. Levick in 1965.[1] Their in-depth experiments in rabbit's retina expanded the anatomical and physiological understanding of the vertebrate visual system and ignited the interest in the field. Numerous studies that followed thereafter have unveiled the mechanism of motion sensing in vision for the most part. Alexander Borst and Thomas Euler's 2011 review paper, "Seeing Things in Motion: Models, Circuits and Mechanisms".[2] discusses certain important findings from the early discoveries to the recent work on the subject, coming to the conclusion of the current status of the knowledge. The content of this page has been largely based on this review paper.
Direction selective (DS) cells
Direction selective (DS) cells in the retina are defined as neurons that respond differentially to the direction of a visual stimulus. According to Barlow and Levick (1965), the term is used to describe a group of neurons that "gives a vigorous discharge of impulses when a stimulus object is moved through its receptive field in one direction."[1] This direction in which a set of neurons respond most strongly to is their "preferred direction". In contrast, they do not respond at all to the opposite direction, "null direction". The preferred direction is not dependent on the stimulus—that is, regardless of the stimulus' size, shape, or color, the neurons respond when it is moving in their preferred direction, and do not respond if it is moving in the null direction. There are three known types of DS cells in the vertebrate retina of the mouse, ON/OFF DS ganglion cells, ON DS ganglion cells, and OFF DS ganglion cells. Each has a distinctive physiology and anatomy.
ON/OFF DS ganglion cells
ON/OFF DS ganglion cells act as local motion detectors. They fire at the onset and offset of a stimulus (a light source). If a stimulus is moving in the direction of the cell's preference, it will fire at the leading and the trailing edge. Their firing pattern is time-dependent and is supported by the Reichardt-Hassenstain model, which detects spatiotemporal correlation between the two adjacent points. The detailed explanation of the Reichardt-Hassenstain model will be provided later in the section. The anatomy of ON/OFF cells is such that the dendrites extend to two sublaminae of the inner plexiform layer and make synapses with bipolar and amacrine cells. They have four subtypes, each with own preference for direction.
ON DS ganglion cells
Unlike ON/OFF DS ganglion cells that respond both to the leading and the trailing edge of a stimulus, ON DS ganglion cells are responsive only to a leading edge. The dendrites of ON DS ganglion cells are monostratified and extend into the inner sublamina of the inner plexiform layer. They have three subtypes with different directional preferences.
OFF DS ganglion cells
OFF DS ganglion cells act as a centripetal motion detector, and they respond only to the trailing edge of a stimulus. They are tuned to upward motion of a stimulus. The dendrites are asymmetrical and arbor in to the direction of their preference.[2]
DS cells in insects
The first DS cells in invertebrates were found in flies in a brain structure called the lobula plate. The lobula plate is one of the three stacks of the neuropils in the fly's optic lobe. The "tangential cells" of the lobula plate composed of roughly about 50 neurons, and they arborize extensively in the neuropile. The tangential cells are known to be directionally selective with distinctive directional preference. One of which is Horizontally Sensitive (HS) cells, such as the H1 neuron, that depolarize most strongly in response to stimulus moving in a horizontal direction (preferred direction). On the other hand, they hyperpolarize when the direction of motion is opposite (null direction). Vertically Sensitive (VS) cells are another group of cells that are most sensitive to vertical motion. They depolarize when a stimulus is moving downward and hyperpolarize when it is moving upward. Both HS and VS cells respond with a fixed preferred direction and a null direction regardless of the color or contrast of the background or the stimulus.
The Reichardt-Hassenstein model
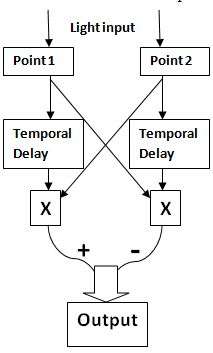
It is now known that motion detection in vision is based on the Hassenstein-Reichardt detector model. This is a model used to detect correlation between the two adjacent points. It consists of two symmetrical subunits. Both subunits have a receptor that can be stimulated by an input (light in the case of visual system). In each subunit, when an input is received, a signal is sent to the other subunit. At the same time, the signal is delayed in time within the subunit, and after the temporal filter, is then multiplied by the signal received from the other subunit. Thus, within each subunit, the two brightness values, one received directly from its receptor with a time delay and the other received from the adjacent receptor, are multiplied. The multiplied values from the two subunits are then subtracted to produce an output. The direction of selectivity or preferred direction is determined by whether the difference is positive or negative. The direction which produces a positive outcome is the preferred direction.
In order to confirm that the Reichardt-Hassenstain model accurately describes the directional selectivity in the retina, the study was conducted using optical recordings of free cytosolic calcium levels after loading a fluorescent indicator dye into the fly tangential cells. The fly was presented uniformly moving gratings while the calcium concentration in the dendritic tips of the tangential cells was measured. The tangential cells showed modulations that matched the temporal frequency of the gratings, and the velocity of the moving gratings at which the neurons respond most strongly showed a close dependency on the pattern wavelength. This confirmed the accuracy of the model both at the cellular and the behavioral level.[3]
Although the details of the Hassenstein-Reichardt model have not been confirmed at an anatomical and physiological level, the site of subtraction in the model is now being localized to the tangential cells. When depolarizing current is injected into the tangential cell while presenting a visual stimulus, the response to the preferred direction of motion decreased, and the response to the null direction increased. The opposite was observed with hyperpolarizing current. The T4 and T5 cells, which have been selected as a strong candidate for providing input to the tangential cells, have four subtypes that each project into one of the four strata of the lobula plate that differ in the preferred orientation.[2]
DS cells in vertebrates
One of the early works on DS cells in vertebrates was done on the rabbit retina by H. Barlow and W. Levick in 1965. Their experimental methods include variations to the slit-experiments and recording of the action potentials in the rabbit retina. The basic set-up of the slit experiment was they presented a moving black-white grating through a slit of various widths to a rabbit and recorded the action potentials in the retina. This early study had a large impact on the study of DS cells by laying down the foundation for later studies. The study showed that DS ganglion cells derive their property from the basis of sequence-discriminating activity of subunits, and that this activity may be the result of inhibitory mechanism in response to the motion of image in the null direction. It also showed that the DS property of retinal ganglion cells is distributed over the entire receptive field, and not limited to specific zones. Interestingly, direction selectivity is contained for two adjacent points in the receptive field separated by as small as 1/4°, but selectivity decreased with larger separations. They used this to support their hypothesis that discrimination of sequences gives rise to direction selectivity because normal movement would activate adjacent points in a succession.[4]
Molecular identity and structure of DS cells in mice
ON/OFF DS ganglion cells can be divided into 4 subtypes differing in their directional preference, ventral, dorsal, nasal, or temporal. The cells of different subtypes also differ in their dendritic structure and synaptic targets in the brain. The neurons that were identified to prefer ventral motion were also found to have dendritic projections in the ventral direction. Also, the neurons that prefer nasal motion had asymmetric dendritic extensions in the nasal direction. Thus, a strong association between the structural and functional asymmetry in ventral and nasal direction was observed. With a distinct property and preference for each subtype, there was an expectation that they could be selectively labeled by molecular markers. The neurons that were preferentially responsive to vertical motion were indeed shown to be selectively expressed by a specific molecular marker. However, molecular markers for other three subtypes have not been yet found.[5]
Neural mechanism: starburst amacrine cells
The direction selective (DS) ganglion cells receive inputs from bipolar cells and starburst amacrine cells. The DS ganglion cells respond to their preferred direction with a large excitatory postsynaptic potential followed by a small inhibitory response. On the other hand, they respond to their null direction with a simultaneous small excitatory postsynaptic potential and a large inhibitory postsynaptic potential. Starburst amacrine cells have been viewed as a strong candidate for direction selectivity in ganglion cells because they can release both GABA and Ach. Their dendrites branch out radiantly from a soma, and there is a significant dendritic overlap. Optical measurements of Ca2+ concentration showed that they respond strongly to the centrifugal motion (the outward motion from the soma to the dendrites), while they don't respond well to the centripetal motion (the inward motion from the dendritic tips to the soma). When the starburst cells were ablated with toxins, direction selectivity was eliminated. Moreover, their release of neurotransmitters itself, specifically calcium ions, reflect direction selectivity, which may be presumably attributed to the synaptic pattern. The branching pattern is organized such that certain presynaptic input will have more influence on a given dendrite than others, creating a polarity in excitation and inhibition. Further evidence suggests that starburst cells release inhibitory neurotransmitters, GABA onto each other in a delayed and prolonged manner. This accounts for the temporal property of inhibition.[2]
In addition to spatial offset due to GABAergic synapses, the important role of chloride transporters has started to be discussed. The popular hypothesis is that starburst amacrine cells differentially express chloride transporters along the dendrites. Given this assumption, some areas along the dendrite will have a positive chloride-ion equilibrium potential relative to the resting potential while others have a negative equilibrium potential. This means that GABA at one area will be depolarizing and at another area hyperpolarizing, accounting for the spatial offset present between excitation and inhibition.[6]
Recent research (published March 2011) relying on serial block-face electron microscopy (SBEM) has led to identification of the circuitry that influences directional selectivity. This new technique provides detailed images of calcium flow and anatomy of dendrites of both starburst amacrine (SAC) and DS ganglion cells. By comparing the preferred directions of ganglion cells with their synapses on SAC's, Briggman et al. provide evidence for a mechanism primarily based on inhibitory signals from SAC's[7] based on an oversampled serial block-face scanning electron microscopy study of one sampled retina, that retinal ganglion cells may receive asymmetrical inhibitory inputs directly from starburst amacrine cells, and therefore computation of directional selectivity also occurs postsynaptically. Such postsynaptic models are unparsimonious, and so if any given starburst amacrine cells conveys motion information to retinal ganglion cells then any computing of 'local' direction selectivity postsynaptically by retinal ganglion cells is redundant and dysfunctional. An acetylcholine (ACh) transmission model of directionally selective starburst amacrine cells provides a robust topological underpinning of a motion sensing in the retina.[8]
Notes
- 1 2 Barlow, H. B., & Levick, W. R. (1965). "The mechanism of directionally selective units in rabbit's retina". The Journal of Physiology. 178 (3): 477–504. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007638. PMC 1357309
 .
. - 1 2 3 4 Borst, Alexander, and Thomas Euler (2011). "Seeing Things in Motion: Models, Circuits, and Mechanisms". Neuron. 71.6: 974–994. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.031.
- ↑ Haag, J. "Fly Motion Vision Is Based on Reichardt Detectors Regardless of the Signal-to-noise Ratio." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 101.46 (2004): 16333-6338.
- ↑ B, Barlow H., and Levick W. R. "The Mechanism of Directionally Selective Units in Rabbit's Retina." The Journal of Physiology 178.3 (1965): 477-504.
- ↑ Kay, Jeremy N et al. "Retinal ganglion cells with distinct directional preferences differ in molecular identity, structure, and central projections." Journal of Neuroscience 31.21 (2011) : 7753-7762.
- ↑ Demb, Jonathan B. "Cellular mechanisms for direction selectivity in the retina." Neuron 55.2 (2007) : 179-186
- ↑ Briggman, Kevin L.; Helmstaedter, Moritz; Denk, Winfried. "Wiring specificity in the direction-selectivity circuit of the retina." Nature 471 (10 March 2011) : 183–188
- ↑ Poznanski, R.R. Cellular Inhibitory Behavior Underlying the Formation of Retinal Direction Selectivity, J. Integr. Neurosci. 9, 299-335, 2010
References
- B, Barlow H., and Levick W. R. "The Mechanism of Directionally Selective Units in Rabbit's Retina." The Journal of Physiology 178.3 (1965): 477-504.
- Borst, A. (2007). Correlation versus gradient type motion detectors: the pros and cons. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 362(1479), 369-74. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1964
- Borst, Alexander, and Thomas Euler. "Seeing Things in Motion: Models, Circuits, and Mechanisms." Neuron 71.6 (2011) : 974-994.
- Carver, Sean et al. "Synaptic Plasticity Can Produce and Enhance Direction Selectivity." PLoS Computational Biology 4.2 (2008) : 12.
- Demb, Jonathan B. "Cellular mechanisms for direction selectivity in the retina." Neuron 55.2 (2007) : 179-186.
- Douglass, John K., and Nicholas J. Strausfeld. "Visual Motion-Detection Circuits in Flies: Parallel Direction- and Non-Direction-Sensitive Pathways between the Medulla and Lobula Plate." J. Neurosci 16 (1996): 4551-562. Print.
- Grzywacz, Norberto M., and Franklin R. Amthor. "Robust Directional Computation in On-off Directionally Selective Ganglion Cells of Rabbit Retina." Visual Neuroscience 24.04 (2007).
- Haag, J. "Fly Motion Vision Is Based on Reichardt Detectors Regardless of the Signal-to-noise Ratio." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 101.46 (2004): 16333-6338.
- Jagadeesh, B et al. "Direction selectivity of synaptic potentials in simple cells of the cat visual cortex." Journal of Neurophysiology 78.5 (1997) : 2772-2789.
- Kay, Jeremy N et al. "Retinal ganglion cells with distinct directional preferences differ in molecular identity, structure, and central projections." Journal of Neuroscience 31.21 (2011) : 7753-7762.
- Levick, William. "Direction selectivity in rabbit retina." The Journal of Physiology 577.Pt 1 (2006) : 1-2.
- Vaney, David I, and W Rowland Taylor. "Direction selectivity in the retina." Current Opinion in Neurobiology 12.4 (2002) : 405-410.
- Wassle, H. "Knock out of direction selectivity in the retina." Neuron 30.3 (2001) : 644-646.
- Yonehara, Keisuke et al. "Identification of Retinal Ganglion Cells and Their Projections Involved in Central Transmission of Information about Upward and Downward Image Motion." PLoS ONE 4.1 (2009) : 14.
- Zhou, Z Jimmy, and Seunghoon Lee. "Synaptic physiology of direction selectivity in the retina." The Journal of Physiology 586.Pt 18 (2008) : 4371-4376.