Stencil lithography
Stencil lithography is a novel method of fabricating nanometer scale patterns using nanostencils, stencils (shadow mask) with nanometer size apertures. It is a resist-less, simple, parallel nanolithography process, and it does not involve any heat or chemical treatment of the substrates (unlike resist-based techniques).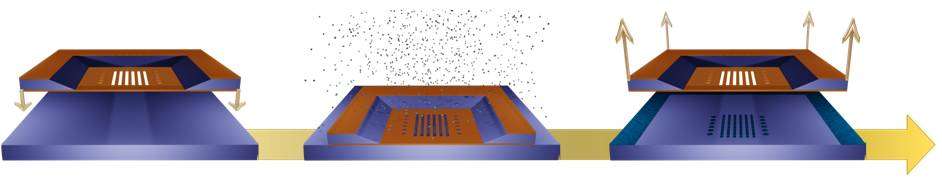
History
Stencil lithography was first reported in a scientific journal as a micro-structuring technique by S. Gray and P. K. Weimer in 1959.[1] They used long stretched metallic wires as shadow masks during metal deposition. Various materials can be used as membranes, such as metals, Si, SixNy, and polymers. Today the stencil apertures can be scaled down to sub-micrometer size at full 4" wafer scale. This is called a nanostencil. Nano-scale stencil apertures have been fabricated using laser interference lithography (LIL), electron beam lithography, and focused ion beam lithography.
Processes
Several process are available using stencil lithography: material deposition and etching, as well as implantation of ions. Different stencil requirements are necessary for the various processes, e. g. an extra etch-resistant layer on the backside of the stencil for etching (if the membrane material is sensitive to the etching process) or a conductive layer on the backside of the stencil for ion implantation.
Deposition
The main deposition method used with stencil lithography is physical vapor deposition. This includes thermal and electron beam physical vapor deposition, molecular beam epitaxy, sputtering, and pulsed laser deposition. The more directional the material flux is, the more accurate the pattern is transferred from the stencil to the substrate.
Etching
Reactive ion etching is based on ionized, accelerated particles that etch both chemically and physically the substrate. The stencil in this case is used as a hard mask, protecting the covered regions of the substrate, while allowing the substrate under the stencil apertures to be etched.
Ion implantation
Here the thickness of the membrane has to be smaller than the penetration length of the ions in the membrane material. The ions will then implant only under the stencil apertures, into the substrate.
Modes
There are three main modes of operation of stencil lithography: static, quasi-dynamic and dynamic. While all the above described processes have been proven using the static mode (stencil doesn't move relative to substate during material or ion processing), only ion implantation has been shown for the non-static modes (quasi-dynamic).
Static stencil
In the static mode, the stencil is aligned (if necessary) and fixed to a substrate. The stencil-substrate pair is placed in the evaporation/etching/ion implantation machine, and after the processing is done, the stencil is simply removed from the now patterned substrate.
Quasi-dynamic stencil
In the quasi-dynamic mode (or step-and-repeat), the stencil moves relative to the substrate in between depositions, without breaking the vacuum.
Dynamic stencil
In the dynamic mode, the stencil moves relative to the substrate during deposition, allowing the fabrication of patterns with variable height profiles by changing the stencil speed during a constant material deposition rate. For motion in one-dimension, the deposited material has a height profile given by the convolution
where is the time the mask resides at longitudinal position , and is the constant deposition rate. represents the height profile that would be produced by a static immobile mask (inclusive of any blurring). Programmable-height nanostructures as small as 10nm can be produced.[2]
Challenges
Despite it being a versatile technique, there are still several challenges to be addressed by stencil lithography. During deposition through the stencil, material is deposited not only on the substrate through the apertures but also on the stencil backside, including around and inside the apertures. This reduces the effective aperture size by an amount proportional to the deposited material, leading ultimately to aperture clogging.
The accuracy of the pattern transfer from the stencil to the substrate depends on many parameters. The material diffusion on the substrate (as a function of temperature, material type, evaporation angle) and the geometrical setup of the evaporation are the main factors. Both lead to an enlargement of the initial pattern, called blurring.
See also
References
- ↑ Gray, S; Weimer, PK (1959). "Production Of Fine Patterns By Evaporation". RCA Review. RCA Corporation. 20 (3): 413–425. ISSN 0033-6831.
- ↑ J. L. Wasserman; et al. (2008). "Fabrication of One-Dimensional Programmable-Height Nanostructures via Dynamic Stencil Deposition". Review of Scientific Instruments. 79: 073909. arXiv:0802.1848
 . Bibcode:2008RScI...79g3909W. doi:10.1063/1.2960573.
. Bibcode:2008RScI...79g3909W. doi:10.1063/1.2960573.
Series in MICROSYSTEMS Vol. 20: Marc Antonius Friedrich van den Boogaart, "Stencil lithography: An ancient technique for advanced micro- and nanopatterning", 2006, VIII, 182 p.; ISBN 3-86628-110-2