New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Railroad Company
|
An NC&F ticket office sits in a park in New Castle, Delaware. | |
| Locale | Delaware and eastern Maryland |
|---|---|
| Dates of operation | 1831–1877 |
| Successor | Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
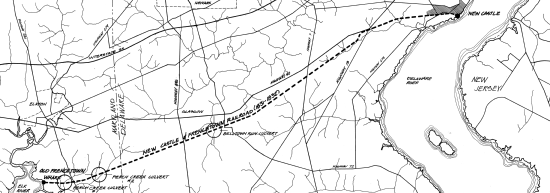
The New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Rail Road (NC&F), opened in 1831, was the first railroad in Delaware and one of the first in the United States. About half of the route was abandoned in 1859; the rest became part of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) route into the Delmarva Peninsula and is still used by Norfolk Southern Railway. The abandoned segment from Porter, Delaware, to Frenchtown, Maryland, the New Castle and Frenchtown Railroad Right-of-Way, was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.[1]
History
When construction began in 1804 on the Chesapeake & Delaware Canal, which would connect the Delaware River to the Chesapeake Bay, merchants and other businessmen of New Castle, Delaware, perceived a threat to their interests and proposed a railroad to connect their own city to the bay. The New-Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike Company was chartered in Delaware on January 24, 1809, and in Maryland on January 6, 1810. It opened in 1815 and 1816, providing a turnpike from New Castle in a west-southwest direction to Old Frenchtown Wharf, Maryland, on Chesapeake Bay. The easternmost section of the road, east of Clark's Corner (under 3 miles), had been built in 1812 by the New Castle Turnpike Company, chartered January 30, 1811.[2]
In 1828, the Maryland General Assembly authorized the company to replace the turnpike with a railroad and change its name to the New-Castle and French Town Turnpike and Rail Road Company.[3] Similar laws did the same for the two companies in Delaware, renaming the New Castle Turnpike Company to the New Castle Turnpike and Railroad Company. The companies merged on March 31, 1830, to form the New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Rail Road Company – with no dash in New Castle – and the new railroad opened in 1831, using horses for about a year before switching to steam locomotives.[4] The chief engineer for the construction of the railroad was John Randel Jr..[5]
The Chesapeake & Delaware Canal finally opened in 1829, becoming a major competitor to the railroad. Another railroad company, later called the Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad (PW&B), began construction along a nearby route in the mid-1830s. In 1838, the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad began operating trains along this route between Baltimore and Philadelphia, bypassing the much smaller and less significant New Castle.[6] On March 15, 1839, the PW&B bought the NC&F, using it as an alternate route.[7]
The New Castle and Wilmington Rail Road was connected to the New Castle end of the system in 1852, and by 1856 the Delaware Railroad had opened, splitting from the New Castle and Frenchtown at Rodney Village, about halfway between the two ends. In 1859, the railroad was abandoned west of Rodney; most of the right-of-way is still cleared.
On March 28, 1877, the New Castle and Frenchtown was merged into the PW&B, which was part of the PRR system. In 1891, the PW&B sold the old New Castle and Frenchtown line, as well as the New Castle and Wilmington, to the Delaware Railroad, which was leased to the PW&B.
The east half of the old alignment was acquired by Penn Central in 1968, then Conrail in 1976, and most recently Norfolk Southern (1999), which uses it to reach the Delmarva Peninsula.
References
Notes
- ↑ National Park Service (2008-04-15). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- ↑ http://www.pencaderheritage.org/main/landmarks/phland_p19.html
- ↑ Maryland General Assembly. Chapter 207 of the 1827 Session Laws of Maryland, passed March 14, 1828.
- ↑ http://www.ls.net/~newriver/de/de1st.htm
- ↑ Holloway, Marguerite (2013), The Measure of Manhattan: The Tumultuous Career and Surprising Legacy of John Randel Jr., Cartographer, Surveyor, Inventor, New York: W. W. Norton, pp. 223=29, ISBN 978-0-393-07125-2
- ↑ Harwood, Jr., Herbert H. (2005). "Philadelphia, Wilmington & Baltimore Railroad". Maryland Online Encyclopedia. Maryland Historical Society. Archived from the original on 2008-07-20.
- ↑ http://www.prrths.com/Hagley/PRR1839%20June%2004.wd.pdf
Bibliography
- Pleasants, Earl. Railroad History Database
- PRR Corporate History
External links
- Historic American Engineering Record - New Castle & Frenchtown Railroad
- Historic American Buildings Survey - New Castle-Frenchtown Railroad Ticket Office, Washington Avenue Crossing (oldest remaining railroad ticket office in the U.S.)
| Preceded by New-Castle and French Town Turnpike and Rail Road Company The New Castle Turnpike and Railroad Company |
The New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Rail Road Company formed by merger March 31, 1830 merged May 15, 1877 |
Succeeded by Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad Company |
| Preceded by |
The President, Managers and Company of the New-Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike Company chartered January 24, 1809 name changed March 14, 1828 |
Succeeded by New-Castle and French Town Turnpike and Rail Road Company |
| Preceded by The President, Managers and Company of the New-Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike Company |
New-Castle and French Town Turnpike and Rail Road Company name changed March 14, 1828 merged March 31, 1830 |
Succeeded by The New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Rail Road Company |
| Preceded by |
The New Castle Turnpike Company chartered January 30, 1811 name changed February 7, 1829 |
Succeeded by The New Castle Turnpike and Railroad Company |
| Preceded by The New Castle Turnpike Company |
The New Castle Turnpike and Railroad Company name changed February 7, 1829 merged March 31, 1830 |
Succeeded by The New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Rail Road Company |