Nioghalvfjerdsbrae
| Nioghalvfjerdsbrae | |
|---|---|
|
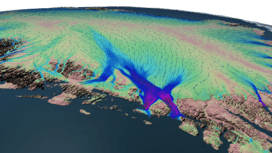
Velocity flow over the Nioghalvfjerdsbrae. | |
 Location within Greenland | |
| Location | Greenland |
| Coordinates | 79°0′N 25°0′W / 79.000°N 25.000°WCoordinates: 79°0′N 25°0′W / 79.000°N 25.000°W |
| Area | 103,314 km2 (39,890 sq mi) |
| Length | 89 km |
| Width | 20 km |
| Terminus | Nioghalvfjerd Fjord, Greenland Sea |
Nioghalvfjerdsbrae (79°00′N 025°00′W / 79.000°N 25.000°W), sometimes referred to as "79 N Glacier", is a large glacier located in northeast Greenland. It drains an area of 103,314 km2 (39,890 sq mi) of the Greenland Ice Sheet with a flux (quantity of ice moved from the land to the sea) of 14.3 km3 (3.4 cu mi) per year, as measured for 1996.[1]
Geography
The glacier has had an 80 km long and 20 km wide floating tongue, widening toward its terminus north of Lambert-Land.[2] There are two calving fronts where the glacier meets the ocean, separated by Hovgaard Island.[3] In August 1997 the southern calving front retreated by 5 km with no significant upstream thinning.[4]
 Map of Northeastern Greenland. |
 View of the terminus of the Nioghalvfjerdsbrae glacier with the southwestern end of Hovgaard Island and Cape Adolf Jensen. |
See also
References
- ↑ Rignot E., Kanagaratnam P. (2006). "Changes in the velocity structure of the Greenland Ice Sheet". Science. 311 (5763): 986–990. doi:10.1126/science.1121381. PMID 16484490.
- ↑ "Nioghalvfjerdsfjorden". Mapcarta. Retrieved 16 June 2016.
- ↑ Water exchange between the continental shelf and the cavity beneath Nioghalvfjerdsbræ (79 North Glacier)
- ↑ Sustained mass loss of the northeast Greenland ice sheet triggered by regional warming
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/15/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.