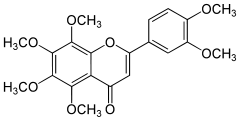
Nobiletin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetramethoxychromen-4-one | |
| Other names
Hexamethoxyflavone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 478-01-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:7602 |
| ChemSpider | 65283 |
| KEGG | C10112 |
| PubChem | 72344 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H22O8 | |
| Molar mass | 402.40 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Nobiletin is a flavonoid isolated from citrus peels. It is an O-methylated flavone that has the activity to rescue bulbectomy-induced memory impairment.[1]
Potential pharmacology
Nobiletin was found to have anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor invasion, proliferation, and metastasis in vitro and in animal studies. Nobiletin was also found to potentially inhibit cartilage degradation.[2]
Nobiletin was shown to augment AMPA receptor activity and long-term potentiation in cell culture.[3]
References
- ↑ Nagase H, Yamakuni T, Matsuzaki K, Maruyama Y, Kasahara J, Hinohara Y, Kondo S, Mimaki Y, Sashida Y, Tank AW, Fukunaga K, Ohizumi Y (2005). "Mechanism of Neurotrophic Action of Nobiletin in PC12D Cells". Biochemistry. American Chemical Society. 44 (42): 13683–13691. doi:10.1021/bi050643x. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 16229458.
Nobiletin is a nonpeptide compound with a low molecular weight from a citrus fruit and has the activity to rescue bulbectomy-induced memory impairment
- ↑ Henrotin, Y.; C. Lambert; D. Couchourel; C. Ripoll; E. Chiotelli (January 2011). "Nutraceuticals: do they represent a new era in the management of osteoarthritis? – a narrative review from the lessons taken with five products". Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 19 (1): 1–21. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2010.10.017. PMID 21035558. Retrieved 2011-12-27.
- ↑ Matsuzaki K, Miyazaki K, Sakai S, Yawo H, Nakata N, Moriguchi S, Fukunaga K, Yokosuka A, Sashida Y, Mimaki Y, Yamakuni T, Ohizumi Y (2008). "Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid with neurotrophic action, augments protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit, GluR1, and the postsynaptic receptor response to glutamate in murine hippocampus". Eur J Pharmacol. 578 (2-3): 194–200. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.09.028. PMID 17976577.
External links
- Nobiletin, phytochemicals.info
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.