Nopaline
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
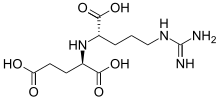
| IUPAC name
N-{1-Carboxy-4-[(diaminomethylene)amino]butyl}glutamic acid[1] | |
| Other names
N2-(D-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-arginine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 19976727 (2R)-2-Amino 388639 2-{[(1R)-1-Carboxybutyl]amino} 19951243 2-{[(1S)-1-Carboxybutyl]amino} |
| PubChem | 426 21118330 (2R)-2-Amino 57105058 (2S)-2-Amino 439546 2-{[(1R)-1-Carboxybutyl]amino} 440320 2-{[(1S)-1-Carboxybutyl]amino} |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H20N4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 304.30 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanoic acids |
Octopine |
| Related compounds |
|
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Nopaline is a chemical compound derived from the amino acids glutamic acid and arginine. It is classified as an opine. Ti plasmids are classified on the basis of the different types of opines they produce. These may be nopaline plasmids, octopine plasmids and agropine plasmids. These opines are condensation products of amino acids and keto acids or may be derived from sugars. The opines are used as carbon and nitrogen sources and metabolized by Agrobacterium.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/24/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.