Ophryacus undulatus
| Ophryacus undulatus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Subfamily: | Crotalinae |
| Genus: | Ophryacus |
| Species: | O. undulatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Ophryacus undulatus (Jan, 1859) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Ophryacus undulatus is a venomous pitviper species found in the mountains of central and southern Mexico. No subspecies are currently recognized.[4]
Description
Adults grow to 55–70 centimetres (21 5⁄8–27 1⁄2 inches) in length and are moderately stout.[2] Elongated supraocular scales form a pair of "horns" or "spines" over the eyes.[3]
The color pattern consists of a silvery-gray ground color overlaid with a series of black dorsal blotches that merge to form a broad wavy stripe. Black speckling is present on the flanks. The top of the head is black.[3]
Geographic range
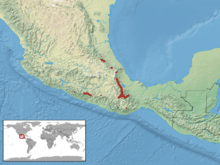
Found in the mountains of central and southern Mexico (Hidalgo, Veracruz, Oaxaca and Guerrero) west of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec at elevations of 1,800–2,800 m (5,900–9,200 ft). The type locality given is "Messico" (Mexico). H.M. Smith & Taylor (1950) proposed that it be restricted to "Orizaba, Veracruz, Mexico."[1]
Habitat
Brush and rock strewn slopes in the vicinity of streams.[3]
Conservation status
This species is classified as Vulnerable (VU) on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species with the following criteria: B1ab(iii) (v3.1, 2001).[5] A species is listed as such when the best available evidence indicates that the geographic range, in the form of extent of occurrence, is estimated to be less than 20,000 km², that estimates indicate it to be severely fragmented or known to exist at no more than 10 locations, and that a continuing decline has been observed, inferred or projected, in area, extent and/or quality of habitat. It is therefore considered to be facing a high risk of extinction in the wild. In 2007 when it was last assessed, the population trend was down.[6]
Behavior
Night-time temperatures throughout its range are low, and this species only seems to be active during the day. Individuals have frequently been seen coiled on or near fallen logs, as well as in bushes and small trees 1–4 m (3.3–13.1 ft) above the ground.[2]
Feeding
The diet consists of rodents and lizards.[2]
Reproduction
Ovoviviparous, with females giving birth to live young.[3]
See also
- List of crotaline species and subspecies
- Crotalinae by common name
- Crotalinae by taxonomic synonyms
- Snakebite
References
- 1 2 McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré T. 1999. Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, vol. 1. Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN 1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN 1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- 1 2 3 4 Campbell JA, Lamar WW. 2004. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. 2 volumes. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca and London. 870 pp. 1500 plates. ISBN 0-8014-4141-2.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Mehrtens JM. 1987. Living Snakes of the World in Color. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. ISBN 0-8069-6460-X.
- ↑ "Ophryacus undulatus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 27 July 2008.
- ↑ Ophryacus undulatus at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 27 July 2008.
- ↑ 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1) at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 27 July 2008.
External links
- Ophryacus undulatus at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 27 July 2008.
