Otto Strandman
| Otto August Strandman | |
|---|---|
| 1st Prime Minister of Estonia | |
|
In office 9 May 1919 – 18 November 1919 | |
| Preceded by |
Konstantin Päts as Prime Minister of the Provisional Government |
| Succeeded by | Jaan Tõnisson |
| 10thState Elder of Estonia | |
|
In office 9 July 1929 – 12 February 1931 | |
| Preceded by | August Rei |
| Succeeded by | Konstantin Päts |
| Personal details | |
| Born |
30 November 1875 Vandu, Lääne-Viru County, Estonia (then Governorate of Estonia, part of the Russian Empire) |
| Died |
5 February 1941 (aged 65) Kadrina, Estonia |
| Nationality | Estonian |
| Political party |
Radical Socialist Party (1917) Estonian Labour Party (1917–1932) National Centre Party (1932–1935) later none |
| Spouse(s) | Lydia Strandman |
| Alma mater | Tartu University; Saint Petersburg University |
| Profession | Lawyer, politician, diplomat |
| Religion | protestant |
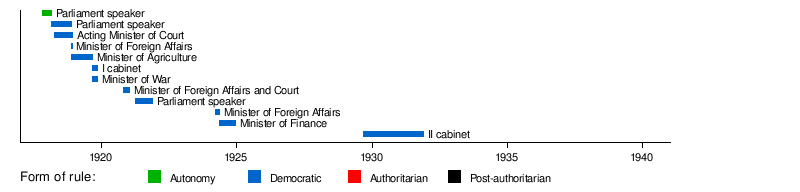
Otto August Strandman (Estonian pronunciation: [ˈoto ˈɑugust ˈstrɑndˈmanˑ]; 30 November [O.S. 18 November] 1875[1] – 5 February 1941) was an Estonian politician, who served as Prime Minister (1919) and State Elder of Estonia (1929–1931). He was one of the leaders of the centre-left Estonian Labour Party, that saw its biggest support after the 1919 and 1920 elections. Strandman was a key figure in composing the radical land reform law and the 1920 Constitution. He also served as Minister of Agriculture (1918–1919), Minister of Justice (acting 1918; 1920–1921), Minister of Finance (1924), Minister of Foreign Affairs (1918, 1920–1921 and 1924) and Minister of War (1919). While he was in the office of Minister of Finance, he stabilized the economy and managed to avoid hyperinflation. Strandman was also the speaker of both the Estonian Provincial Assembly (1917–1918) and Riigikogu (1921). He was a diplomat, serving as an envoy in Warsaw (1927–1929), when he made contacts with Polish politicians, and in Paris (1933–1939). During the Soviet Occupation in 1941, Strandman was ordered to show up to the NKVD headquarters. Already knowing about his fate, he committed suicide in his home in Kadrina.
Early life
Otto Strandman was born on 30 November [O.S. 18 November] 1875[1] in the village of Vandu, Undla Parish, Viru County, then part of the Governorate of Estonia of the Russian Empire. His father, Hans Strandman, was a shoolteacher and Otto was his third child.[2]
Strandman was first educated by his father, until he went to the municipal school of Rakvere in 1886 and later to Emperor Alexander State High School in Tallinn and 5th and 7th High School in Saint Petersburg. He graduated as an extern in 1896 after his exams in the Estonian Governorate High School of Tallinn.[3]
After graduation, Strandman served as an official at the Tallinn Office of the State Bank of the Russian Empire until he went on to study law at the University of Tartu in 1899. In 1901 he continued his studies at the University of Saint Petersburg, that he graduated in 1903.[4]
Career
Early career
Strandman worked as a lawyer in Narva and Tallinn, became known for his eloquence and was therefore elected to be a member of Tallinn city council from 1904 to 1905. As a lawyer, he defended Estonians against Baltic Germans and state officials.[2]
Strandman was also active in Estonian national organizations and became an activist on self-government reform, where he supported national autonomy in the Baltic governorates. Strandman was among the politicians, who were supposed to compose the draft of self-government reform,[5] but in the course of the 1905 Revolution, Strandman was forced to flee abroad, as were many other Estonian activists. During the revolution, his views were much more radical socialist than later in his life. During his exile years, Strandman lived in Switzerland and other European countries. In Switzerland, Strandman and other Estonian exiles eventually did form the draft of self-government reform, but it was never implemented. Strandman returned to the Russian Empire in 1906, but he was banned from living in the Baltic governorates for three years, forcing him to live in Narva and Saint Petersburg.[2] He returned to Estonia in 1909 and worked as an attorney, defending participants of the 1905 Revolution. He was also a keen supporter of free speech in the media. In 1917, he became the prosecutor of the Tallinn District Court.[3]
In March 1917, Strandman and some other known politicians, who were known supporters of autonomy,[2] were chosen to compose the draft of self-government reform, that eventually created the Autonomous Governorate of Estonia.[6] Strandman was again elected to Tallinn city council and in the summer of 1917, to the Estonian Provincial Assembly (Maapäev), where he was part of the leftist Radical Socialist Party, led by Jüri Vilms.[2] He served as the Chairman (speaker) of the assembly between 25 October 1917 and 27 November 1918, although with periods of non-activity in between, due to the October Revolution and German Occupation.[3] After the October revolution, Strandman led the Provincial Assembly session of 28 November [O.S. 15 November] 1917, where the assembly declared itself the highest legitimate power in Estonia.[2] After his work as the speaker of the parliament, Strandman was acknowledged for his neutrality and punctuality.[7]
Leader of the centre-left
After Jüri Vilms was mysteriously executed in Finland, Otto Strandman took over as acting Minister of Court. He also became one of the leaders of the Radical Socialist Party, that was named Estonian Labour Party and eventually became a centre-left party. Strandman was however arrested by Germans in the summer of 1918.[3]
After the German Occupation Strandman continued in the Provisional Government, first as Minister of Foreign Affairs and then as Minister of Agriculture,[8] when he also served as a deputy for Minister of Foreign Affairs Jaan Poska.[9] As Minister of Agriculture, Strandman became the key person in composing and implementing the land reform law. Being one of the leaders of the Labour Party, he fought hard to make the land reform as radical as possible.[3] In result, the land that belonged to Baltic German nobility, was given to ethnic Estonians.
His diplomatic career started in December 1918, when he was part of the delegation to Sweden as Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs, asking for support in the War of Independence. Eventually Sweden sent a group of volunteers to the war. To pay for his trip to Stockholm, Strandman was forced to sell his own furniture.[3]
In the Constituent Assembly elections of 1919, Estonian Labour Party took 30 of the 120 seats and the majority was held by centre-left parties. This gave the Labour Party a chance to shape Estonian politics on a larger scale. Otto Strandman became the first Prime Minister of the country on 8 May 1919 and he additionally became the Minister of War.
Strandman's first cabinet was a centre-left coalition with the Estonian People's Party and the Estonian Social Democratic Workers' Party. The Estonian People's Party left the coalition in September and Strandman's cabinet resigned on 18 November 1919, being in office for half a year.[10]
The Estonian Labour Party with Ants Piip headed the one-party minority government between 26 October 1920 and 25 January 1921, when Otto Strandman served as both the Minister of Foreign Affairs and Minister of Court.[11] As Minister of Foreign Affairs, he established diplomatic relations between Estonia and Soviet Russia, making Estonia one of the first countries to do so.[12]
The 1920 elections made Labour Party the biggest party in Estonia with 22 of the 100 seats in Riigikogu, the first constitutional parliament, but centre-right parties had also gained strength. Estonian Labour Party remained in the coalition, headed by State Elder Konstantin Päts of Farmers' Assemblies. Strandman went on to serve as the first President (speaker) of the Riigikogu between 4 and 18 January November 1921.
Juhan Kukk headed another Labour Party cabinet in 1922–1923, but Strandman was given minister positions only in the Christian Democrat Friedrich Karl Akel's cabinet, where he was the Minister of Foreign Affairs between 26 and 14 March May 1924 and then Minister of Finance until 16 December 1924.[13]
Economic policies
Strandman had figured in financial affairs before. On 7 and 19 December 1923, he accused long-term inflationist Minister of Finance Georg Vestel in the parliament for incorrect spending of state treasury. It was Strandman's criticism that eventually led to the fall of Konstantin Päts's cabinet and caused him to stay away from power from 1924 to 1931.[14]
After the War of Independence, many businesses were started in a short time period and the industry was developed on loans, that eventually led to financial difficulties. As Minister of Finance, Strandman proposed a plan for economic redevelopment, that was supposed to reduce loans, lower the state budget and achieve a trade surplus by raising customs duties. At first, his actions saw little effect and he was criticised from both left- and right-wing parties, but eventually the Estonian mark stabilized, integrating the Estonian economy more with Europe.[15] He also supported building the economy on agriculture rather than transit between Russia and Europe, regarding Denmark as a model agricultural country.[3] In the media, his policies were mockingly called UMP (Uus majanduspoliitika – "New Economic Policy" (nep)) and KUMP (Kõige uuem majanduspoliitika – "Newest Economic Policy") after the economic policy in the Soviet Union at the time. In May 1924, Strandman didn't blame his predecessor Georg Vestel for deliberately creating hyperinflation, only for sheer optimism about his policies.[14]
For almost five years, Otto Strandman didn't hold any important offices. He remained active in parliamentary politics and became known for his eloquence. As leader of the centre-left, his work continued to have a great effect on the economy since he achieved for same kind of policies as he had implemented during his term as Minister of Finance. Economic historian Jaak Valge has said, that it was thanks to Otto Strandman's rapid and decisive work that Estonia was able to avoid hyperinflation in the early 1920s. It was Otto Strandman, who made the suggestion to name the new Estonian currency the "kroon" after Scandinavian countries.[3]
Late political career
As the Labour Party slowly turned from leftist to centrist, its popularity fell, leaving its highlights to the 1919 Constituent Assembly and 1920 Riigikogu elections. Labour Party achieved only 12 of the 100 seats in 1923 elections, 13 in 1926 and 10 in 1929, until it finally merged with other centrist parties to form the National Centre Party in 1932.
During a governmental crisis in July 1926, the speaker of the Riigikogu Karl August Einbund made Otto Strandman the proposal to form a cabinet. His economic programme still consisted of lowering the budget and reducing loans, that was unacceptable to the right wing Settlers party and Farmers' Assemblies.[16]
From 1927 to 1929, Strandman served as Estonian envoy to Poland, Czechoslovakia and Romania, residing in Warsaw. In June 1929 he unexpectedly resigned[17] and returned to Estonian politics to head his second cabinet, starting from 9 July 1929. It was a coalition between his Labour Party, People's Party, Christian People's Party, Farmers' Assemblies and the Settlers party, combining almost all political parties from the centre-left to right. Before taking office, he criticized the parliament for becoming a "factory of inadequate laws".[7] His cabinet remained in office until 12 February 1931.[3] It is however ironic, that the Great Depression reached Estonia when the head of government was Otto Strandman, a man, who had always supported cautious economic and financial policies. It was however thanks to his strong skills in economics and finance, that the coalition lasted for a relatively long time, 1 year and 7 months.[14]
During his time in office, he made a state visit to Poland in February 1930, where he met both President Ignacy Mościcki and Marshal Józef Piłsudski to form a Baltic Entente, that didn't however find Polish support. On his return home, he visited Vilnius, which was controlled by Poland at the time. Lithuanian Minister of Foreign Affairs protested that Estonia is not treating the Vilnius dispute neutrally, damaging Estonian-Lithuanian relations, which somewhat healed by 1931.[18] In August 1930, Strandman hosted President Mościcki in Estonia.[19]
Membership in the parliament:
- 1917–1919 Estonian Provincial Assembly (Maapäev)
- 1919–1920 Estonian Constituent Assembly
- 1920–1923 I Riigikogu
- 1923–1926 II Riigikogu
- 1926–1927 III Riigikogu
- 1929–1932 IV Riigikogu
- 1932 V Riigikogu
Late diplomatic career and death
From 1933 to 1939 Strandman was the Estonian envoy to France, Belgium, Spain and the Vatican, residing in Paris. In 1936 he supported Juhan Kukk, Ants Piip, Jaan Teemant and Jaan Tõnisson, who signed a memorandum addressed to Prime Minister in duties of the State Elder Konstantin Päts, demanding civil freedoms and an end to his authoritarian rule.[20] In 1938, Strandman became a judge at the Permanent Court of International Justice in the Hague.[21]
In 1939, Strandman returned to Estonia, but resigned from public life due to bad health. As he wasn't active in politics, he was left alone after the Soviet occupation in 1940. In 1941 however, Strandman achieved a formal notice to arrive in front of the NKVD. He knew of his fate and decided to shoot himself to death in his home in Kadrina on 5 February 1941. He was buried in Tallinn Sisekalmistu cemetery.[3]
Cultural activities
Strandman was in the board of the "Estonia" Society and Tallinn Savings and Loans Society (Tallinna Vastastikune Krediitühisus).[4] He was a member of the Estonian Students' Society since 1899[3] and received honorary doctorates from the University of Tartu in 1928 and Warsaw University in 1930. Strandman renounced all honours and awards, that had been given to him.[7]
Personal life
In 1907, Strandman married Lydia Hindrikson (1889–1934) . Their first two children, daughter Hella (1909–1913) and son Hans (1911–1913) died early. Their second daughter Lydia (1914–1966) died after the war.[22]
Awards
1920 – Cross of Liberty III/I
1921 – Order of the Estonian Red Cross III
1928 – Order of the Estonian Red Cross II/II
1929 – Order of the Estonian Red Cross I/II
1930 – Order of the Cross of the Eagle I
See also
References
- 1 2 "Otto Strandmani sünd" (in Estonian). Histrodamus. Retrieved 8 June 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Histrodamus – Poliitikud: Otto Strandmani lugu
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Pillak, Peep. Eesti Päevaleht – Riigimees Otto Strandman 130, 03.12.2005
- 1 2 Heads of State of the Republic of Estonia – Otto Strandman
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 54
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 150
- 1 2 3 Riigikogu pressiteated – Ene Ergma sõnavõtt Otto Strandmani mälestustahvli avamisel Tallinnas, 30 November 2005
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 169
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 184-185
- ↑ Vabariigi Valitsus – Vabariigi Valitsus 09.05.1919 – 18 November 1919
- ↑ Vabariigi Valitsus – Vabariigi Valitsus 26 October 1920 – 25 January 1921
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 221
- ↑ Vabariigi Valitsus – Vabariigi Valitsus 26 March 1924 – 16 December 1924
- 1 2 3 Sirp – Otto Strandman manitseb tänaseid eelarvetegijaid, 12.09.2008
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastsaneerimaus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 264
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 290
- ↑ Eesti Suursaatkond Varssavis – Sõjalisest missioonist saatkonnaks
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 332
- ↑ XX sajandi kroonika, I osa; Eesti Entsüklopeediakirjastus, Tallinn, 2002; p. 339
- ↑ Meie parlament ja aeg – 1936
- ↑ BHR – Otto Strandman
- ↑ Välisministeerium – Eesti välisteenistus. Biograafiline leksikon 1918–1991, p. 110