Oxadiazole
Oxadiazoles are a class of heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound of the azole family; with the molecular formula C2H2N2O. There are four isomers of oxadiazole:
-
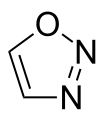
1,2,3-oxadiazole
-

1,2,4-oxadiazole
-
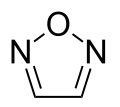
1,2,5-oxadiazole
(furazan) -
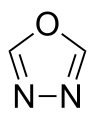
1,3,4-oxadiazole
1,2,4-Oxadiazole, 1,2,5-oxadiazole, and 1,3,4-oxadiazole are known, but the 1,2,3-isomer is unstable ring-opens to form the diazoketone tautomer.[1] The stable oxadiazoles appear in a variety of pharmaceutical drugs including raltegravir, butalamine, fasiplon, oxolamine, and pleconaril.
References
- ↑ John A. Joule; Keith Mills (28 May 2013). Heterocyclic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. p. 842. ISBN 1-118-68164-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.