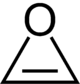
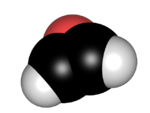
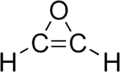Oxirene
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Oxirene | |||
| Other names
acetylene oxide, 1,2-epoxyethene, oxacyclopropene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 157-18-6 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:30973 | ||
| ChemSpider | 140985 | ||
| MeSH | C012469 | ||
| PubChem | 160438 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2O | |||
| Molar mass | 42.04 g/mol | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related molecules with 3-membered rings |
Ethylene oxide cyclopropane cyclopropene aziridine thiirane thiirene | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Oxirene is a hypothesized heterocyclic chemical compound which contains an unsaturated three-membered ring containing two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. As the configuration is extremely strained, no consensus exists whether the structure constitutes a molecule or whether it is merely a transition state.[1] The substance is therefore mainly evaluated by molecular modeling techniques.
Experimental indications exist that oxirene (as intermediate or transition state) occurs in the Wolff rearrangement.
References
- ↑ Mawhinney, Robert C; Goddard, John D (2003). "Assessment of density functional theory for the prediction of the nature of the oxirene stationary point". Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM. 629: 263. doi:10.1016/S0166-1280(03)00198-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.