Pier 40 at Hudson River Park
| Pier 40, The Pier | |
|
Pier 40 (front) and piers 45 and 46, as seen from One World Observatory | |
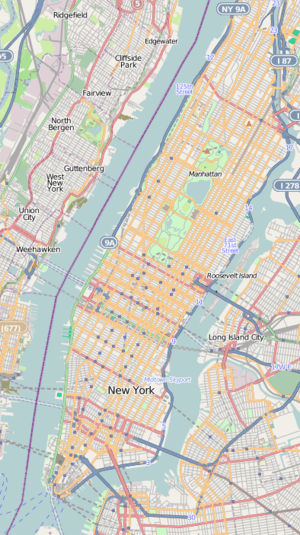 Pier 40 at Hudson River Park  Pier 40 at Hudson River Park  Pier 40 at Hudson River Park  Pier 40 at Hudson River Park Location of Pier 40 at Hudson River Park | |
| Address | 353 West Street, New York, NY 10014 |
|---|---|
| Location | Greenwich Village |
| Coordinates | 40°43′45″N 74°0′45″W / 40.72917°N 74.01250°WCoordinates: 40°43′45″N 74°0′45″W / 40.72917°N 74.01250°W |
| Owner |
State of New York City of New York |
| Operator | Hudson River Park Trust |
| Type | Multi-purpose |
| Seating type | Movable bleachers |
| Field size | 400 × 400 feet |
| Field shape | Square |
| Acreage | 15 |
| Surface | Turf |
| Construction | |
| Broke ground | July 31, 1958[1] |
| Opened |
October 24, 1962 (as ship terminal)[2][3] May 12, 2005 (as Hudson River Park)[4][5] |
| Renovated | 1998–2005 |
| Construction cost | $19 million |
| Tenants | |
| New York Knights | |
Pier 40 at Hudson River Park, more commonly known as Pier 40, is a parking garage, sports facility, and former marine terminal located at the west end of Houston Street in Manhattan, New York City, within Hudson River Park. It is home to the New York Knights of the American National Rugby League (ANRL), though it is primarily used by youth and high school athletics.
The pier is the largest structure in Hudson River Park at over 14 acres in size,[6] and is the home to the Hudson River Park Trust's offices.[7] Various park tenants host activities as well. Sports include baseball, football, soccer, kayaking, rowing, trapeze arts, and rugby among others.
History
.jpg)
Prior to the construction of Pier 40, five city-owned "finger" piers were located at the site. These were from south-to-north Pier 37 (at Charlton Street), Pier 38 (at King Street), Pier 39 (at West Houston Street), Pier 40 (at Clarkson Street), and Pier 41 (at Leroy Street). Companies using the piers in the early 20th Century included the Southern Pacific Transportation Company, the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (DL&W), and the Atlantic Transport Line. By the 1950s, the piers were used by the DL&W and the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad.[8][9][10][11][12][13][14]
The current Pier 40 was proposed as a passenger and cargo terminal in February 1956 by the city's Marine and Aviation department. The plan was put forward to allow the Holland America Line to move its area operations from Hoboken, New Jersey on the other side of the Hudson River, where the company was based for 73 years. It was the first terminal of its kind to be built by the city, and was designed as a "massive hollow square" with three levels to accommodate cars, taxis, and commercial trucks. The massive four block structure replaced the five smaller "finger" piers. Construction began in 1958 at the cost of over $18 million, and the Pier began operations in 1962, with Holland America signing a 20-year lease for over $1.2 million in annual rent.[8][9][10][15][16][17][18] Holland America also moved its offices from the Financial District to Pier 40.[18] In its first year in operation, Pier 40 served over 2,000 passengers daily.[19] In 1971, the Pier was taken over by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey.[20] Holland America moved their operations to the New York Passenger Ship Terminal in Hell's Kitchen in 1974.[21][22] Pier 40 ceased serving ships at that time, and ended all operations around 1983.[1][4][20][21][22][23][24]
Following the ceasing of maritime operations, in 1982 the Pier was purchased by the State of New York for the failed Westway project.[20][22] Under the New York State Department of Transportation's operations,[25] its primary use was as a parking complex for cars, buses and trucks, as well as commercial warehousing.[22][26][27][28] Bus, truck, and warehousing activity ended in 2004.[3][23][29][30]
The facility was rededicated under the Hudson River Park act of 1998.[31][32] At this time, two small athletic fields opened on the pier's roof.[4] Between 1998 and 2003, several plans abound for the redevelopment of the site. One was an entertainment complex featuring movie theaters and Cirque du Soleil performances. Another plan sought to construct a public high school along with swimming pools and retail space, in addition to conventional sports fields.[27] Additional plans called for a branch of the Guggenheim Museum[33] and a big-box store.[34][35] Ultimately, a plan backed by the community won out,[36] and the pier currently serves the dual purpose of commercial parking garage (located in the outer perimeter of the pier) and a multi-purpose sports facility (encompassing the center of the facility and small sections of the upper level). The main field (occupying the former cargo level) began construction in 2004, and opened in May 2005 with then-Governor George Pataki and professional soccer player Eddie Johnson in attendance.<ref name=Villager-Pier40-Opening-2005 /[5][27] The sports fields were intended as an interim solution, until a major development would take place.[30][37] According to the Hudson River Park Trust, the facility generates $6 million in operating revenue and 40% of the entire park's annual operating budget.[6][38]
Current condition and use
Pier 40's design resembles a square doughnut, with the three decks hollowed in the center by the central courtyard.[9][16][36] The outer facade consists of tan brick and blue-grey enamel.[16] The pier's base is made of concrete.[9][15] Extending 800 feet (240 m) west out of Manhattan island over the Hudson River,[15][39] the pier is held up by over 3,500 steel H-pile girders reinforced by concrete sunk into the river.[8][15]
According to several reports, the Pier is severely dilapidated and gradually sinking into the Hudson River. Sections of the roof have fallen in, and portions of the garage, a stairwell, bathrooms, and one of the upper fields, have been closed since 2012. A 2014 report found that over half of the facility's 3,500 steel girders that hold it above the river are severely deteriorated, possibly due to the electrical rust-protection system being shut down during the 1970s fiscal crisis. The turf field is also subject to flooding and warping after heavy precipitation, even though turf fields are typically designed to optimize drainage. In spite of the revenue the facility generates, Hudson River Park officials have discussed closing the park due to the $7 million annual financial burden required to maintain it.[6][15][23][29][36][40]
Following Hurricane Sandy in 2012, the Pier was closed after being engulfed by over 12 feet of water.[24] The fields reopened on December 19 after $50,000 in donations to fix the damaged turf surface,[41] while full power was restored by spring 2013.[42]
As a marine terminal
The pier's three decks were used for the loading and unloading of cars, taxis, and trucks, which alleviated congestion on local streets. The ground floor was dedicated to cargo operations, with the central courtyard utilized for the parking and loading of up to 350 trucks simultaneously. The second floor was used for passenger operations, serving taxis picking up arriving passengers, and featuring a furnished waiting room. The roof served as parking for over 700 cars. Ramps connected the three levels.[2][9][10][16]
As Hudson River Park
.jpg)
The pier's outer decks now act as a parking garage. The car park (a self-parking facility) has a 1,700 car capacity (formerly accommodating approximately 2,000) and currently serves over 1,500 drivers.[3][23][29][30]
The upper-level recreational area, opened in 1998, features two fields (one small field and one soccer field) and a "flying trapeze" operated by the Trapeze School of New York.[4][23][31][43][44][45] The fields were resurfaced in 2004.[46]
The 400-by-400-foot (120 by 120 m) main athletic field at ground level (called the courtyard field) is constructed of modern artificial turf manufactured by FieldTurf, consisting of plastic grass blades submerged in recycled rubber pellets. Construction of the field began in 2004, and the field was opened in May 2005.[4][37][43][46][47] The regulation-size baseball field is located at the southwest corner of the park, while the Little League/softball field is located at the northeast corner. Both fields feature imitation-dirt turf cut-outs, base anchors, dugouts, and synthetic turf pitching mounds.[37] Indoor batting cages are located near the baseball field. The center of the park (east-to-west) is marked up for football, with movable goal posts and practice sleds. Several movable soccer goals are also located around the ground floor field, which can be set up into two or four soccer pitches covering each half or each corner of the field respectively.[44][45] At some point, black nets were installed around the field to prevent balls from flying into the asphalt walkway that surrounds the perimeter of the sports field. The facility also features twelve stadium lighting fixtures, allowing night games to be played.[48]
Prior to 2008, Public Schools Athletic League-sanctioned high school baseball games could not be played at Pier 40. This was because the portable mounds owned by the facility, which were 13 feet in diameter, did not meet the specifications of the league. The portable mounds (as opposed to a permanent dirt mound) were required to maintain the multi-purpose status of the field. In 2008, after lobbying by the nearby Stuyvesant High School, a new mound was purchased from an Iowa-based company that was 18 feet in diameter. The new mound, consisting of a center and two side pieces, was the first mound of its kind, and allowed for PSAL league games to be played.[47][49] The mound serves as the template for other turf mounds across the city, including those at DeWitt Clinton Park in Midtown, Harlem River Park in East Harlem, and Joe Austin Park adjacent to Thomas A. Edison High School in Queens.
Because of the multiple teams and groups using the park and limited space, balls from different sports will inevitably spillover into other games and practices.
Future development
When established as a park in 1998, Pier 40 was zoned for exclusively entertainment and retail purposes, with half of the pier required to be set aside for recreation.[29][31][32] Due to the facility's condition, however, several proposals have been floated to increase revenue to the park for repairs, which have been estimated to cost anywhere from tens to hundreds of millions of dollars.[24][50] A 2012 proposal from local real estate developer Douglas Durst (who served as the chairman of Friends of Hudson River Park group until late 2012) would consolidate the current parking facilities from a self-park to three-level stacked parking, freeing up 500,000 square feet on the roof for commercial space. The plan failed to gain support.[23][24] A 2014 proposal would demolish and redevelop the St. John's Terminal Building across the street (owned by the Atlas Group) into a residential and retail facility over the course of 10 years, which would require the sale of Pier 40's air rights but would generate and estimated $100 million in revenue.[6][51] This plan reportedly fell through due to public outcry and political opposition.[52]
In 2012, reports surfaced that the then-new Major League Soccer team New York City FC, which currently play at Yankee Stadium in the Bronx, were seeking to develop a new stadium at the Pier 40 site; renderings of this proposed stadium were leaked to Reddit.[50]
Tenants
Professional
Amateur and youth
- ASA College – baseball (practice only),[25][53] lacrosse (practice only)[25][54]
- Stuyvesant High School – football,[55] baseball,[47] softball, lacrosse (practice only)
- Xavier High School – football (practice only), rugby (practice only)
- Greenwich Village Little League (GVLL), Downtown Little League, Pier40Baseball – youth baseball[25]
- Downtown United Soccer Club & Gotham Girls FC – youth soccer[25]
References
- 1 2 "Flashback: Cementing Pier 40's place in Hudson history". The Villager. August 5, 2008. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- 1 2 Bamberger, Werner (October 25, 1962). "PIER 40 DEDICATED BY CITY OFFICIALS; Terminal May Be Ready for Use in 2 Months". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 Kilgannon, Corey (July 25, 1999). "NEIGHBORHOOD REPORT: HUDSON RIVER WATERFRONT; Anchoring a Cruise Ship Pier for Earthly Pleasures". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Anderson, Lincoln (May 18, 2005). "Things are kicking at the new Pier 40 athletic field". The Villager. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- 1 2 Governor George Pataki (May 12, 2005). "Governor Opens New 3.2 Acre Athletic Field in Hudson River Park". Project Vote Smart. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Bagli, Charles V. (May 15, 2014). "Possible Deal May Bring Money to Repair Pier 40 in Manhattan". The New York Times. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- ↑ "CONTACT US". Hudson River Park. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 "WORK BEGINS SOON ON MAMMOTH PIER: Contract Signing Will Clear Way for Holland-America Facility, Port's Biggest". The New York Times. March 28, 1958. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Rebuilding New York City's Waterfront: 1959 Progress (PDF). New York City Department of Marine & Aviation. 1959. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 Rebuilding New York City's Waterfront: A Progress Report to Robert F. Wagner, Mayor (PDF). New York City Department of Marine & Aviation. September 5, 1956. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- ↑ Supplementary Report: Department of Docks, For the Eight Months Ending December 31, 1897. 1898. pp. 457–459. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- ↑ New York (N.Y.). Dept. of Docks and Ferries (1903). City of New York, Department of Docks and Ferries: Annual Report, For the Year Ending December 31, 1903. The Department. p. 80. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- ↑ "PIER 1 DISAPPEARS FROM CITY HISTORY: 85-Year-Old Landmark Is Reduced to Debris". The New York Times. December 24, 1961.
- ↑ "PICKETS TO LEAVE 10TH STREET PIER: Agree to Let B. & O. Move After Getting Assurances Tenancy Is Temporary". The New York Times. May 19, 1958. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Condition Monitoring Inspection: Pier 40" (PDF). Hudson River Park Trust. March 2015. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Berkvist, Robert (April 28, 1963). "PEERLESS PIER 40; City's Newest West Side Ship Terminal Represents a Dockside Revolution A PEERLESS PIER FOR NEW YORK'S WEST SIDE". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- ↑ Ryan, Joseph J (September 12, 1957). "Holland-America Line Signs 20-Year Contract for New Pier; Four-Ship Terminal Costing $18,723,000 to Rise at West Houston St.--Lease Ends Two Years of Negotiation 6 Per Cent Rental Set". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- 1 2 "New York City Marine Facility Now Operating" (PDF). Niagara Falls Gazette. New York. Fultonhistory.com. February 25, 1963. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ↑ "PIER A YEAR OLD; City Aide Feted by Holland-America to Mark Move". The New York Times. March 13, 1964. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 Hine, Bill; Smith, Robert (July 8, 2008). "Talking Point: Authority should be zapped for Pier 40's sorry state". The Villager. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- 1 2 Brouwer, Norman; La Rocco, Barbara (2004). "Epilogue". A maritime history of New York (PDF). Brooklyn, N.Y.: Going Coastal. pp. 262–295. ISBN 978-0972980319. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 West Side Highway Project: Final Environmental Impact Statement. Federal Highway Administration, New York State Department of Transportation, United States Department of Transportation. January 4, 1977. pp. 9, 53, 58, 60, 172. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cuozzo, Steve (August 28, 2012). "Pier 40: Durst to the rescue". New York Post. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Chaban, Matt (December 16, 2012). "Sinking Pier 40: Durst Leaves Hudson River Park Amid Mutiny Over Its Future". The New York Observer. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Anderson, Lincoln (March 7, 2013). "Champs pitch towers plan; Durst goes to bat for reuse". The Villager. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ↑ "West Side Pier Closed On Structural Grounds". The New York Times. Associated Press. August 31, 1987. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 Editorial (February 7, 2008). "Turning a Pier Into a Park". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ↑ Allee King Rosen and Fleming, Inc. (May 1994). Route 9A Reconstruction Project: Final Environmental Impact Statement; Appendix B: Land Use and Socioeconomic Conditions. New York State Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, United States Department of Transportation. pp. B–7, B–46, B–55, B–57. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Foderaro, Lisa W. (August 17, 2012). "Repair Costs Could Bring Down a Popular Pier". The New York Times. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 Amateau, Albert (January 9, 2004). "Trust sued over Pier 40 delays". Downtown Express. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 Anderson, Lincoln (December 1, 2006). "Cirque tries to swing Pier 40 deal". The Villager. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- 1 2 Martin, Douglas (July 30, 1998). "Hudson Park Draws Closer To Reality; Proponents Celebrate Approval by Albany". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- ↑ "A Pier, Once Ignored, Is Suddenly a Favorite". The New York Times. December 10, 1998. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ↑ Pristin, Terry (November 24, 2002). "Big-Box Plan, but With Icing on Top". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ↑ Pristin, Terry (February 14, 2003). "Big-Box Store Backed for Pier 40 in Village". The New York Times. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- 1 2 3 Foderaro, Lisa W. (April 3, 2015). "How Diller and von Furstenberg Got Their Island in Hudson River Park". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 Roy, Zachary (April 1, 2005). "Pier 40 field expected to open in April". Downtown Express. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ↑ "PIER 40: Construction and Design Status". Hudson River Park. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- ↑ Associated Press (April 26, 1967). "New Pier for Liners Planned in N.Y. City" (PDF). Knickerbocker News. New York. Fultonhistory.com. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ↑ "Water world at Pier 40". The Villager. June 7, 2006. Retrieved 24 March 2015.
- ↑ Swalec, Andrea (December 20, 2012). "With $50K in Donations, Pier 40 Ball Fields Reopen After Sandy". West Village, New York: DNA.info. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- ↑ "Lights on at Pier 40". Hudson River Park. Retrieved 2013-12-05.
- 1 2 "PIER 40 SPORTS FIELD PREPARATION HITS OVERTIME; OPENING IS SET FOR MID-APRIL". FieldTurf. 2004. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- 1 2 "PIER 40 - SOCCER FIELDS MAP: U11 & U12 (7 v 7)" (PDF). Downtown United Soccer Club. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- 1 2 "PIER 40 - SOCCER FIELDS MAP: U11 & U12 (9 v 9)" (PDF). Downtown United Soccer Club. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- 1 2 "2004 Annual Report and Financing Plan" (PDF). Hudson River Park Trust. 2004. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 Anderson, Lincoln; Singh, Aman (May 10, 2005). "Oh oh, there's another mound problem; at Pier 40". The Villager. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- ↑ Roy, Zachary (April 5, 2005). "Pier 40 sports field preparation hits overtime; opening is set for mid-April". The Villager. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- ↑ "About Us". Friends of Stuyvesant Baseball. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- 1 2 Diaz, Cesar (June 4, 2012). "The Problems With Pier 40". New York, New York: U.S. National Soccer Players. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- ↑ Rosenberg, Zoe (November 12, 2014). "Pier 40 Air Rights Deal Could Mean Affordable Housing Nearby". Curbed. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- ↑ Budin, Jeremiah (June 9, 2014). "Pier 40's Secret $100 Million Air Rights Memorandum Is Dead". Curbed. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
- ↑ Jean-Lubin, Daniel (March 28, 2013). "Founded on computer programming, ASA now has a top baseball program". The Villager. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ↑ Jean-Lubin, Daniel (April 4, 2015). "In second season, ASA lax team netting lots more wins". The Villager. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ↑ "Peglegs leg it up to Pier 40". The Villager. September 21, 2005. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
External links
- Official website
- Pier 40 Report − 2015