Potomac Flotilla
| Potomac Flotilla | |
|---|---|
|
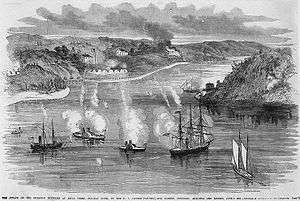
Attack on the Confederate Batteries at Aquia Creek by the Potomac Flotilla. | |
| Active | 1861 - 1865 |
| Country |
|
| Branch |
|
| Type | naval squadron |
The Potomac Flotilla, or the Potomac Squadron was a unit of the United States Navy created in the early days of the American Civil War to secure Union communications in the Chesapeake Bay, the Potomac River and their tributaries, and to disrupt Confederate communications and shipping in the same.
History
American Civil War
On April 22, 1861 Commander James H. Ward, who was the commander of the receiving ship USS North Carolina at the New York Navy Yard, wrote to Secretary of the Navy Gideon Wells to put forth a plan for the protection of the Chesapeake Bay area. Ward suggested a “Flying Flotilla” of light draft vessels to operate in the Chesapeake and its tributaries. His commander Captain Samuel L. Breese, commandant of the New York Navy Yard, endorsed his plan. Wells accepted this proposal and wrote back to Wells and Breese on April 27, 1861 authorizing them to begin carrying out Ward’s plan. On May 1, 1861 the first vessels for the new flotilla were acquired. On May 16, 1861 Ward set out from the New York Navy Yard with three vessels, the Thomas Freeborn, Reliance and Resolute. He arrived at the Washington Navy Yard on May 20, 1861 on board his flagship, the Thomas Freeborn.[1]
On June 27, 1861 Ward’s flotilla engaged the Confederates at Mathias Point, Virginia. While he was sighting the bow gun of the Thomas Freeborn, Ward was shot through the abdomen and died within an hour due to internal hemorrhaging. He was the first United States Naval officer to be killed during the war.[2]
After the death of Ward the flotilla was led by a succession of short-term commanders until the fall of 1862 when Commodore Andrew A. Harwood took command. He was in turn succeeded by Commander Foxhall A. Parker on December 31, 1864.[3]
On July 18, 1865 the Navy Department ordered Parker to disband the flotilla on July 31, 1865. Most of the flotilla’s remaining vessels were sent to the Washington Navy Yard to be decommissioned.[4]
Name of the Flotilla
It wasn’t until August 1861 that the flotilla became known as the Potomac Flotilla. The designation of Flying Flotilla was dropped when Ward’s force arrived in the theatre of operations. The flotilla was then referred to by a variety of names, including: Flotilla, Potomac River; Potomac Blockade; Flotilla in the Chesapeake; etc. In early August 1861 the flotilla commander and the Navy Department began to consistently refer to the command as the Potomac Flotilla.[5]
Operations
1861
Engagement with the Confederate batteries at Aquia Creek, Virginia, 29 May – 1 June 1861
Affair at Mathias Point, Virginia, 27 June 1861
Engagement with the Confederate batteries at Potomac Creek, Virginia, 23 August 1861
Engagement with the Confederate battery at Freestone Point, Virginia, 25 September 1861
1862
Engagement at Cockpit Point, Virginia, 3 January 1862
Expedition up the Rappahannock River to Tappahannock, Virginia, 13–15 April 1862
Expedition up the Rappahannock River to Fredericksburg, Virginia, 20 April 1862
Expeditions to Gwynn’s Island and Nomini Creek, Virginia, 3–4 Nov, 1862
Engagement at Port Royal, Virginia, 4 December 1862
Engagement at Brandywine Hill, Rappahannock River, Virginia, 10–11 December 1862
1863
Destruction of salt works on Dividing Creek, Virginia, 12 January 1863
Destruction of Confederate stores at Tappahannock, Virginia, 30 May 1863
Capture of U. S. steamers Satellite and Reliance, 16 August 1863
1864
Expedition to the Northern Neck of Virginia, 12 January 1864
Expedition up the Rappahannock River, Virginia, 18–21 April 1864
Expedition to Carter’s Creek, Virginia, 29 April 1864
Expedition to Mill Creek, Virginia, 12–13 May 1864
Expedition up the Rappahannock River, Virginia, 16–19 May 1864
Expedition to the Northern Neck of Virginia, 11–21 June 1864
Expedition to Milford Haven and Stutt’s Creek, Virginia, 24 September 1864
1865
Expedition to Fredericksburg, Virginia, 6–8 March 1865
Expedition up the Rappahannock River, 12–14 March 1865
Operations in Mattox Creek, Virginia, 16–18 March 1865
Ships of the Squadron
When Commander James H. Ward departed from New York Navy Yard on May 16, 1861 his flotilla consisted of three vessels. The strength of the flotilla would be steadily increased until it reached a strength that hovered between fifteen and twenty-five vessels.[6]
| Ship | Rate | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casco | 4th | Ironclad Monitor | Casco class |
| Chimo | 4th | Ironclad Monitor | Casco class |
| Mahopac | 4th | Ironclad Monitor | Canonicus class |
| Saugus | 4th | Ironclad Monitor | Canonicus class |
| Pawnee | 2nd | Screw Sloop | |
| Seminole | 3rd | Screw Sloop | |
| Wachusett | 3rd | Screw Sloop | Commander Wilkes' Flagship |
| Allegheny | 4th | Screw Sloop | Receiving Ship at Baltimore |
| Harriet Lane | 3rd | Sidewheel Gunboat | from United States Revenue Cutter Service |
| Mahaska | 3rd | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Port Royal | 3rd | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Anacostia | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Aroostook | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Crusader | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Currituck | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Dawn | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Don | 4th | Screw Gunboat | Blockade runner captured by USS Pequot 4 March 1864 off Beaufort, North Carolina. |
| Dragon | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| E. B. Hale | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Eureka | 4th | Screw Gunboat | Steamer captured by USS Anacostia 20 April 1862 in Rappahannock River, Virginia. |
| Fuchsia | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Little Ada | 4th | Screw Gunboat | Blockade runner captured by USS Gettysburg 9 July 1864 in South Santee River, South Carolina. |
| Mystic | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Penguin | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Pocahontas | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Teaser | 4th | Screw Gunboat | ex-Confederate captured by USS Maratanza 4 July 1862 in James River, Virginia |
| Tulip | 4th | Screw Gunboat | Sunk by boiler explosion off Ragged Point, Virginia, 11 November 1864 |
| Valley City | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Western World | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Wyandotte | 4th | Screw Gunboat | |
| Adela | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | Blockade runner captured by USS Quaker City 7 July 1862 off New Providence in the Bahamas |
| Banshee | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | Blockade runner captured by USAT Fulton & USS Grand Gulf 21 November 1863 off Wilmington, North Carolina |
| Ceres | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Coeur de Lion | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Commodore Barney | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | ex-Ferryboat |
| Commodore Read | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | ex-Ferryboat |
| Delaware | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Jacob Bell | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Isaac N. Seymour | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| John L. Lockwood | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Mercury | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Morse | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | ex-Ferryboat |
| Mount Washington | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | Known as USS Mount Vernon to 4 November 1861 |
| Nansemond | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Satellite | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | Captured by Confederate boarding party 23 August 1863 in Rappahannock River, sunk at Port Royal, Virginia, 28 August 1863 |
| Stepping Stones | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | ex-Ferryboat |
| Thomas Freeborn | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | Commander Ward's Flagship |
| Underwriter | 4th | Sidewheel Gunboat | |
| Union | 4th | Screw Auxiliary | |
| Baltimore | 4th | Sidewheel Auxiliary | Ordnance Vessel, Washington Navy Yard |
| Cactus | 4th | Sidewheel Auxiliary | Supply Ship |
| Ella | 4th | Sidewheel Auxiliary | Picket & Dispatch Vessel |
| Ice Boat | 4th | Sidewheel Auxiliary | Icebreaker |
| King Philip | 4th | Sidewheel Auxiliary | Dispatch Vessel, known as USS Powhatan to 4 November 1861 |
| Philadelphia | 4th | Sidewheel Auxiliary | Transport Ferry |
| Wyandank | 4th | Sidewheel Auxiliary | Storeship |
| Juniper | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Leslie | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Moccasin | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Periwinkle | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Primrose | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Reliance | 4th | Screw Tug | Captured by Confederate boarding party 23 August 1863 in Rappahannock River, sunk at Port Royal, Virginia, 28 August 1863 |
| Rescue | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Resolute | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Tigress | 4th | Screw Tug | Sunk 10 September 1861 in collision with merchant ship State of Maine off Indian Head, Maryland |
| Verbena | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| Watch | 4th | Screw Tug | Known as USS A. C. Powell until Aug 1862, known as USS Alert from August 1862 to 2 February 1865 |
| Young America | 4th | Screw Tug | ex-Confederate, captured 24 April 1861 by USS Cumberland in Hampton Roads |
| Zeta | 4th | Screw Tug | |
| General Putnam | 4th | Sidewheel Tug | Also known as USS William G. Putnam |
| Heliotrope | 4th | Sidewheel Tug | |
| Island Belle | 4th | Sidewheel Tug | Tug & Dispatch Boat |
| Yankee | 4th | Sidewheel Tug | |
| E. H. Herbert | - | Tug | Chartered Vessel |
| Edwin Forrest | - | Tug | Chartered Vessel |
| James Murray | - | Tug | Chartered Vessel |
| Bibb | - | Sidewheel Steamer | from United States Coast Survey |
| Corwin | - | Sidewheel Steamer | from United States Coast Survey |
| Adolph Hugel | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| Arletta | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| Dan Smith | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| George Mangham | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| Matthew Vassar | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| Racer | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| Sophronia | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| T. A. Ward | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| William Bacon | 4th | Sailing Schooner | Mortar Schooner |
| Bailey | - | Sailing Schooner | from United States Coast Survey |
| Chaplin | 4th | Sailing Schooner | |
| Dana | - | Sailing Schooner | from United States Coast Survey |
| Howell Cobb | - | Sailing Schooner | from United States Coast Survey |
| Picket Boat No. 4 | - | Screw Picket Boat | |
| Picket Boat No. 6 | - | Screw Picket Boat |
Commanders
| Squadron Commander | From | To | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commander James Harmon Ward | late April 1861 | 27 June 1861 | Killed in Action |
| Commander Stephen Clegg Rowan | 27 June 1861 | 10 July 1861 | Commander pro tem |
| Commander Thomas Tingey Craven | 10 July 1861 | 2 December 1861 | |
| Lieutenant Abram D. Harrell | 2 December 1861 | 6 December 1861 | Commander pro tem |
| Lieutenant Robert Harris Wyman | 6 December 1861 | early July 1862 | |
| Lieutenant Commander Samuel Magaw | early July 1862 | 1 September 1862 | Commander pro tem |
| Commodore Charles Wilkes | 1 September 1862 | 10 September 1862 | |
| Commodore Andrew Allen Harwood | 10 September 1862 | 31 December 1863 | |
| Commander Foxhall Alexander Parker, Jr. | 31 December 1863 | 31 July 1865 |
References
- In these notes the abbreviation ORN is used for the work Official Records of the Union and Confederate Navies in the War of the Rebellion.
- Notes
- ↑ ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 4 (1896), pp. 420, 430, 443, 458, 467, 471.
- ↑ ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 4 (1896), pp. 539–41.
- ↑ ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 4 (1896), pp. 541, 570–1, 575, 757–8, 760–1. ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 5 (1897), pp. 3, 72, 75, 82, 84, 379.
- ↑ ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 5 (1897), pp. 576, 578.
- ↑ ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 4 (1896), pp. 488, 504, 509, 511, 596–600.
- ↑ ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 4 (1896), pp. xv-xvi, 458, 508, 570, 666. ORN, Ser. I, Vol. 5 (1897), pp. xv-xvi, 60–1, 75, 100, 108, 204–5, 245–6, 260, 287, 361–2, 391, 366–7, 374, 380, 408–9, 461, 496, 502, 506, 508, 515, 531, 548–9, 567, 571–4.
- Bibliography
- Official Records of the Union and Confederate Navies in the War of the Rebellion, Series I, Volume 4. (Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1896).
Official Records of the Union and Confederate Navies in the War of the Rebellion, Series I, Volume 5. (Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1897). - Silverstone, Paul H. Warships of the Civil War Navies. (Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press, 1989). ISBN 0-87021-783-6
-
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Naval History & Heritage Command document "Commander James H. Ward".
This article incorporates public domain material from the Naval History & Heritage Command document "Commander James H. Ward".