French Congo
| French Congo | ||||||||||
| Congo français | ||||||||||
| French colony | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
 | ||||||||||
| Capital | Brazzaville | |||||||||
| Languages | French (official) Fang, Myene, Kongo, Lingala | |||||||||
| Religion | Christianity, Bwiti, Islam, traditional religions | |||||||||
| Political structure | Colony | |||||||||
| History | ||||||||||
| • | Established | 1882[1] | ||||||||
| • | Renamed Middle Congo | 1903 | ||||||||
| • | Reestablished as French Equatorial Africa | 1910 | ||||||||
| Currency | French franc | |||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Today part of | | |||||||||
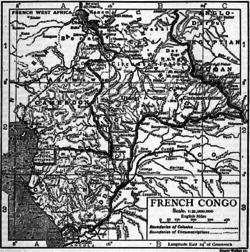
The French Congo (French: Congo français) or Middle Congo (French: Moyen-Congo) was a French colony which at one time comprised the present-day area of the Republic of the Congo, Gabon, and the Central African Republic.
History
The French Congo began at Brazzaville on 10 September 1880 as a protectorate over the Bateke people along the north bank of the Congo River,[1] was formally established as the French Congo on 30 November 1882,[1] and was confirmed at the Berlin Conference of 1884–85. Its borders with Cabinda, Cameroons, and the Congo Free State were established by treaties over the next decade. The plan to develop the colony was to grant massive concessions to some thirty French companies. These were granted huge swaths of land on the promise they would be developed. This development was limited and amounted mostly to the extraction of ivory, rubber, and timber. These operations often involved great brutality and the near enslavement of the locals.
Even with these measures most of the companies lost money. Only about ten earned profits. Many of the companies' vast holdings existed only on paper with virtually no presence on the ground in Africa.
The French Congo was sometimes known as Gabon-Congo.[2] It formally added Gabon on 30 April 1901,[1] was officially renamed Middle Congo (French: Moyen-Congo) in 1903, was temporarily divorced from Gabon in 1906, and was then reunited as French Equatorial Africa in 1910 in an attempt to emulate the relative success of French West Africa.
A 1906 study, L’Expansion coloniale au Congo français (The colonial expansion of French Congo) was published in conjunction with the French Colonial Exposition in Marseille.[3]
List of Commissioners-General
The colony was administered under four commissioners-general (commissionaires généraux) prior to its reorganization into Middle Congo.[1]
- Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza (January 1883 – 1897)
- Louis Albert Grodet (1897–1898)
- Henri Félix de Lamothe (1898–1901)
- Emile Gentil (1901–1903)
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to French Congo. |
- French Equatorial Africa
- List of French possessions and colonies
- French colonial empire
- Belgian Congo
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Histoire militaire des colonies, pays de protectorat et pays sous mandat. 7. "Histoire militaire de l'Afrique Équatoriale française". 1931. Accessed 9 October 2011. (French)
- ↑ Payeur-Didelot. "Gabon. - Colonie française du Gabon-Congo, 1/3,700,000". 1894. (French)
- ↑ Rouget, Ferdinand (1906). The Colonial Expansion of French Congo (in French). Émile Larose - via World Digital Library. Retrieved 2014-06-19.
Further reading
- Petringa, Maria. Brazza, A Life for Africa. Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse, 2006. ISBN 978-1-4259-1198-0. Describes Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza's extensive explorations of what became French Congo, and later, French Equatorial Africa.