Commodore REU
Commodore's RAM Expansion Unit (REU) range of external RAM add-ons for their Commodore 64/128 home computers was announced at the same time as the C128.[1] The REUs came in three models, initially the 1700 (128 KB) and 1750 (512 kB), and later the 1764 (256 kB, for the C64).
The need for the REU came about when Commodore management decided to not use the final version of the custom Memory Management Unit (MMU) which then limited the size of memory in spite of early discussion of a larger memory map. Engineers traveling to the 1985 CES show were confronted with flyers and billboards advertising a memory size that was no longer supported and finally the top management asked where the additional memory (Up to 512K) would plug in.
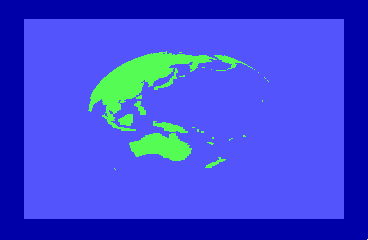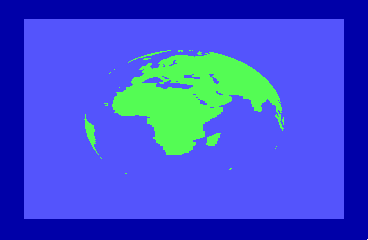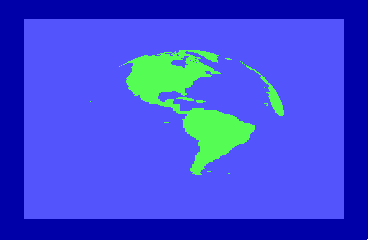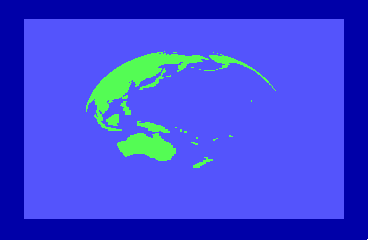
By the time of the 1985 CES show in Chicago, the engineers were able to display a spinning globe of the earth as a demonstration of Direct Memory Access (DMA) by the new REU units.
The REU hardware was designed by Frank Palia and the dedicated Integrated Circuit (IC) was designed by Victor Andrade. Fred Bowen and Terry Ryan adapted the kernel and Basic to accommodate the REU natively and Hedley Davis wrote the globe spinning demo which was an impressive display of animation in the mid 1980s.
Hardware description
Although the C128 could access more than 64 kB of RAM through bank switching, the memory inside the REU could only be accessed by memory-transfers (STORE/LOAD/SWAP/COMPAREs) between the main memory and the REU memory, thus, giving an equivalent to a (slow) small memory window. Additionally, the C128's built-in BASIC 7.0 had three statements, STASH,FETCH, and SWAP, for storing and retrieving data from the REU.

Officially, only the 1700 and 1750 were supported on the C128. The 256 kB model, the 1764, was released for the C64 at the same time. There were only minor differences between the three models. The factory unit could not support the 1764 and it bundled 2.5 ampere C64 power supply unit, which supported the computer and its devices and was defined by the level of need the device had for a regulated power source with enough RAM.[2]
The 1700 utilizes eight 4164 64kx1 DRAMs, the 1764 has eight 41256 256kx1 DRAMs, and the 1750 has sixteen 41256 DRAMs.
In practice, the difference between the 1764 and the earlier units had little effect on compatibility, and people used 1700s and 1750s successfully with the C64, and 1764s successfully with the C128, although the C64's stock power supply was inadequate to reliably handle the power load of any of them. Some dealers unbundled the 1764 and the power supply in order to sell the power supply to C64 users, and/or upgrade the 1764 to 512 kB.
During the late 1980s, there was a shortage of DRAM caused by the Reagan Administration enacting anti-dumping restrictions on Japanese manufacturers, thus 1750s were rare and expensive. However it was comparatively easy to upgrade a 1700 or 1764 to 512 kB. Several firms did this commercially, either selling upgraded units or upgrading customer-supplied units.
In the early 1990s, DIY modification schemes to increase the capacity of an REU to one megabyte or higher appeared on various online services.
Model differences
The 1700s circuit board was identical to that of the 1750, and a trace marked J1 indicated the size of the chips used. On the 1750 and 1764, this trace was cut.
The 1700 and 1750 had a resistor at position R4 that, according to Commodore engineer Fred Bowen, compensated for subtle differences in the expansion port on the C64 and C128. The 1764 lacked that resistor. Bowen and other CBM engineers recommended against using a 1764 with a C128 unless the resistor was added, or a 1700/1750 with a C64 unless the resistor was removed.
It was possible to check for the presence of a 1750 by reading memory address $DF00's bit 4, which was 1 on a 1750, and 0 on a 1700 or 1764. However, since this procedure would not distinguish between a 1700 and a 1764, many programmers wrote to the RAM itself to find out the amount of memory installed.
REU software support
Very little software made use of the REUs. Like other add-on products from Commodore, their relatively small installed base relative to the huge number of C64s made software developers hesitant to invest much time and effort in supporting it, and the lack of commercial support kept sales lower than they otherwise might have been.
The REUs came with software to utilize the extra memory as a RAM disk, but the RAM disk's compatibility with commercial software was spotty, as some commercial software relied heavily on various quirks of the Commodore 1541 floppy drive. Additionally, many commercial programs simply overwrote the memory space occupied by the RAM disk software.
The GEOS operating system had built in support for the REU as a RAM disk, as did the C128's version of CP/M, and some disk copy programs used the REU to facilitate high-speed copying with a single disk drive. GEOS as well as other programs even used the REU for quick memory transfers within the host machine's main memory by storing a memory block into the REU and then fetching it back to another location. Using this method, only the actual data to be transferred needed to travel on the machine's data bus—unlike the ordinary method, which had the computer's CPU do the transfer, thus spending at least three quarters of the bus capacity on instruction fetches and only one quarter or less on payload data.
Due to its high speed relative to Commodore's floppy drives or even the commercially available hard drives, the REU also became popular with BBS operators.
See also
- Super 1750 Clone
- geoRAM
- RAMLink
- Creative Micro Designs 2 MB REU, (1750 XL)
References
- ↑ Parallelus. "Commodore 64 - The Best Selling Computer In History - Commodore Computers: VIC20 C64 PET C128 Plus4 - All 8 Bit Machines". Commodore Computers: VIC20 C64 PET C128 Plus4 - All 8 Bit Machines. Retrieved 2016-02-08.
- ↑ "Industrial Power Supply Products - ICP America". www.icpamerica.com. Retrieved 2016-02-08.
External links
- REU Games & Utilities
- REU Programming documentation
- Source code of RAMDOS, a RAM disk program for the Commodore RAM Expansion Unit
- REU Programming - by Robin Harbron