Riverside Cemetery Gatehouse
|
Riverside Cemetery Gatehouse | |
|
Riverside Cemetery Gatehouse in 2014 | |
   | |
| Location | 3607 Pearl Rd., Cleveland, Ohio |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 41°27′25″N 81°41′55″W / 41.45694°N 81.69861°WCoordinates: 41°27′25″N 81°41′55″W / 41.45694°N 81.69861°W |
| Area | less than one acre |
| Built | 1897 |
| Architect | Charles W. Hopkinson |
| Architectural style | Gothic Revival and Romanesque Revival |
| MPS | Brooklyn Centre MRA |
| NRHP Reference # | 87000445[1] |
| Added to NRHP | March 19, 1987 |
Riverside Cemetery Gatehouse is a historic office building located in Riverside Cemetery at 3607 Pearl Road in Cleveland, Ohio. It was completed in 1897, and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1987.
Constructing the gatehouse
The Riverside Cemetery Association was formed on November 15, 1875.[2] Riverside Cemetery was opened on July 8, 1876, on a bluff overlooking the west bank of the Cuyahoga River in the unincorporated village of Brooklyn Centre (now a neighborhood which is part of Cleveland, but then an independent settlement).[3] It was a garden-style cemetery, and at the time of its dedication the largest cemetery on Cleveland's west side.[4]
As the cemetery was being laid out in 1875, the cemetery association constructed a wooden building in the southwest corner of the property near the corner of Pearl Road and Willowdale Avenue.[5][6] But as the cemetery grew, this structure proved too small and a larger office building was needed.[5] The cemetery's trustees approved construction of a new building at their annual meeting held on December 9, 1895.[7]
Noted local architect Charles W. Hopkinson was hired to develop the plans for the new building.[8][9] The date on which Hopkinson was hired is not known, but he submitted plans to the cemetery trustees probably in April 1896. The trustees approved his plans on May 4. Hopkinson had recommended that the building be constructed of granite. But granite was expensive, and the trustees asked the architect to determine the cost of using red brownstone (a building material popular at the time). The cost differential was significant, and the trustees chose brownstone.[5]
Construction contracts were let on June 30, 1896,[5] and construction began on July 9, 1896.[9]
The architectural style of the building has been variously described as "French château",[9][10] Gothic Revival,[8] and Romanesque Revival.[5][6] One source called it a combination of Gothic Revival and Romanesque Revival.[11] The structure consists of a steel beam frame[11] and red-colored brownstone from a quarry near Longmeadow, Massachusetts,[11][10][12] mortared with Portland cement.[9][11] The base of the veranda which wrapped around the building was poured cement.[11] The design featured a turret on the southwest corner that reached beyond the roof, dormer windows on the second floor, and buttresses around the building.[8]
The construction was largely completed by the end of 1896, although interior work continued into early 1897.[5]
The final cost of the building was variously reported as $18,000 ($512,856 in 2016 dollars),[11] $19,000 ($541,348 in 2016 dollars),[9] and $20,000 ($569,840 in 2016 dollars).[10][13][lower-alpha 1]
About the building
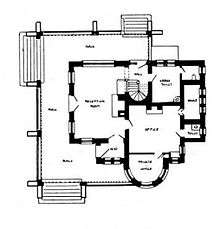
The Riverside Cemetery Gatehouse has two above-ground stories and a basement. As originally constructed, the first floor contained a reception room,[13][9][10] office,[9][10] fireproof vault,[10] and a ladies' bathroom.[11][13][10] The floors on the first floor reception room and ladies' bathroom were covered with mosaic tile.[11][13][10] The reception room was the largest on the first floor. It was roughly 16 by 22 feet (4.9 by 6.7 m) in size, with an arched,[11] coffered, Tudor-style, 16-foot (4.9 m) high oak ceiling.[11] The walls of the reception room were lined with 1.5-inch (3.8 cm) thick[5] enameled brick in a warm yellow color.[11][13] The reception room also featured a gas-fired fireplace with a wide mantel, and an "art window" made of 2,955 pieces of clear and stained glass.[11] The office measured 18 by 25 feet (5.5 by 7.6 m).[11] Its walls were tinted plaster,[11] it had a ceiling panelled in oak, and it featured oak flooring.[10]
A narrow, winding staircase led to the second floor.[10] Two meeting rooms existed on the second floor for the use of the trustees.[11][9][13][10] With the exception of the first floor reception room and office, each of the rooms on the first and second floor were panelled with quarter-sawn oak.[9][10] Chandeliers of Flemish brass lit the reception room, office, and both second floor rooms.[10]
The basement consisted of closets and storage space, and contained a furnace room.[9][10]
A 10-foot (3.0 m) wide[13] veranda with a coffered roof[11] supported by arches[10] wrapped around the building on its north, west, and south sides.[9][13] The roof was made of red[8][5] Spanish-made[11] terracotta tile,[8][11] with copper flashing.[11] A turret jutted 25 feet (7.6 m) above the second floor.[9][10]
History of the building
The building was originally lit by natural gas, but this was converted to electricity in the early 20th century.[5] At some point, the ladies' bathroom was divided, so that a men's bathroom could be added.
Shortly prior to 1992, the gatehouse underwent a significant renovation.[14] The ceiling in the office was covered by dropped ceiling of sound-dampening tiles, and the north and south entrances to the building closed off.[5]
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Riverside Cemetery Gatehouse (Cleveland). |
- Notes
- Citations
- ↑ National Park Service (2009-03-13). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- ↑ "Riverside Cemetery". The Plain Dealer. November 16, 1875. p. 4.
- ↑ "Riverside Cemetery: Formal Opening of the Grounds". The Plain Dealer. July 10, 1876. p. 4.
- ↑ Segall, Grant (May 12, 2016). "Riverside Cemetery, a West Side landmark, celebrates 140 years". The Plain Dealer. Retrieved November 18, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "The Administration Building History" (PDF). The Tradition. Summer 2011. p. 3. Retrieved November 20, 2016.
- 1 2 Chatman, Angela D. (September 29, 1990). "West Side Cemetery Rich With History". The Plain Dealer. p. Saturday Real Estate 5.
- ↑ "An Indian History". The Plain Dealer. December 10, 1895. p. 8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Gregor 2010, p. 77.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "New Office And Waiting Room At Riverside Cemetery". The Plain Dealer. June 26, 1897. p. 10.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "Office of the Riverside Cemetery, Cleveland, O.". The Monumental News. November 1897. p. 638. Retrieved November 20, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 "Convention Echoes". Park and Cemetery. October 1896. p. 348. Retrieved November 20, 2016.
- ↑ "Calls It Trumpery". The Plain Dealer. December 15, 1896. p. 8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gilbert, P.T. (September 27, 1896). "Riverside". The Plain Dealer. p. 17.
- ↑ Armstrong, Klein & Armstrong 1992, p. 242.
Bibliography
- Armstrong, Foster; Klein, Richard; Cara, Armstrong (1992). A Guide to Cleveland's Sacred Landmarks. Kent, Ohio: Kent State University Press. ISBN 9780873384544.
- Gregor, Sharon E. (2010). Rockefeller's Cleveland. Charleston, S.C.: Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 9780738577111.