Russian Constituent Assembly election, 1917
Russian Constituent Assembly election, 1917

|
|
|
|
|
|
The elections to the Russian Constituent Assembly that were organized as a result of events in the Russian Revolution of 1917 in the Russian Republic and were held on 25 November 1917 (although some districts had polling on alternate days), around 2 months after they were originally meant to occur. It is generally reckoned as the first truly free election in Russian history.
The Bolsheviks, who had seized power in the October Revolution, believed that it would consolidate their power and prove that they had a clear popular mandate to govern. Instead, the election yielded a clear victory for the Socialist Revolutionary Party (SRs), who polled almost double the votes of the Bolsheviks. However, the candidate lists had been drawn up before the SR split took place; therefore, right SRs were overwhelmingly overrepresented, leaving out left SRs who were part of the VTsIK coalition government with the Bolsheviks.[1] The Constituent Assembly convened on 18 January 1918. However, the other parties refused to give their support to Bolshevik leader and premier Vladimir Lenin's idea of a soviet republic. The VTsIK dissolved the Assembly the next day, leaving the All-Russian Congress of Soviets as the governing body of Russia.
As it turned out, this would be the last even partially free election held in Russia until the 1990 republic election. While SRs and Mensheviks were allowed to take part in the 1918 elections to local Soviets, the Bolsheviks ejected them and forced numerous reelections until they obtained their desired majorities. By the end of 1918, all opposition parties had been banned, marking the onset of the Bolshevik dictatorship.
Various academic studies have given alternative results. However, all clearly indicate that the Bolsheviks were clear winners in the urban centres, and also took around two-thirds of the votes of soldiers on the "Western Front." Nevertheless, the SRs topped the polls on the strength of support from the country's rural peasantry.
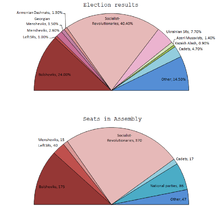
A study by Oliver Henry Radkey found the following breakdown (note that the figures for Socialist Revolutionaries includes the Ukrainian Socialist Revolutionaries, while the Kadet figure includes other "rightists" as well. The total number of deputies returned for "Others" includes 39 Left Socialist-Revolutionaries and four Popular Socialists, as well as 77 others from various local groups).
| Party |
Votes[2] |
Percent |
Deputies |
| Socialist-Revolutionary Party (SRs) |
17,100,000 |
41.0 |
380 |
| Bolsheviks |
9,800,000 |
23.5 |
168 |
| Constitutional Democratic Party (Kadets) |
2,000,000 |
4.8 |
17 |
| Mensheviks |
1,360,000 |
3.3 |
18 |
| Others |
11,140,000 |
26.7 |
120 |
| Total (turnout 48.44%) |
41,700,000 |
100 |
703 |
| Party |
Votes |
Percent |
| Socialist-Revolutionary Party (SRs) |
17,943,000 |
40.4 |
| Bolsheviks |
10,661,000 |
24.0 |
| Ukrainian Socialist-Revolutionary Party |
3,433,000 |
7.7 |
| Constitutional Democratic Party (Kadets) |
2,088,000 |
4.7 |
| Georgian Social Democratic (Menshevik) Party |
662,000 |
1.5 |
| Musavat (Azerbaijan) |
616,000 |
1.4 |
| Armenian Revolutionary Federation (Dashnaktsutiun) (Armenia) |
560,000 |
1.3 |
| Left Socialist-Revolutionaries (Borotbists) |
451,000 |
1.0 |
| Alash Orda (Kazakhstan) |
407,000 |
0.9 |
| Various liberal parties |
1,261,000 |
2.8 |
| Various national minority parties |
407,000 |
0.9 |
| Various socialists |
401,000 |
0.9 |
| Unaccounted |
4,543,000 |
10.2 |
| Region | Bolshevik vote %[5] |
| Total | 23.4 |
| Baltic Fleet | 62.6 |
| Black Sea Fleet | 20.5 |
| Northern Front | 56.1 |
| Western Front | 66.9 |
| Southwestern Front | 29.8 |
| Romanian Front | 14.8 |
| Petrograd | 45 |
| Moscow | 47.9 |
| Transcaucasia | 4.6 |
| Estonia | 40.4 |
| Livonia | 71.9 |
| Vitebsk | 51.2 |
| Minsk | 63.1 |
| Smolensk | 54.9 |
| Belorussia (previous 3) | 57.5 |
| Siberia | 9.9 |
| Workers | 86.5 |
The Mensheviks got just 3.3% of the national vote, but in the Transcaucasus they got 30.2% of the vote. 41.7% of their support came from the Transcaucasus. In Georgia around 75% of the population voted for them.[6]
References
Further reading
- Badcock, Sarah. "'We're for the Muzhiks' Party!'Peasant Support for the Socialist Revolutionary Party During 1917." Europe-Asia Studies 53.1 (2001): 133-149.
- Rabinovitch, Simon. "Russian Jewry goes to the polls: an analysis of Jewish voting in the All‐Russian Constituent Assembly Elections of 1917." East European Jewish Affairs 39.2 (2009): 205-225.
- Radkey, Oliver Henry. Russia goes to the polls: the election to the all-Russian Constituent Assembly, 1917 (Cornell University Press, 1989)
- Smith, Scott Baldwin. Captives of Revolution: The Socialist Revolutionaries and the Bolshevik Dictatorship, 1918–1923 (University of Pittsburgh Pre, 2011)
- Von Hagen, Mark. Soldiers in the proletarian dictatorship: the Red Army and the Soviet socialist state, 1917-1930 (Cornell University Press, 1990)