South Carolina Circuit Court
The South Carolina Circuit Court is the state court of general jurisdiction of the U.S. state of South Carolina. It consists of a civil division (the Court of Common Pleas) and a criminal division (the Court of General Sessions).
The Circuit Court is the state trial court of general jurisdiction in South Carolina. It is also a superior court, having limited appellate jurisdiction over appeals from the lower Probate Court, Magistrate's Court, and Municipal Court, and appeals from the Administrative Law Judge Division, which hears matters relating to state administrative and regulatory agencies.
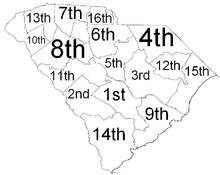
South Carolina's 46 counties are divided into 16 judicial circuits:
- First Circuit – Calhoun, Orangeburg, Dorchester
- Second Circuit – Aiken, Barnwell, Bamberg
- Third Circuit – Lee, Sumter, Clarendon, Williamsburg
- Fourth Circuit – Dillon, Chesterfield, Darlington, Marlboro
- Fifth Circuit – Kershaw, Richland
- Sixth Circuit – Chester, Fairfield, Lancaster
- Seventh Circuit – Cherokee, Spartanburg
- Eighth Circuit – Abbeville, Newberry, Laurens, Greenwood
- Ninth Circuit – Berkeley, Charleston
- Tenth Circuit – Oconee, Anderson
- Eleventh Circuit – McCormick, Edgefield, Lexington, Saluda
- Twelfth Circuit – Florence, Marion
- Thirteenth Circuit – Pickens, Greenville
- Fourteenth Circuit – Allendale, Colleton, Hampton, Beaufort, Jasper
- Fifteenth Circuit – Georgetown, Horry
- Sixteenth Circuit – York, Union
Each has at least one resident circuit judge who maintains an office in his or her home county within the circuit. There are currently 46 circuit judges who serve the 16 circuits on a rotating basis. Court terms and assignments determined by the Chief Justice based upon recommendations of Court Administration. Circuit court judges are elected by the South Carolina General Assembly to staggered terms of six years.
External links
- Official information from the South Carolina Judicial Department