System 1
| A version of the classic Mac OS operating system | |
|
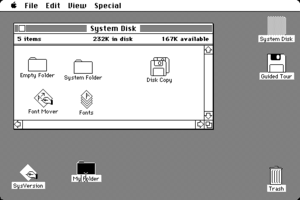
The original "System 1" desktop | |
| Developer | Apple Computer, Inc. |
|---|---|
| OS family | Macintosh |
| Source model | Closed source |
| Released to manufacturing | January 24, 1984 |
| Latest release | 1.1 / May 5, 1984 |
| Kernel type | Monolithic |
| License | Proprietary |
| Succeeded by | System 2 |
| Support status | |
| Unsupported, historic | |
"System 1", originally named Macintosh System Software, was the first Apple Macintosh operating system and the beginning of the classic Mac OS series. It ran on the Motorola 68000 microprocessor. System 1 was released on January 24, 1984, along with the original Macintosh, the first in the Macintosh family of personal computers. It received one update, "System 1.1" on May 5, 1984, before being succeeded by System 2.[1]
Features
This operating system introduced many features that would appear for years to come, some even still existing in the current macOS, and a few existing in other graphical operating systems such as Microsoft Windows.
The features of the operating system included the Finder and menu bar. In addition to this, it popularized the graphical user interface and desktop metaphor, which was used under license from Xerox PARC.
Due to the limited amount of RAM and the lack of an internal hard disk in the original Macintosh, there was no multitasking with multiple applications, although there were desktop accessories that could run while another application was loaded. Also, items in the Trash were permanently deleted when the computer was shut down or an application was loaded (quitting the Finder).
Menu bar
The menu bar was a new and revolutionary part of the OS. Similar to the one found on the Lisa OS, the Macintosh menu bar had 5 basic headers when on the desktop: the Apple menu, File, Edit, View, and Special. When in an application, the menus would change to better fit the application's uses.[2]
While within the Finder, the Apple menu contained the "About the Finder" information, along with the desktop accessories. "File" had drop-downs such as Open, Eject, and Close. "Edit" had drop-downs for cutting, copying, and pasting. "Special" was responsible for managing the hardware and other system functions, and was always the rightmost entry on the menu bar in the Finder. In System 1, the menu had items related to emptying the Trash, cleaning up the desktop, and disk options. By System 6, the menu allowed the user to choose an alternate startup program to be run instead of the Finder at boot time; the feature was replaced in System 7 by the "Startup Items" folder in the System Folder.
Desk accessories
System 1 came with multiple desk accessories (DA). These included an Alarm Clock, Calculator, Control Panel, Key Caps, Note Pad, Puzzle, and Scrapbook. The difference between the desktop accessories and a normal application is that multiple desktop accessories could be run at once, opposed to applications where only one could run at a time. Along with that, the desktop accessories could run on top of an application.
- Alarm Clock — This DA could be used just like an alarm clock, as the computer would beep, and the menu bar would flash when the alarm's set time was reached. It could also be used as an easier way to change/set the time and date on the computer. When opened, it would show the time and date set on the computer.
- Calculator — It was a basic calculator capable of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It featured the basic 10 buttons for input.
- Control Panel — The control panel was used to adjust some of the setting on the computer. What made the original control panel unique from other Mac OS control panels was the intended absence of any text. This was chosen to demonstrate the graphical user interface. Representation was achieved by using symbols. It could be used to adjust settings such as volume, double click speed, mouse sensitivity, and desktop background. On the Macintosh 128K, Macintosh 512K, and the Macintosh Plus the screen brightness was controlled by a mechanical adjustment wheel beneath the screen.
- Key Caps — A DA used to show the layout of the original Macintosh keyboard. It did not show what happened when keys were pushed along with special characters (Command, Shift, Option).
- Note Pad — A note taking DA that would save text entered into it on the floppy disk. Multiple note pages could be written when using the folded corner symbol in the bottom left corner of the note page.
- Puzzle — It was a basic 1-15 slide puzzle, similar to the picture puzzle found in later versions of the Mac OS.
- Scrapbook — This DA was similar to a cut, copy, and paste library. In it, you could store text selections and photos which could then be transferred to other applications.
See also
- GEM/1 (a similar GUI released around the same time by Digital Research, also with roots at Xerox PARC)
- Apple v. Digital Research
References
- ↑ Mesa, Andy. "The Early Mac OS". The Apple Museum. Retrieved 2015-02-15.
- ↑ Conachey, Andrew. "Innovative Macintosh System 1". Low End Mac. Retrieved 2016-08-15.