States of the Weimar Republic
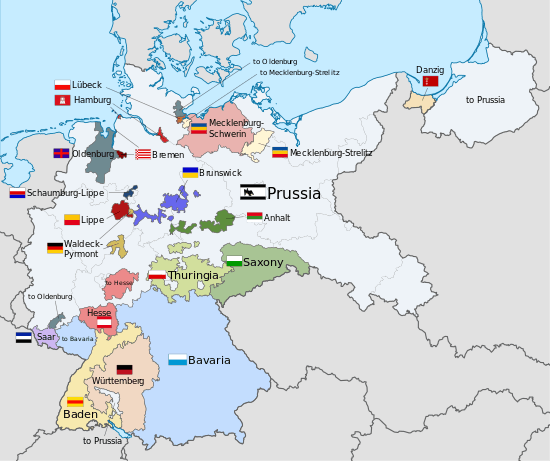

Upon the conclusion of World War I, Germany suffered significant territorial losses from the Treaty of Versailles. After the German Revolution, the 21 constituent states of Germany abolished their monarchies and continued as republics alongside the three pre-existing city-states within the new Weimar Republic. The former Ernestine duchies continued briefly as republics before merging to form the state of Thuringia in 1920, except for Saxe-Coburg, which became part of Bavaria. Additionally, the Saar Basin and the city of Danzig were detached from Germany and placed in the care of the League of Nations.
These states were gradually de facto abolished under the Nazi regime via the Gleichschaltung process, as the states were largely re-organised into several smaller Gaue as the administrative regions of the Nazi Party. Most of the remaining states were formally dissolved by the Allies at the end of World War II and ultimately re-organised into the modern states of Germany.
List of states
Free States
| State | Full name | Capital | Established | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anhalt | Free State of Anhalt Freistaat Anhalt |
Dessau | 1918 | Merged into Saxony-Anhalt in 1945. |
| Baden | Republic of Baden Republik Baden |
Karlsruhe | 1918 | Split into Württemberg-Baden and South Baden in 1945. |
| Bavaria | Free State of Bavaria Freistaat Bayern |
Munich | 1918 | |
| Brunswick | Free State of Brunswick Freistaat Braunschweig |
Braunschweig | 1918 | Split and merged into Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt in 1946. |
| Coburg | Free State of Coburg Freistaat Coburg |
Coburg | 1918–20 | Merged into Bavaria in 1920. |
| Hesse | People's State of Hesse Volksstaat Hessen |
Darmstadt | 1918 | Split into Greater Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate in 1945. |
| Lippe | Free State of Lippe Freistaat Lippe |
Detmold | 1918 | Merged into North Rhine-Westphalia in 1947. |
| Mecklenburg-Schwerin | Free State of Mecklenburg-Schwerin Freistaat Mecklenburg-Schwerin |
Schwerin | 1918 | Merged into Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in 1933. |
| Mecklenburg-Strelitz | Free State of Mecklenburg-Strelitz Freistaat Mecklenburg-Strelitz |
Neustrelitz | 1918 | Merged into Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in 1933. |
| Oldenburg | Free State of Oldenburg Freistaat Oldenburg |
Oldenburg | 1918 | Split into Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein and Rhineland-Palatinate in 1946. |
| Prussia | Free State of Prussia Freistaat Preußen |
Berlin | 1918 | Abolished in 1947. |
| Saxony | Free State of Saxony Freistaat Sachsen |
Dresden | 1918 | |
| Reuss | People's State of Reuss Volksstaat Reuß |
Gera | 1918–20 | Merged into Thuringia in 1920. |
| Schaumburg-Lippe | Free State of Schaumburg-Lippe Freistaat Schaumburg-Lippe |
Bückeburg | 1918 | Merged into Lower Saxony in 1946. |
| Thuringia | Free State of Thuringia Freistaat Thüringen |
Erfurt | 1920 | Merged from the Free States of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, Saxe-Meiningen, Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt, Schwarzburg-Sondershausen and the People's State of Reuss. |
| Saxe-Meiningen | Free State of Saxe-Meiningen Freistaat Sachsen-Meiningen |
Meiningen | 1918–20 | Merged into Thuringia in 1920. |
| Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach | Free State of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach Freistaat Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach |
Weimar | 1918–20 | Merged into Thuringia in 1920. |
| Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt | Free State of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt Freistaat Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt |
Rudolstadt | 1918–20 | Merged into Thuringia in 1920. |
| Schwarzburg-Sondershausen | Free State of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen Freistaat Schwarzburg-Sondershausen |
Sondershausen | 1918–20 | Merged into Thuringia in 1920. |
| Waldeck-Pyrmont | Free State of Waldeck-Pyrmont Freistaat Waldeck-Pyrmont |
Arolsen | 1918–29 | Pyrmont merged into Prussia in 1921; Waldeck merged into Prussia in 1929. |
| Württemberg | Free People's State of Württemberg Freier Volksstaat Württemberg |
Stuttgart | 1918 | Split into Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern in 1945. |
Free and Hanseatic Cities
| State | Full name | Capital | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bremen | Free and Hanseatic City of Bremen Freie Hansestadt Bremen |
Bremen | |
| Hamburg | Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg |
Hamburg | |
| Lübeck | Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck Freie und Hansestadt Lübeck |
Lübeck | Merged into Prussia in 1937. |
Other territories
After World War I, the Saar Basin was occupied and governed jointly by the United Kingdom and France from 1920 to 1935 under a League of Nations mandate.[1] After a plebiscite was held in 1935, the region was returned to Germany.[2]
In accordance with the Treaty of Versailles, the city of Danzig (now Gdańsk, Poland) was detached from Germany on 15 November 1920 and turned into a semi-autonomous city-state under the protection of the League of Nations.[3][4] The Treaty stated that it was to remain separate from both Germany and the newly independent Poland, but was not its own sovereign state.[5] After the Nazis invaded Poland in September 1939, the city's autonomous status was revoked and it was annexed by Germany.
See also
- Provinces of Prussia
- States of the German Confederation
- States of the German Empire
- Administrative divisions of Nazi Germany
- Administrative divisions of East Germany
- States of Germany
References
- ↑ Article 45-50 with Annex, Treaty of Versailles
- ↑ M G Callagher. "The Saar Plebiscite, 1935". Moodle.kkc.school.nz. Retrieved 2014-05-02.
- ↑ Loew, Peter Oliver (February 2011). Danzig – Biographie einer Stadt (in German). C.H. Beck. p. 189. ISBN 978-3-406-60587-1.
- ↑ Samerski, Stefan (2003). Das Bistum Danzig in Lebensbildern (in German). LIT Verlag. p. 8. ISBN 3-8258-6284-4.
- ↑ Kaczorowska, Alina (2010-07-21). Public International Law. Routledge. p. 199. ISBN 0-203-84847-0.
- Solsten, Eric (1999). Germany: A Country Study. DIANE Publishing Company. ISBN 0-7881-8179-3.