Superior ganglion of vagus nerve
| Superior ganglion of vagus nerve | |
|---|---|
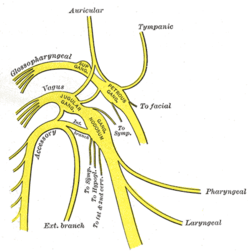 Plan of upper portions of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. (Jugular ganglion visible near center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglion superius nervi vagi, ganglion jugulare |
| TA | A14.2.01.154 |
The superior ganglion of the vagus nerve or jugular ganglion is a well-marked ganglionic enlargement of the vagus nerve. It is located in the middle part of the jugular foramen. It contains afferent somatosensory neuronal cell bodies that provide sensory information from the external auditory meatus (auricular branch), cranial meninges (meningeal branch), and the external surface of the tympanic membrane. Their central fibers synapse in the Trigeminal nerve nuclei.[1]
It is a grayish color, spherical in form, and about 4 mm. in diameter.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Netter's Human Anatomy, 4th Edition
See also
External links
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (X)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/16/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.