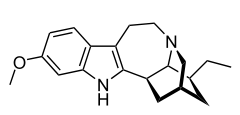
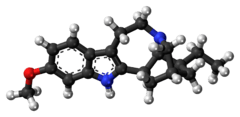
Tabernanthine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 83-94-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6326116 |
| ChemSpider | 4885254 |
| UNII | TV52I1S16D |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H26N2O |
| Molar mass | 310.43 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Tabernanthine is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga.[1]
It has been used in laboratory experiments to study how addiction affects the brain.[2]
Tabernanthine persistently reduced the self-administration of cocaine and morphine in rats.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "The Alkaloids of Tabernanthe iboga. Part IV.1 The Structures of Ibogamine, Ibogaine, Tabernanthine and Voacangine - Journal of the American Chemical Society (ACS Publications)".
- ↑ Levi MS, Borne RF (October 2002). "A review of chemical agents in the pharmacotherapy of addiction". Curr. Med. Chem. 9 (20): 1807–18. doi:10.2174/0929867023368980. PMID 12369879.
- ↑ Glick SD, Kuehne ME, Raucci J, Wilson TE, Larson D, Keller RW Jr, Carlson JN (September 1994). "Effects of iboga alkaloids on morphine and cocaine self-administration in rats: relationship to tremorigenic effects and to effects on dopamine release in nucleus accumbens and striatum.". Brain Res. 657 (1-2): 14–22. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(94)90948-2. PMID 7820611.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/14/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.