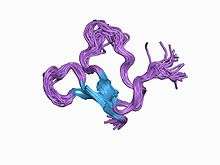
Tachystatin
Tachystatins are antimicrobial chitin-binding peptides from Japanese horseshoe crab. Amino acid residues Tyr(14) and Arg(17) in Tachystatin B are thought to be the essential residues for chitin binding.[2] These small proteins contain a cysteine-stabilised triple-stranded beta-sheet with an inhibitor cystine knot motif and show features common to membrane-interactive peptides. Tachystatin A is thought to have an antimicrobial activity similar to defensins.[1]
References
- 1 2 Fujitani N, Kawabata S, Osaki T, Kumaki Y, Demura M, Nitta K, Kawano K (June 2002). "Structure of the antimicrobial peptide tachystatin A". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (26): 23651–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111120200. PMID 11959852.
- ↑ Fujitani N, Kouno T, Nakahara T, Takaya K, Osaki T, Kawabata S, Mizuguchi M, Aizawa T, Demura M, Nishimura S, Kawano K (April 2007). "The solution structure of horseshoe crab antimicrobial peptide tachystatin B with an inhibitory cystine-knot motif". J. Pept. Sci. 13 (4): 269–79. doi:10.1002/psc.846. PMID 17394123.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR022717