The Royal Canadian Mounted Police in Quebec
 | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 1920 |
| Headquarters |
Montréal (Québec 45°30′N 73°34′W / 45.500°N 73.567°W |
| Motto |
Maintiens le droit Defending the Law |
| Employees | 1500 |
| Minister responsible |
|
| Agency executive |
|
| Parent department | Public Safety Canada |
| Website | http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/qc/index-eng.htm |
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police in Quebec, which is commonly referred to as "C" Division, plays a federal policing role in the Province of Quebec. Approximately 1,500 police officers, civilian members and public servants dedicate their efforts to a number of business lines, including financial integrity, national and border security, and organized crime enforcement. The RCMP in Quebec relies on dedicated resources to conduct investigations, provide VIP protective services and undertake crime prevention initiatives in communities in all areas of Quebec.
The role of the RCMP in Quebec is strictly to enforce federal statutes. "C" Division differs in that respect from its RCMP counterparts in most Canadian provinces and from its policing partners in Quebec, that are guided by the concept of community policing. However, by joining forces and intelligence capabilities with its partners in Canada and abroad, "C" Division is able to conduct successful interterritorial investigations.[1]
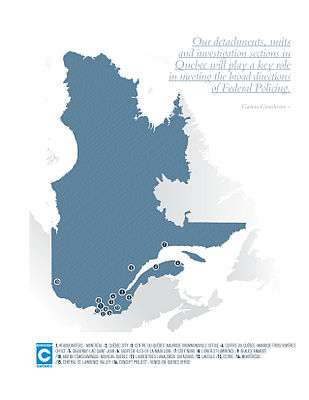
Structure
In addition to its headquarters located in Montréal, "C" Division is composed of detachments that are divided geographically into two districts, namely East and West districts. Detachment locations
History
In 1920, the Federal Government authorized the Royal Canadian Mounted Police to establish its first detachment in Quebec, specifically in Montréal. Staffed with ten members, this office with barracks was housed in an old building located at 283 Sherbrooke Street, across from the main entrance of McGill University. The building was demolished in 1940. The officer commanding this detachment was a superintendent named Wilcox, who was known mostly for his work in Western Canada. Later that year the RCMP opened a one-man detachment in Québec City, thus serving the two largest urban centres in the province. Shortly after, the RCMP provided police presence along the international border to collect customs fees and to secure the border from illegal immigrants.
Back then, "C" Division was tasked with the responsibility of enforcing some forty federal statutes. Around 1921, the RCMP opened a few detachments near Indian reserves for the purposes of maintaining law and order and enforcing the Indian Act, governing in particular the control and sale of alcoholic beverages.

It is interesting to note that between 1920 and 1932, the RCMP considered the Province of Quebec as a simple district without alphabetical designation, whereas Eastern Ontario was designated as "A" Division and Western Ontario as "O" Division. Back then the letter "C" was used to designate the Province of Manitoba, whose divisional post was located in Brandon. Detachment work consisted mainly in the application of Indian legislation, the Customs Act and the Migratory Birds Convention Act, while drug and counterfeit currency enforcement was an important part of police work in Montréal.
The first major change for the Royal Canadian Mounted Police in Quebec occurred in 1932, when it absorbed the Customs and Excise Preventive Service. All 175 members and 35 vessels and crews that were once the responsibility of that department came under the direction of the RCMP. This is how the RCMP Marine Service came to be.
Operating with a limited complement of 33 members and 4 detachments in 1931, the RCMP then grew to a membership of 156 men and 31 detachments in Quebec. Given the additional duties brought about by the merger with the Customs and Excise Preventive Service, RCMP officers had to patrol the territory by land, sea and air to fight against alcohol smuggling and other forms of contraband, or to provide assistance to vessels in distress.
Due to the increased workforce, the RCMP had to rethink its district structure. The term district, used by the Force to designate its area of jurisdiction in the Province of Quebec, which was then under the command of Superintendent Dawn, was replaced by "C" Division.
Over the years, the RCMP has kept in step with the times, becoming a modern organization that uses sophisticated investigative techniques to fulfill its expanded mandate. Its reputation keeps growing worldwide.[2]
Defining events of their role and history

RCMP participation was required in numerous events of major importance that took place in the Province of Quebec, as the responsibilities of the Force include protecting VIPs during their visits to Canada and providing assistance to other police departments in the province during major events.
- Visit of Winston Churchill and Franklin Roosevelt to Québec City in 1943
In 1943, as the Second World War was raging in Europe, US and Canadian troops joined their European allies on the front lines. Since 1939, the two heads of state have held five conferences for the purpose of developing strategies to defeat the enemy’s devastating offensive. They chose Québec City for their sixth conference. So from August 17 to 24, 1943, US President Franklin Delano Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill met within the walls of this fortified town for the Québec Conference, hosted by Canadian Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King. Along with high-ranking officers of their respective armies, they planned military operations that led to the Allied victory over Axis forces.
- Visit of French General Charles de Gaulle to Québec City on July 12, 1944
During his trip to America a few weeks after the Allied landings in Normandy, General Charles de Gaulle visited Québec City and Montréal. Even though his stop in Montréal lasted only a few hours, he attended a formal reception held in his honour at the Windsor Hotel. A number of dignitaries gathered for the occasion, including Quebec Premier Adélard Godbout.[3]
- Expo 67 and the visit of Charles de Gaulle

With the opening of the Universal Exhibition in Montréal, Expo 67, Quebec became the focus of attention worldwide for an entire summer. The President of France, General Charles de Gaulle, made an official visit to Quebec on that occasion. From the balcony of Montréal City Hall, he said "Vive le Québec libre!" [May Quebec Live Long and Free], drawing cheers from an ecstatic crowd.[4]
.jpg)
- 1976 Summer Olympic Games in Montréal
On July 17, 1976, the entire world watched on as the opening ceremonies of 21st Olympic Games unfolded in Montréal. The world-renowned Olympic Stadium, Montréal's architectural landmarks, was built for that occasion. The building features the world's highest leaning tower.

- The 2001 Summit of the Americas in Québec City
From April 20 to 22, 2001, 34 democratically elected heads of state and government of North America, Central America, South America and the Caribbean met in Québec City for the third Summit of the Americas. The meeting is probably best remembered for the security measures put in place for the event and for the numerous public demonstrations that were held as the meetings took place. The Québec Summit attracted more than 50,000 demonstrators from across the Americas, ranking it among the top alterglobalist protest events to this day. This international event, in which the RCMP played a key role, was marked by the largest security operation in Canadian history.
- The 2008 Francophonie Summit in Québec City
In October 2008, the largest ceremonial event ever to be held in Canada took place in Québec City, as 70 heads of state attended the 12th Conference of Heads of State and Government of Countries Using French as a Common Language, commonly called the Francophonie Summit. This Summit provides world leaders sharing the French language with an opportunity to discuss topics such as international policy, the environment, Francophone cooperation, human rights, education, culture and democracy. The Summit is held every two years and is the highest authority in La Francophonie. Security for the Francophonie Summit, which was provided by the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, Service de police de la Ville de Québec and Sûreté du Québec, also required the collaboration of several federal, provincial and municipal partners and agencies.
RCMP services in Quebec
The RCMP is committed to preserving the peace, upholding the law and providing quality service to the community across "C" Division. This commitment is demonstrated through the leadership provided by "C" Division in all its areas of responsibility. Although its primary focus is on the fight against major organized crime at the national and international levels, the RCMP has diverse responsibilities in Quebec.[5] This section provides an overview of the duties performed by RCMP officers in "C" Division.
Organized crime enforcement
Organized crime is one of five strategic priorities established by the RCMP. It is defined by the Criminal Code as crime committed by any group of at least three people that has as one of its main purposes or activities the facilitation or commission of one or more serious offences where the primary motive is profit. Organized crime networks are an international problem that ignores national boundaries. This is why the RCMP advocates partnerships with the public and other Canadian and foreign law enforcement organizations to carry out its investigations.[6]
Integrated Proceeds of Crime Unit (IPOC)
IPOC investigators hit criminal organizations by targeting the proceeds of crime and the very motivation behind any criminal activity, i.e. profit, by seizing the assets purchased by criminal elements with "dirty" money. IPOC investigators work in conjunction with other RCMP units and several outside agencies, police departments, foreign enforcement agencies, banks and professional corporations.
Combined forces Special Enforcement Unit (CFSEU)
The Combined Forces Special Enforcement Unit (CFSEU) is an integrated, multidisciplinary team that is tasked with investigating major crime in partnership with local, national and international agencies in an effort to curtail the expansion and development of organized crime in Quebec.
Aboriginal Combined forces Special Enforcement Unit (A-CFSEU)
The mission of the Aboriginal CFSEU is to maintain social cohesion within Aboriginal communities by leading an ongoing fight against criminal organizations operating on First Nations territories. Its goal is to investigate, pursue and dismantle criminal organizations whose negative impact and intimidation methods pose a direct threat to the best interests and well-being of Quebec’s Aboriginal communities.
Financial Integrity
The mission of Financial Integrity investigators is to lead an effective and dynamic fight against organized crime in order to protect the integrity of the Canadian economy. Their role is to prevent what is known as “white collar crime”, whether national or international in scope, through federal law enforcement. They bring a high degree of expertise in applying innovative and effective investigative techniques.
Federal Investigation Section
The strategic objective of the Federal Investigation Section program is to ensure the health and safety of communities, protect the public and maintain Canada's economic integrity. The primary mandate of the Federal Investigation Section is to enforce federal statutes and related regulations through a combination of proactive and reactive strategies. The proactive program is a well-balanced approach of prevention, education and enforcement measures partnered with affected client communities. Reactive investigations are initiated in response to requests for RCMP assistance received from other federal departments and agencies.
The Federal Investigation Section investigates criminal offences under federal statutes with the help of the appropriate federal department. Through the provisions of 18 Memoranda of Understanding, the Section also provides assistance to partner agencies as well as various federal agencies and stakeholders in conducting investigations under any one of some 250 federal statutes. The program is enforced through five sub-sections:
- Fight against Counterfeit Pharmaceuticals
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Assistance to Federal Agencies and Joint Projects
- Our Missing Children
Integrated Technological Crime Unit (ITCU)
The Integrated Technological Crime Unit (ITCU) is composed of police investigators and civilian members and is responsible for investigating computer crimes of national or international scope and providing technical assistance to other investigative units. The ITCU investigates offences such as unauthorized access to a computer or computer network (computer intrusion or hacking), mischief in relation to data (theft, manipulation, deletion, etc.), and possession of equipment or passwords facilitating these offences. The mandate of the ITCU is four-fold: investigation, computer support, intelligence and prevention.
Investigation
- Investigate computer crimes where the federal government is the victim.
- Conduct and coordinate investigations of criminal or terrorist activities targeting Canada’s national critical infrastructure from a technological perspective.
- Assist in joint national security investigations of technological significance.
- In cases where the computer crime is as significant as the substantive offence, investigate jointly with the RCMP unit having primary jurisdiction for the substantive offence.
- In cases where the RCMP does not have primary jurisdiction, conduct, with the consent of the police service having jurisdiction, national or international interest investigations of offences involving considerable financial loss or are extremely complex.
- Investigate local technological crimes at the request of the police service having primary jurisdiction, subject to resource availability and in accordance with applicable legislation.
Commercial Crime Section
Commercial Crime Section members investigate, control and prevent what is known as "white collar crime", whether national or international in scope, through federal law enforcement. Their efforts are focused on the following areas: counterfeiting, bribery and corruption, fraudulent bankruptcy and major general fraud.
Integrated Market Enforcement Team (IMET)
The mandate of the Integrated Market Enforcement Team (IMET) is to investigate major cases of financial fraud involving large-cap companies for which allegations of fraud could significantly shake or undermine investor confidence in Canadian financial markets. Investigations deal with major financial crime offences, i.e. fraud, fraudulent manipulation of stock market operations, false financial statements, fraudulent bankruptcies, secret commissions, etc.
Border Integrity
The "C" Division Border Integrity Program contributes to the national security of Canada and protects Canadians from terrorism, organized crime and other border-related criminality, while allowing for the secure and effective international movement of people and goods.[7] To achieve this goal, “C” Division works in close partnership with provincial, national and international government agencies as well as the community at large.
The various sections and teams contributing to ensure border security include:
The members of Immigration and Passport Section focus their efforts on detecting and disrupting the main criminal activities relating to immigration, passport and citizenship: organized migrant smuggling, services provided by so-called immigration consultants, fraudulent corporate use of the immigration program, human trafficking, forgery of citizenship cards, visas, passports and other documents. The RCMP works in close partnership with Citizenship and Immigration Canada and Foreign Affairs.
The members of Customs and Excise Section fight all forms of smuggling activity involving national and international organized crime. Their investigations focus mainly on illicit alcohol, tobacco products, firearms and jewelry.
The Integrated Border Enforcement Teams work in close cooperation with their partners in Canada and the United States. The IBET mandate is to target criminal activity and to ensure national security at the border.
The Coastal/Airport Watch Program was established to assist in the identification of persons, vessels, vehicles and aircraft that may constitute a threat to Canada’s national security, or that may be involved in illegal activity.
The National Ports Strategy is part of the organization's overall mandate to ensure border integrity. In "C" Division, the investigators’ role consists in coordinating the collection of intelligence for the
Members of the Airport Federal Investigation Section are responsible for fighting organized crime at the Montreal – Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport and for assisting airport partners and authorities and co-operating with them to ensure passenger safety.
This joint marine security initiative is led by the RCMP and the Canadian Coast Guard to further enhance national security and strengthen Canada's response to potential threats. It strengthens marine enforcement presence in a region heavily traveled by both small and large craft. It involves the deployment of vessels conducting joint security patrols on the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence waterway.
-
Illegal migrant arrested at the border
-
Border enforcement
-
Customs and Excise Section detecting/stopping illegal tobacco products
-

Air surveillance
-

Port security
-

Marine safety
National security
As a result of the ever-changing nature of threats to national security and the ongoing sophistication in the use of technology by the cells responsible for terrorist acts, the fight against terrorism must be increasingly efficient and develop new threat prevention and detection strategies. Given the international nature of many of the threats affecting Canadians, national security also intersects with international security. At the same time, there is a growing number of international security threats that impact directly on Canadian security.
Integrated National Security Enforcement Team (INSET)
Everywhere in its jurisdiction, the Integrated National Security Enforcement Team (INSET) is responsible for enforcing the laws relating to criminal activity that constitutes a direct or indirect threat to national security or interests, or that may interfere with the conduct of government business. Its scope includes espionage, sabotage, insurgency, treason, terrorism, extremism, offences committed against Canadian or foreign VIPs or diplomats, and offences committed for the purpose of supporting or funding individuals involved in the commission of such offences. The Integrated National Security Enforcement Team meets the need for more efficient prevention and detection by adopting an integrated approach with various local, national and international partners to facilitate the sharing of information leading to the detection and arrest of individuals who conspire to commit terrorist acts or engage in criminal activity linked to terrorism.
Criminal Intelligence
Intelligence is of primary importance for an organization like the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, whose ultimate mandate is to serve and protect all Canadian citizens. The Criminal Information Analytical Section is responsible for collecting and analyzing information on the criminal elements operating in the province. The Section offers direct intelligence support to all other RCMP sectors in Quebec, in addition to providing sound advice to management on the development of national and provincial crime control strategies.
Protective Services
The RCMP is a leader in the delivery of protective services, a significant area of activity for federal police in Quebec that leaves no room for error.[8] RCMP officers carry out high-risk duties while protecting VIPs and their spouses, including the Prime Minister of Canada and the Governor General, foreign heads of state and dignitaries visiting Quebec.

VIP Security Services (VIPSS) have two very important mandates to fulfill. The first one consists in providing consular liaison to the consulates within our jurisdiction. This requires a close liaison between members to ensure the physical security of the consulates and consuls general. VIPSS members are also responsible for handling various requests from consulates.
VIPSS members maintain contact with the consulates to ensure that all is well, and they use those opportunities to build communication and collaborative contacts with representatives of foreign countries.
The second mandate of VIPSS relates to Internationally Protected Persons (IPPs), as defined in the Criminal Code, who must be provided with varying levels of protection while in Canada. Consequently, VIPSS provide physical protection to foreign heads of state, ambassadors and consuls visiting Quebec.
VIPSS also provide personal protection to the Prime Minister of Canada, the Governor General, two former Prime Ministers as well as the leaders of Canadian political parties during federal elections. Members of VIPSS carry out the following duties:
- bodyguard
- motorcade driver
- site security
- House of Commons security
- aircraft protective services
Overview of major investigations over the past 15 years
The history of the RCMP is marked with numerous major investigations of national and international scope. Below is an overview of some of the investigations that have made the RCMP in Quebec famous.
Project Colisée

The largest raid against the mafia in Canadian history[9] took place on November 22, 2006. The partners of the Combined Forces Special Enforcement Unit dealt a serious blow to traditional organized crime by conducting numerous searches on that day in the Montréal region. Ninety persons, including Nicolo Rizzuto, Paolo Renda, Francesco Arcadi and Rocco Sollecito were charged with nearly 1,000 counts of indictment. These charges were laid as part of Project Colisée, the purpose of which was to tackle a major criminal organization on several fronts.
Project Colisée was a wide-ranging investigation aimed at curbing the growth and development of organized crime in Canada. Project Colisée was led by the Combined Forces Special Enforcement Unit (CFSEU), a joint unit coordinated by the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) and also involving the Sûreté du Québec, Service de police de la ville de Montréal (SPVM), Service de protection des citoyens de Laval, Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA), and Canada Revenue Agency.
An eight-fold investigation
Through Project Colisée, CFSEU investigators were able to infiltrate the criminal organization and to take it by surprise in various ways by identifying and arresting the leaders of the organization, by uncovering conspiracies to import cocaine via the Montréal Trudeau Airport, to import 1,300 kilograms of cocaine to Canada by container, to bribe CBSA officers and to import indeterminate quantities of drugs using their services, by exposing an online bookmaking business that allegedly generated $26 million over a period of 18 months, and by uncovering an attempt to commit murder, cocaine trafficking activity and a cannabis route to the United States through the Akwesasne Territory. A total of thirty-six searches were conducted in order to freeze and seize assets derived from criminal activity, including $3 million worth of real property and $3.5 million in cash.
Timeline
- 2004: Project Colisée is launched on the basis of several years of investigation; it involves close to 700 police officers from the RCMP, Sûreté du Québec and other law enforcement agencies.
- November 22, 2006, 6:00 a.m.: a series of searches are conducted, leading to the arrest of 71 persons believed to be linked to the Italian mafia, and to the seizure of real property, bank accounts and cash.
- November 22, 2006, 2:00 p.m.: the first suspects appear at the Montréal Court House.
- December 7, 2006: the Court orders a publication ban.[10]
Project Celsius

On April 18, 2012, a police operation conducted by the RCMP resulted in the arrest of nine suspects in connection with the importation of a series of hashish shipments totalling 43.3 metric tonnes. This international police operation was conducted with the collaboration of law enforcement authorities in Pakistan, Italy, Belgium and the United States.
This investigation, dubbed Project CELSIUS, was initiated in the summer of 2010 by the Montréal RCMP Dug Section jointly with the RCMP National Ports Enforcement Teams in Montréal and Halifax. It serves as an example of the firm commitment made by the RCMP to fight domestic criminal organizations with international ramifications that infiltrate legitimate businesses in our country in order to engage in criminal activity, thus compromising the safety of our communities.
The investigation was initiated after the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) found drugs in offshore containers at the ports of Montréal and Halifax in 2009 and 2010.
This investigation shows that the criminal organization involved purchased drugs from the Middle East, primarily from Pakistan. The hashish was hidden in containers that were shipped by boat and transited through several ports before being routed to Canada. Some of the suspicious containers were seized in Pakistan, while others were intercepted en route to Canada, specifically in Italy and Belgium.
Project Chabanel

On May 10, 2006, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police conducted a one-of-a-kind police operation, seizing off the shores of Africa an impressive 22.5-ton shipment of hashish intended for the Canadian market directly from the hands of its suppliers. Three conspirators linked to the West End Gang criminal organization were arrested, resulting in the elimination of an 'import" cell of this Montreal-based criminal organization.
This operation, dubbed Project "Chabanel", was carried out in close cooperation with Canada's Department of National Defence and RCMP liaison officers in England, Morocco, Pakistan, the United Arab Emirates and Spain. For more than a year and a half, the investigators of Montreal and Halifax RCMP Drug Sections carefully worked out every detail of this international police operation.
The investigation was launched on the basis of information to the effect that a subject linked to the West End Gang was involved in a major hashish importation conspiracy from Africa. The organization first had to find a crew and ship suitable for deep-water navigation and for transporting the drugs.
Project “Chabanel” was therefore initiated by the RCMP. A vessel was chartered for the purposes of the operation. The vessel traveled to a predetermined location approximately 200 miles off the coast of Angola in Southern Africa. At this point the drugs were transferred from the supply vessel, whose crew was primarily made up of Filipino sailors, to the RCMP vessel. The RCMP complement spent more than 43 days at sea in order to seize the 22.5 tons of hashish and thus prevent its distribution to communities in Canada.
HMCS Fredericton, a Department of National Defence frigate, followed the RCMP vessel at a distance and provided necessary assistance throughout the journey, ensuring the safety of the police officers and serving as command post.
Once transhipment was completed to the RCMP vessel, the drugs were brought into Canada and taken to Montreal under heavy police escort. The drug shipment was to be delivered to the West End Gang on June 2, 2006. This is when the arrests were made. The federal police seized the 22.5 tons of hashish and CAN$195,000 from the criminal organization.
"C" Division of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, which is responsible for the enforcement of federal statutes in Quebec and southeastern Ontario, was proud to be the recipient of the IACP/ChoicePoint Award for Excellence in Criminal Investigations that was awarded to its Montreal Drug Section by the International Association of Chiefs of Police for this operation carried out in the open sea. The RCMP shared this award with the Department of National Defence.
Project Compote
Inn 1990, the RCMP Integrated Proceeds of Crime Unit conducted an investigation, dubbed Project Compote, in which the police opened its own exchange office, the Centre international monétaire de Montréal, for the purpose of arresting drug traffickers using this exchange office to launder drug money. All employees in that office were in fact RCMP officers who had been trained beforehand by the National Bank of Canada to act as professional tellers.[11] This police investigation led in late August 1994 to the arrest of 46 persons. Over $165 million, including $140 million from criminals, were intercepted through this storefront operation.
Project Cléopâtre
In June 2006, more than 350 police officers took part in a large-scale operation aimed at dismantling a criminal organization specializing in the trafficking and exportation of marijuana and ecstasy to the United States, as well as money laundering. A total of 42 searches were conducted in the Estrie and Montreal regions, leading to the arrest of 36 subjects, including the alleged leader of this ring, a resident of Kanesetake.
This major investigation, dubbed "Project CLÉOPÂTRE", was carried out by members of the Aboriginal Combined Forces Special Enforcement Unit (A-CFSEU). The members of this network were charged with criminal organization offence, drug trafficking, conspiracy to traffic in drugs, money laundering, and possession of prohibited weapons. A total of 125 charges were laid against 36 suspects.
As a result of this major international police operation, the A-CFSEU was awarded on October 16, 2006 the prestigious Motorola Webber Seavey Award for Quality in Law Enforcement at the IACP Annual Conference in Boston. The award recognizes innovative policing programs that can serve as models for law enforcement agencies worldwide.
The Norbourg case
On June 18, 2008, Montréal RCMP confirmed the conclusion of its investigation into criminal wrongdoings that affected approximately 9,200 shareholders of mutual funds managed by Norbourg. This criminal investigation showed that six persons allegedly participated in or facilitated the commission of fraud offences for a total of approximately 95 million dollars. This investigation conducted by the Integrated Market Enforcement Team (IMET) led to the arrest of six persons with close ties to Norbourg, including Norbourg CEO Vincent Lacroix.
The six suspects were charged with conspiracy to commit fraud, conspiracy to commit forgery, forgery, fraud and money laundering. The crimes for which the suspects were charged were allegedly committed between September 20, 2002, and August 25, 2005. A total of 922 counts of indictment were laid as a result of this IMET criminal investigation.
This investigation was a strategic priority intended not only to establish the alleged wrongdoings, but also to prove the criminal intent of the perpetrators. It was launched on the basis of a search of Norbourgs business premises carried out on August 25, 2005.
The search led to the seizure and analysis of approximately 1,500 boxes containing more than one million miscellaneous documents and millions of computer files. The criminal investigation focussed on the analysis of 125 questionable transactions from which the IMET identified 112 alleged misappropriations of funds recorded between 2002 and 2005.
The evidence gathered as part of the IMET investigation also demonstrated that the accused developed and implemented a system by which documents were allegedly forged and used to conceal evidence of misappropriation of funds and the origin of those funds, enabling Vincent Lacroix to make a number of personal and corporate acquisitions.
Commitment to communities and employees
In addition to conducting investigations, RCMP members also strive to attend a variety of community and multicultural events. The commitment of "C" Division to regional events includes various educational initiatives, charitable activities and national/international conferences.
Drug and organized crime awareness service
"C" Division investigators are working hard to curb drug traffickers' activity. But one unit in particular is more oriented toward prevention, i.e. the Drug and Organized Crime Awareness Service (DOCAS). DOCAS is composed of police officers and substance use/abuse experts who take an active interest in new trends and realities in the field in order to be proactive in identifying issues related to drug use in various environments.
DOCAS is committed through partnerships to making communities safer and healthier by providing all Canadians with the resources needed to meaningfully reduce substance use/abuse and organized crime-related problems. DOCAS is further committed to:
- Engaging communities by promoting the benefits of healthy lifestyle choices and in providing Canadians with the skills and information they need to make educated and informed decisions;
- Providing leadership through the coordination of drug awareness and prevention programs/initiatives geared toward supply and demand reduction;
- Improving the understanding of Canadians about the reach and influence of organized crime, and its impacts on individuals and on society as a whole;
- Mobilizing the Canadian public to become a significant law enforcement partner to effectively combat and reduce the influence of organized crime in Canada.
The objectives of DOCAS include engaging, supporting and training the various stakeholders who work with those affected by substance abuse. The services provided by DOCAS are intended for:

- Law enforcement agencies;
- Addiction workers;
- Community stakeholders;
- Health professionals;
- College and university personnel and students (for inquiries about children and teenagers, please contact your local police service);
- Parents of teenagers and young adults (16-24);
- Aboriginal communities;
- Consultative committees;
- Private and public sectors (employee assistance programs);
- Government agencies.
Reference tool
In the fall of 2013, the Drug and Organized Crime Awareness Service (DOCAS) launched a new drug information/awareness tool. The Drug Awareness Chart is a reference tool on today's most common substances and new trends. It also includes prevention and referral information.
The Chart has been distributed to RCMP clients and partners across the Province of Quebec, i.e.: fellow police officers, addiction workers, health professionals, community workers, correctional officers, educators and personnel of various agencies.
Mobile application
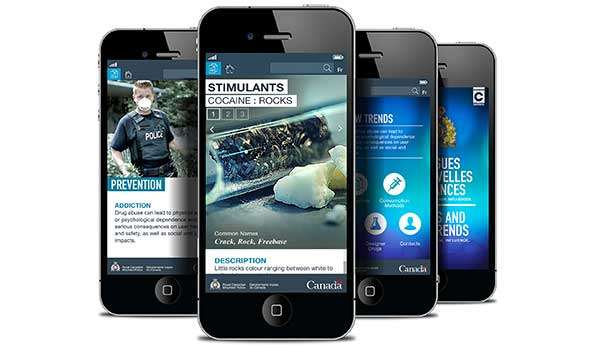
A mobile application on drugs[12] is now available for free in the App Store and Google Play. The new application includes information from the Drug Awareness Chart, launched in November 2013.
This application provides timely and convenient access to a wide range of information about drugs and related trends in Canada.
Download the application for instant access to everything you should know about drugs:
- main substances used;
- synthetic drugs;
- consumption methods;
- effects and consequences;
- visible signs and symptoms;
- legal status;
- addiction;
- … and much more.
The RCMP drug application was designed by experts to give you the straight facts about drugs and the risks associated with drug use. The information is presented in a straightforward, user-friendly manner to provide you with a clear, accurate picture of the subject matter.
The application will promote drug awareness among young people and their parents alike. It is intended for the general public, law enforcement agencies, addiction workers, educators, the various stakeholders in the fields of health, social and correctional services, and government agency personnel.
Healthy Enterprise – Elite Certification
In 2012, the RCMP was awarded the Healthy Enterprise – Elite certification by the Bureau de normalisation du Québec (BNQ).[13] Through this certification, the BNQ acknowledged the commitment made by “C” Division to take concrete action to better the health and wellness of its employees.).[14] The RCMP is the first federal agency and the first police force in Canada to be awarded this certification. The BNQ praised the RCMP for the quality of its infrastructure, including fitness facilities in almost all of its detachments, and for taking steps to promote healthy living among its employees.
The RCMP is now part of a group of only 14 businesses and organizations in Quebec boasting the Healthy Enterprise – Elite certification.[15]
International Peace Operations

Since 1989, Canada has deployed police officers to international peace missions around the world. They assist in rebuilding and strengthening police services in countries that have experienced conflict or upheaval.
By building the capacity of foreign police to maintain law and order, Canadian police, in cooperation with international partners, help create a safer and more stable environment. This in turn paves the way for long-term development and can also prevent illicit activities from spilling across borders into other countries, including Canada.[16] The RCMP manages the deployment of Canadian police, including planning and evaluating missions, selecting and training personnel from across the country as well as providing support throughout deployment. Canadian police who serve abroad come from municipal, provincial and regional police forces as well as the RCMP, and represent a variety of backgrounds.
They play a wide range of roles within each mission, from training and mentoring their police counterparts and providing humanitarian assistance to ensuring security for elections and investigating human rights violations.
Serving on a mission is a unique opportunity for police officers to contribute to public safety in unstable countries. Mission experience also enables our police to improve their leadership, problem-solving and intercultural skills, which ultimately benefits participating police services and the communities they serve.
Quick Facts:
- Canadian police involvement in international peace operations began in 1989. 2014 will mark 25 years of deployments.
- To date, more than 3,000 Canadian police have served on close to 60 peace operations around the world.
- In 1995, municipal, provincial and regional police agencies began participating in peace operations.
- Today, close to 130 Canadian police officers are serving in peace operations in Afghanistan, Haiti and the West Bank. In addition, a senior police advisor is posted to Canada's Permanent Mission to the United Nations in New York.
"C" Division Ceremonial Troop
Created in 1988, the RCMP Ceremonial Troop is composed of volunteers posted to various sections in "C" Division.
Troop members visit homes for the elderly and children's hospitals, help collect funds on behalf of non-profit organizations, and represent Canada in a variety of public events at home and abroad.
Corp "C" Division Ceremonial Troop[17]

The "C" Division Pipes & Drums Band is based at the Royal Canadian Mounted Police Headquarters in Montréal and serves communities in the region.
The Band is composed of police and civilian volunteers who share and showcase their musical talents for the benefit of the communities they serve. Music has a powerful appeal to the young and old alike, and this initiative provides a unique opportunity to bring the community closer to its national police service. The mandate of the Band is to benefit the community through music.

The Band performs for the public and in support of regional and local community events, including charity fund raisers, sports and cultural ceremonies, fairs, festivals, parades, memorial services and ceremonial functions on behalf of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police and other organizations.
The performances are adapted to specific occasions requiring:
- A parade band
- A show band
- Small ensembles
- A solo piper
References
- ↑ "The RCMP in Quebec - About Us".
- ↑ "The RCMP in Quebec - About Us".
- ↑ Bilan du siècle - Université de Sherbrooke http://bilan.usherbrooke.ca/bilan/pages/evenements/762.html
- ↑ De Gaulle - Encyclopédie du patrimoine culturel de l'Amérique française http://www.ameriquefrancaise.org/fr/article-8/De_Gaulle_et_«_Vive_le_Québec_libre!_».html
- ↑ Our Services in Quebec http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/qc/info/a_propos-about-eng.htm
- ↑ Organized Crime - "C" Division http://www.rcmp.gc.ca/soc-cgco/index-eng.htm
- ↑ "Border Integrity".
- ↑ Protective Services - "C" Division http://www.rcmp.gc.ca/pp/index-eng.htm
- ↑ Projet Colisée: une rafle historique - La Presse, November 23, 2006 http://www.lapresse.ca/dossiers/operation-colisee/200810/07/01-27221-projet-colisee-une-rafle-historique.php
- ↑ Radio-Canada - Project Colisée. http://www6.radio-canada.ca/nouvelles/societe/2006/11/22/009-operation-colisee.shtml#!
- ↑ Book : Mafia Inc.: The Long, Bloody Reign of Canada's Sicilian Clan by André Cédilot and André Noël, Les Éditions de l'Homme, chapter 9
- ↑ http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/qc/nouv-news/app/app-eng.htm
- ↑ Bureau de normalisation du Québec - "C" Division Certificate http://www-es.criq.qc.ca/pls/owa_es/bnqw_entr_enr.affiche_cert_es?p_lang=en&p_nom_entr=&p_munic=&p_regi_adm=&p_prov=&p_pays=&p_sic=&p_nace=&p_norme=BNQ%209700-800/2008-02-25&p_no_cert=44992-1-01
- ↑ The Healthy Enterprises Group - Elite Certification http://www.groupeentreprisesensante.com/coming-soon.html
- ↑ BNQ - List of Certificates and Attestations http://www-es.criq.qc.ca/pls/owa_es/bnqw_entr_enr.liste_enr?p_lang=en&p_type_bnq=ES&p_nom_entr=&p_munic=&p_regi_adm=&p_code_ics=&p_prov=&p_pays=&p_sic=&p_nace=&p_norme=BNQ%209700-800/2008-02-25&p_id_prog_certif=&p_id_prog_certif2=&p_produit=
- ↑ International Peace Operations http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/po-mp/index-eng.htm
- ↑ Corp "C" Division Ceremonial Troop http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/pd-ct/index-eng.htm
External links
- Official website
- Additional information on the Drug and Organized Crime Awareness Service
- Additional information on technological crime