Thiouracil
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
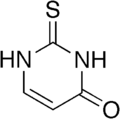
| IUPAC name
2-Thioxo-1H-pyrimidin-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 141-90-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:348530 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL345768 |
| ChemSpider | 1066108 |
| KEGG | C19304 |
| MeSH | Thiouracil |
| PubChem | 1269845 |
| UNII | 59X161SCYL |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4N2OS | |
| Molar mass | 128.15 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Thiouracil refers both to a specific molecule consisting of a sulfated uracil, and a family of molecules based upon that structure.
Medical use
The substance is a historically relevant anti-thyroid preparation. Astwood E.B. used it in 1943 as therapy of Graves' disease for the first time.[1] It remains in use.
Thiouracil inhibits thyroid activity by blocking the enzyme thyroid peroxidase.[2] Its use in recent times has been replaced by advent of more potent and safer antithyroid drugs.
References
- ↑ Gerabek, W. (2005). Enzyklopädie Medizingeschichte. p. 152. ISBN 9783110157147.
- ↑ Nagasaka, A.; Hidaka, H. (1976). "Effect of Antithyroid Agents 6-Propyl-2-Thiouracil and l-Methyl-2-Mercaptoimidazole on Human Thyroid Iodide Peroxidase". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 43 (1): 152–8. doi:10.1210/jcem-43-1-152. PMID 947933.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.