Customs and traditions of the Royal Navy
There are many customs and traditions associated with the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom, many of these traditions have carried on to other Commonwealth navies, such as Canada, Australia and New Zealand. These include formal customs including separate crests associated with ships, ensigns and fleet reviews. There are also several less formal customs and traditions including Naval slang commonly referred to as Jack Speak and the traditional games of Uckers and Euchre. Winston Churchill probably never dismissed the customs of the Royal Navy as "..nothing but rum, sodomy and the lash.”
Heraldry
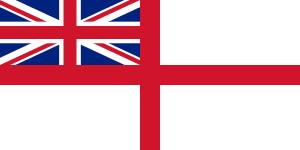
Ensigns
Commissioned ships and submarines wear the White Ensign at the stern whilst alongside during daylight hours and at the main-mast whilst under way. When alongside, the Union Jack is flown from the jackstaff at the bow, but can only be flown underway on special circumstances i.e.: when dressed with masthead flags (when it is flown at the jackstaff), to signal a court-martial is in progress (when it is flown from the starboard yardarm) or to indicate the presence of an Admiral of the Fleet, including the Lord High Admiral or the Monarch (when it is flown from the highest hoist).[1]
Ships badges
The Royal Navy assigns badges to every ship, submarine, squadron and shore establishment. Prior to the age of steam ships, ships were identified by their figurehead. With the removal of the figurehead, ships badges and mottoes were created to graphically represent the ships. The official process for creating the badge was initiated by Charles ffoulkes after World War I who was appointed as the Admiralty Advisor on Heraldry. Soon after his appointment The Ships' Badges Committee was established. This was amalgamated in 1983 with the Ships' Names Committee (founded in 1913) to create the Ships' Names and Badges Committee. The Naval Crown adorns the top of all the badges. The frame is gold rope. Originally, different classes of ships had different shapes, but currently all ships and submarines have a circular design. Shore establishments have an offset square design.
Fleet reviews
The Fleet Review is an irregular tradition of assembling the fleet before the monarch. For example, at the most recent Review on 28 June 2005 to mark the bi-centenary of the Battle of Trafalgar, 167 ships of the RN, and 30 other nations, were present. The fleet review in 2005 showed the marked contrast between the size of the Navy in 2005 compared to the last review in 1977. In total the Royal Navy had 67 ships on display, with the largest ship present being the French carrier Charles De Gaulle at over 200 feet longer than HMS Invincible.[2]
Service nicknames
Nicknames for the service include The Andrew or Andrew Miller (of uncertain origin, possibly after a zealous press ganger)[3][4] and The Senior Service.[5][6] It is also referred to as the Grey Funnel Line: ship owning companies, or lines, painted their steam ship's funnels in distinctive colours such as Cunard's red and black or the eponymous Blue Funnel Line, and the Royal Navy's funnels are plain grey.
Naval salute
Originally subordinates would remove their headgear to a superior. In a book called New Art of War, printed in 1740, it is stated that;
- When the King or Captain General is being saluted each Officer is to time his salute so as to pull off his hat when the person he salutes is almost opposite him.
Queen Victoria instituted the hand salute in the Navy to replace uncovering when she sent for certain officers and men to Osborne House to thank them for rendering help to a distressed German ship, and did not like to see men in uniform without headdress. During the age of sail, ships' officers were always worried about mutiny and it therefore became custom that whenever an officer approached, the rating would prove that he was not armed. This was done by knuckling the forehead and later evolved into the modern Navy salute with the hand at 45 degrees palm facing in. The reason that the palm faces in is because sailors' hands were covered in tar from the sheets and rigging and it was considered unseemly to show an officer or a member of the Royal family a dirty palm.
Toasts
The Toasts of the Royal Navy are a set of traditional drinking toasts.
| Day | Toast |
|---|---|
| Sunday | "Absent Friends" |
| Monday | "Our Ships at Sea" |
| Tuesday | "Our Men" |
| Wednesday | "Ourselves" (as no one else is likely to be concerned for us!) |
| Thursday | "A Bloody War or a Sickly Season" (and a quick promotion!) |
| Friday | "A Willing Foe and Sea-Room" |
| Saturday | "Wives and Sweethearts" (may they never meet)[7] or "May our sweethearts become our wives, and our wives remain our sweethearts".[8] |
In June 2013 the Tuesday and Saturday toasts were officially changed under orders from the Second Sea Lord, Vice-Admiral David Steel, to reflect the fact that women have been at sea in the Royal Navy for nearly two decades. Officially the Tuesday toast is now "Our Sailors" and the Saturday toast is "Our Families". However, the majority of personnel prefer the traditional toasts and they are still overwhelmingly used.[7]
The words in brackets are understood but unspoken (with the exception of "Wives and Sweethearts", which someone will normally quip after the toast). By tradition, these toasts were proposed immediately after the loyal toast, on the relevant day of the week.
While most of these toasts are self-explanatory, "a bloody war or a sickly season" refers to the desire and likelihood of being promoted when many people die: during war or sickness.[9] The Navy traditionally makes the loyal toast seated, due to the evident danger of low deckheads on wooden sailing ships.
The toasts are typically given by the youngest officer present at the mess dinner.[10]
Affiliation
Ships will engage in a number of affiliations. It is often misunderstood that ships are named after places when normally they are associated with the local lord e.g. the Duke of Marlborough. There were however a number of vessels named after places during World War II after schools, cadet units and charities. At one time every Sea Cadet unit in the UK had an affiliated ship (with the exception of Kettering, which is affiliated with 800 Naval Air Squadron; Yeovilton, now disbanded; and Yeovil unit which, due to its location on RNAS Yeovilton (HMS Heron), is affiliated with 848 Helicopter Squadron). However, now that Sea Cadet units outnumber Royal Navy vessels, this is no longer possible.
Naval slang
The RN has evolved a rich volume of slang, known as Jack-speak.[11] Nowadays the British sailor is usually Jack (or Jenny) rather than the more historical Jack Tar, which is an allusion to either the former requirement to tar long hair or the tar-stained hands of sailors. Nicknames for a British sailor, applied by others, include Matelot (pronounced "matlow", and derived from the French for sailor), and Limey, from the Lime-juice given to British sailors to combat scurvy - mainly redundant in use within the Royal Navy. Royal Marines are fondly known as Bootnecks or often just as Royals.[5]
Uckers and Euchre
Uckers is a two player board game similar to Ludo that is traditionally played in the Royal Navy. It is fiercely competitive and rules differ between ships and stations (and between other services).
Euchre, pronounced you-ker, is a card game also played on board ships, in naval establishments and also in pubs in Cornwall and Devon. It is similar to Trumps, and equally competitive. Euchre involves nominated partners, is played only with the nine card and higher, apart from the two of spades - called the "Benny" - (making 25 cards in all) and uses the eight and seven cards as a score board. The winner is the first team to score 15.
Songs and marches
There are several songs that are commonly associated with the Royal Navy including "Heart of Oak" (the official quick march) and "Rule, Britannia!"
References
- ↑ "Use of the Union Jack at Sea". Flags of the World. Retrieved 2007-07-14.
- ↑ "French top gun at Fleet Review". London: The Times. 2005-06-26. Retrieved 2007-07-12.
- ↑ Admiralty Manual of Seamanship. HMSO. 1964.
- ↑ "FAQs;Royal Navy's nickname". National Maritime Museum. Retrieved 2007-07-14.
- 1 2 Jolly, Rick. Jackspeak. Maritime Books Dec 2000. ISBN 0-9514305-2-1.
- ↑ "Naval Slang". Royal Navy. Archived from the original on 2007-07-02. Retrieved 2007-07-14.
- 1 2 Davies, Emily (22 June 2013). "Navy ditches toast to 'wives and sweethearts' for the first time in 200 years because there are now so many women at sea". Daily Mail. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- ↑ Cherry-Garrard, Apsley; Paul Theroux (2004). The Worst Journey in the World: Antarctic 1910-1913. Lyon's Press. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-59228-212-8. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ↑ Gibowicz, Charles J. (September 2007). Mess Night Traditions. AuthorHouse. pp. 155–157. ISBN 978-1-4259-8446-5. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ↑ A. Metaxas, "Metaxas' Personal Authoritative Manual on Naval Traditions"
- ↑ "The joy of 'Jackspeak'". Today. 28 September 2011. BBC Radio 4.
External links
- Royal Navy Life and Customs in World War 2
- Officer/Rating Relationships in the Royal Navy 1941-1972 by Lt Cdr G Mason RN Rtd