Treaty of Ribemont
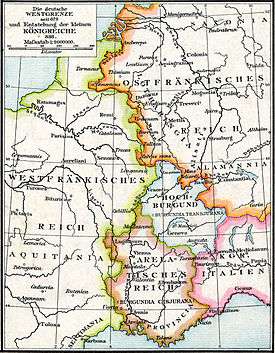
The Treaty of Ribemont in 880 was the last treaty on the partitions of the Frankish Empire. It was signed by the German king Louis the Younger and the kings of Western Francia, Louis III and Carloman.
After the death of Charles the Bald, Louis the Younger secured the friendship of Charles' successor Louis the Stammerer with the Treaty of Fourons in November 878. The two nephews promised to accept the successions of their respective sons. The treaty was put to the test when Louis the Stammerer died in April 879. A western delegation led by Gauzlin, bishop of Paris and later protector of the city during the Viking raids, invited Louis the Younger to take control of West Francia. Because his wife Luitgard also supported this idea, Louis the Younger invaded West Francia. He reached as far as Verdun, but he retreated after his nephews, the kings Louis III of France and Carloman of France, gave up their share of Lotharingia to him.
Meanwhile, Boso of Provence, a noble of Carolingian descent, proclaimed himself king of the Provence. Moreover, the Vikings resumed their attacks. To deal with these threats, the Carolingian kings decided to put aside their differences so as to deal with the threats together. They met at Ribemont, in present-day Aisne. In return for Louis the Younger's neutrality, the kings of France confirmed Louis' possession of the parts of Lotharingia that had been given to him since the Treaty of Meerssen. This left them free to deal with Boso.
The border between France and the Holy Roman Empire remained largely the same until the Late Middle Ages.
Earlier Frankish partitions were:
- Treaty of Verdun (843)
- Treaty of Prüm (855)
- Treaty of Meerssen (870)