Trochlea of superior oblique
| Trochlea of superior oblique | |
|---|---|
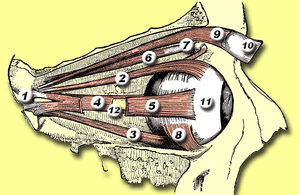 Rectus muscles: 2 = superior, 3 = inferior, 4 = medial, 5 = lateral Oblique muscles: 6 = superior, 8 = inferior Other muscle: 9 = levator palpebrae superioris Other structures: 1 = Annulus of Zinn, 7 = Trochlea, 10 = Superior tarsus, 11 = Sclera, 12 = Optic nerve | |
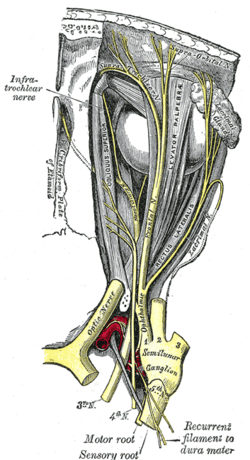 Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above. (Trochlea visible at upper left but not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Trochlea musculi obliqui superioris bulbi |
| TA | A15.2.07.017 |
| FMA | 49065 |
The trochlea of superior oblique is a pulley-like structure in the eye. The tendon of the superior oblique muscle passes through it. Situated on the superior nasal aspect of the frontal bone, it is the only cartilage found in the normal orbit. The word trochlea comes from the Greek word for pulley.
Actions of the superior oblique muscle
In order to understand the actions of the superior oblique muscle, it is useful to imagine the eyeball as a sphere that is constrained – like the trackball of a computer mouse – in such a way that only certain rotational movements are possible. Allowable movements for the superior oblique are (1) rotation in a vertical plane – looking down and up (depression and elevation of the eyeball) and (2) rotation in the plane of the face (intorsion and extorsion of the eyeball).
The body of the superior oblique muscle is located behind the eyeball, but the tendon (which is redirected by the trochlea) approaches the eyeball from the front. The tendon attaches to the top (superior aspect) of the eyeball at an angle of 51 degrees with respect to the primary position of the eye (looking straight forward). The force of the tendon’s pull therefore has two components: a forward component that tends to pull the eyeball downward (depression), and a medial component that tends to rotate the top of the eyeball toward the nose (intorsion).
The relative strength of these two forces depends on which way the eye is looking. When the eye is adducted (looking toward the nose), the force of depression increases. When the eye is abducted (looking away from the nose), the force of intorsion increases, while the force of depression decreases. When the eye is in the primary position (looking straight ahead), contraction of the superior oblique produces depression and intorsion in roughly equal amounts.
To summarize, the actions of the superior oblique muscle are (1) depression of the eyeball, especially when the eye is adducted; and (2) intorsion of the eyeball, especially when the eye is abducted. The clinical consequences of weakness in the superior oblique (caused, for example, by fourth nerve palsies) are discussed below.
This summary of the superior oblique muscle describes its most important functions. However, it is an oversimplification of the actual situation. For example, the tendon of the superior oblique inserts behind the equator of the eyeball in the frontal plane, so contraction of the muscle also tends to abduct the eyeball (turn it outward). In fact, each of the six extraocular muscles exerts rotational forces in all three planes (elevation-depression, adduction-abduction, intorsion-extorsion) to varying degrees, depending on which way the eye is looking. The relative forces change every time the eyeball moves – every time the direction of gaze changes. The central control of this process, which involves the continuous, precise adjustment of forces on twelve different tendons in order to point both eyes in exactly the same direction, is truly remarkable.
The recent discovery of soft tissue pulleys in the orbit – similar to the trochlea, but anatomically more subtle and previously missed – has completely changed (and greatly simplified) our understanding of the actions of the extraocular muscles.[1] Perhaps the most important finding is that a 2-dimensional representation of the visual field is sufficient for most purposes.
Additional images
 Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
See also
References
- ↑ Demer JL. Pivotal Role of Orbital Connective Tissues in Binocular Alignment and Strabismus. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 2004;45:729-738