Whitney Avenue Historic District
|
Whitney Avenue Historic District | |
 | |
  | |
| Location | Roughly bounded by Burns St., Livingston St., Cold Spring St., Orange St., Bradley St., and Whitney Ave., New Haven, Connecticut |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 41°19′23″N 72°54′53″W / 41.32306°N 72.91472°WCoordinates: 41°19′23″N 72°54′53″W / 41.32306°N 72.91472°W |
| Area | 203 acres (82 ha) |
| NRHP Reference # | 88003209[1] |
| Added to NRHP | February 2, 1989 |
The Whitney Avenue Historic District is a historic district in the East Rock neighborhood of New Haven, Connecticut. It is a 203-acre (82 ha) district which included 1,084 contributing buildings when it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989.[1]
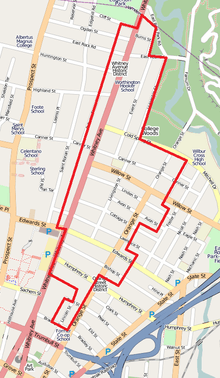
It is bordered by Edgerton Park and East Rock Park on the north. It abuts the Prospect Hill Historic District to the west and the Orange Street Historic District on the east. Yale University facilities border on the southwest and south.[2]:59 The district is named after Whitney Avenue, the principal thoroughfare in the district, which is lined with mansions or other larger houses, while the smaller streets included in the district have mostly smaller homes.
Per its NRHP nomination, the district
is significant as a well-preserved middle and upper-class residential neighborhood which reflects the process of suburbanization in New Haven during the late 19th and early 20th centuries...and which has retained its integrity with few intrusions or alterations.... The houses in the district embody the distinctive characteristics of several periods and types of domestic architecture, including locally outstanding examples of Queen Anne, Shingle, Colonial Revival, Tudor Revival, and other styles....[2]:51
The district includes 749 "major" buildings: mostly houses but also schools, small commercial buildings, and a firehouse. Including smaller outbuildings such as garages and carriage houses, there were a total of 1,113 buildings in 1989. Besides the 1,084 contributing buildings, the district then included 29 non-contributing buildings.[2]:1 Since that time, some of the contributing buildings have been demolished, such as some garages behind houses, but the character of the district is generally preserved.
Residential structures

Large mansions are primarily along Whitney Avenue and Livingston Street.[2]:4
Significant Queen Anne style houses include the William Allen House, at 357 Whitney Avenue, a principal example among a row of Queen Anne houses.[2]:55[3]
Significant Shingle style houses include:
- 519 Whitney Avenue, at the corner of Canner Street (pictured above)
- the Charles Atwater House (pictured at right, also as Photo #21 in accompanying NRHP nomination photos, and as photo #1 in New Haven Preservation Trust photos) at 321 Whitney Avenue, at the corner of Edwards Street, designed by Babb, Cook and Willard[2]:55
- the Abner Hendee House at 703 Whitney Avenue[2]:55
Significant Colonial Revival ones include:
- C. Maeller House, 591 Whitney Avenue[2]:56[3]:pic #4
- Coyle House, nearby[2]:56
- 369 Whitney Avenue[2]:56
- Dr. Henry Hessler House, 1930, designed by J. Frederick Kelly, at 370 Livingston (accompanying photo #11)[2]:33,56[3]:pic #10
- Ray Reigeluth House, at 340 Livingston Street, from 1928–29, which represents an "apogee" of revival, being an exact copy of the Julius Deming House on North Street in the Litchfield Historic District in Litchfield, Connecticut, designed by architect Dwight Smith (accompanying photo #10)[2]:33,56
- Louis Ullman House, 1916, at 294 Livingston (accompanying photo #9)[2]:33
There are significant Tudor Revival houses including, for example, the Dr. Edwin Butler House, at 640 Whitney Avenue, from 1913.[2]:56[3]:pic #5
Other assorted styles are represented, including, notably, the Colin Ingersoll House at 475 Whitney Avenue, a spectacular Chateauesque style building designed by architect Joseph Northrup[2]:57[3]
There are apartment buildings mixed into the housing stock, particularly of U-shaped forms and particularly along Whitney Avenue. Examples appear in photos 16 and 29 (Brighton Court, in Spanish Colonial Revival, c.1915, at 663-667 Whitney Avenue) of accompanying photo collection.[2]:5
Institutional buildings
Institutional purposes are now served by many of the buildings built originally as mansions along Whitney Avenue. At the time of the National Register listing, there were ten churches in the district, four of which were deemed to contributing properties. There are also several schools and a fire station.[2]:5 Institutional structures, specifically built as such, include:
- First Baptist Church, 1902, designed by Leoni Robinson in Late Gothic Revival style, at 205 Edwards Street (see Photo 3 in accompanying photo collection)[2]:18
- St. Thomas's Episcopal Church, 1931, at 830 Whitney Avenue[2]:47
- Evangelical Covenant Church
- St. John's Episcopal Church, 1895, at 400 Humphrey, a Gothic style church designed by William Halsey Wood[2]:22
- Swedish Emanuel Congregational Church, a Colonial Revival style from 1925, at 590 Orange Street[2]:34
- Epworth Methodist Episcopal Church, in Romanesque style from 1892, at 655 Orange Street[2]:34
- First Unitarian/Universalist Society, c. 1910, at 608 Whitney Avenue
- Worthington Hooker School, Beaux Arts style, 1900, brick and terra cotta, (photo 1 in accompanying photos)[2]:12,57
- Whitney Station, of the New Haven Fire Department, an International style building at 348 Whitney Avenue[2]:41
- Troop A Armory, at 869 Orange Street, in Late Gothic Revival style from 1906
Commercial buildings
Per the NRHP nomination, small commercial buildings or "houses which have been fitted with storefronts", primarily at corners or along Orange Avenue are included in, and serve, the district.[2]:5 An unusual example is the Hall-Benedict Drug Company Building, a building on Orange Street, which is separately listed on the National Register.
Summary
Per the NRHP nomination,
In summary, the district is distinguished by its exceptional number of architecturally significant houses; the wide, shady, tree-lined streets which provide an appropriate setting for those houses; and by the high proportion of buildings which have retained their integrity of materials and design. Together these attributes create the sense of historic and architectural cohesiveness which makes this area a distinctive cultural resource.[2]:58[4]
Relationship to neighborhoods
The historic district primarily in the East Rock neighborhood but also extending into the Prospect Hill neighborhood of the city of New Haven, Connecticut. The row of properties on the west side of Whitney Avenue is officially in the Prospect Hill neighborhood planning area.
See also
References
- 1 2 National Park Service (2009-03-13). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 William E. Devlin and Bruce Clouette (June 9, 1988). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination: Whitney Avenue Historic District" (PDF). National Park Service. and Accompanying 32 photos from 1988 (captions pages 60-62 of text document)
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Photo Gallery, Whitney Avenue Historic District". New Haven Preservation Trust.
- ↑ "Whitney Avenue Historic District". New Haven Preservation Trust.
External links
- Whitney Avenue Historic District, New Haven Preservation Trust website (includes 11 photos)
- Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS) No. CT-282, "Atwater-Ciampolini House, 321 Whitney Avenue, New Haven, New Haven County, CT", 8 photos, 7 data pages, supplemental material
- 1st Unitarian Universalist Society of New Haven, 608 Whitney Avenue, New Haven