Yamal–Europe pipeline
| Yamal–Europe pipeline | |
|---|---|
 Location of Yamal–Europe pipeline | |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia, Belarus, Poland |
| General direction | north-south-west |
| From | Torzhok |
| Passes through | Vuktyl, Ukhta, Gryazovets, Torzhok, Smolensk, Minsk, Zambrów, Włocławek, Poznań |
| To | Górzyca |
| Runs alongside | Northern Lights pipeline |
| General information | |
| Type | natural gas |
| Partners |
Gazprom PGNiG Gas-Trading S.A. |
| Operator |
Gazprom Gazprom Transgaz Belaru EuRoPol Gaz |
| Commissioned | 1997 |
| Technical information | |
| Length | 4,196 km (2,607 mi) |
| Maximum discharge | 33×109 m3/a (1.2×1012 cu ft/a) billion cubic meters per year |
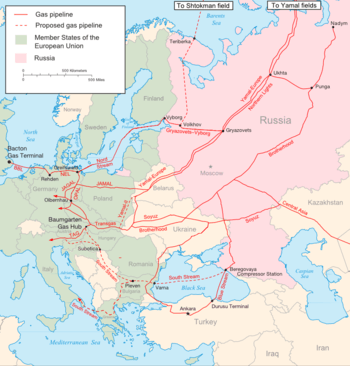
The Yamal–Europe natural gas pipeline is a 4,196 kilometres (2,607 mi) long pipeline connecting natural gas fields in Western Siberia and in the future on the Yamal peninsula, Russia, with Germany.
History
Planning for the Yamal–Europe pipeline started in 1992. Intergovernmental agreements between Russia, Belarus and Poland were signed in 1993. In 1994, Wingas, the joint venture of Gazprom and Wintershall, a subsidiary of BASF, started building the German section of the pipeline. The first gas was delivered to Germany through the Belarus-Polish corridor in 1997. The Belarus and Polish sections were completed in September 1999 and the pipeline reached its rated annual capacity of about 33 billion cubic metres (1.2 trillion cubic feet) of natural gas in 2005, after completion of all compressor stations.
Route
The pipeline starts at the Torzhok gas hub in Russia and is fed by the Northern Tyumen Regions (SRTO) – Torzhok gas pipeline. Its length includes around 402 kilometres (250 mi) in Russia, 575 kilometres (357 mi) in Belarus and 683 kilometres (424 mi) in Poland.[1] The German gas system is connected to the Yamal–Europe pipeline through the JAGAL pipeline.
Notwithstanding its name, the pipeline is initially supplied by gas fields in the Nadym Pur Taz District of the Tyumen Oblast and not from Yamal peninsula. It would be supplied from the Bovanenkovo field of Yamal peninsula after construction of the 1,100 kilometres (700 mi) long Bovanenkovo-Ukhta pipeline, a part of the Yamal project.[2]
Technical features
The capacity of the pipeline is 33 billion cubic metres (1.2 trillion cubic feet) of natural gas per annum.[3] The diameter of the pipeline is 1,420 millimetres (56 in). The pressure in the pipeline is provided by 14 compressor stations.[1]
Ownership
The Russian section of the pipeline is owned and operated by Gazprom. The Belarusian section is owned by Gazprom and operated by Gazprom Transgaz Belaru.[3] The Polish section is owned and operated by EuRoPol Gaz S.A., a joint venture of the Polish PGNiG, Russian Gazprom (both 48% of shares) and Polish Gas-Trading S.A. (4% of shares).
Second pipeline
Since 2005, there have been plans to build the second leg of the pipeline. On 1 November 2007, the Russian minister of industry and energy Viktor Khristenko said that Russia has dropped the idea of building the second leg of a pipeline, preferring construction of the Nord Stream pipeline.[3] As of April 2013, Russia has shown interest in reviving the project, with an estimated $5 billion investment that could lead to the completion of the pipeline by 2019.[4]
References
- 1 2 "Yamal – Europe". Gazprom. Retrieved 2015-03-22.
- ↑ "Gazprom starts developing the Yamal gas fields". East Week. The Centre for Eastern Studies (150). 2008-12-17. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- 1 2 3 "Russia drops second leg of gas pipeline via Belarus". RIA Novosti. 2007-11-01. Retrieved 2008-12-31.
- ↑ Russia revives $5bn Yamal-Europe pipeline project.
External links
- Yamal-Europe, Gazexport website
- EuRoPol Gaz website