(131697) 2001 XH255
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Kleyna, J., Sheppard, S. S., Jewitt, D. C. |
| Discovery date | 11 December 2001 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | (131697) 2001 XH255 |
|
TNO 4:5 resonance[2][3] | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 4110 days (11.25 yr) |
| Aphelion | 37.907 AU (5.6708 Tm) (Q) |
| Perihelion | 32.339 AU (4.8378 Tm) (q) |
| 35.123 AU (5.2543 Tm) (a) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.079253 (e) |
| 208.16 yr (76030.5 d) | |
| 318.51° (M) | |
| 0° 0m 17.046s / day (n) | |
| Inclination | 2.8512° (i) |
| 323.17° (Ω) | |
| 217.87° (ω) | |
| Earth MOID | 31.3433 AU (4.68889 Tm) |
| Jupiter MOID | 26.8986 AU (4.02397 Tm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 100 km (assumed)[4] |
| 0.09 (assumed) | |
| 23.6[5] | |
| 8.2[1] | |
|
| |
(131697) 2001 XH255, provisionally known as 2001 XH255, is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) that has a 4:5 resonance with Neptune.[2]
It will come to perihelion in 2041.[1]
Assuming a generic TNO albedo of 0.09, it is about 100 km in diameter.[4]
Resonance
According to the Deep Ecliptic Survey and Minor Planet Center, (131697) 2001 XH255 has a 4:5 resonance with Neptune.[2][3] It comes as close as 32.2 AU from the Sun and has a fairly low orbital eccentricity of 0.07 with an inclination of only 2.86 degrees.[1]
The Neptune 4:5 resonance keeps it more than 7 AU from Neptune over a 14000-year period.[6]
It has been observed 21 times over 5 oppositions and has an orbit quality code of 3.[1]
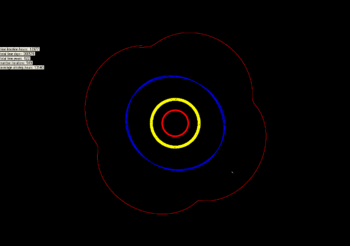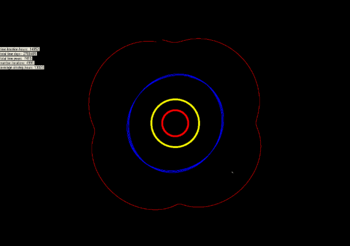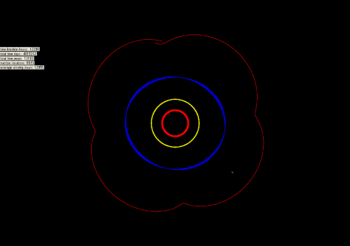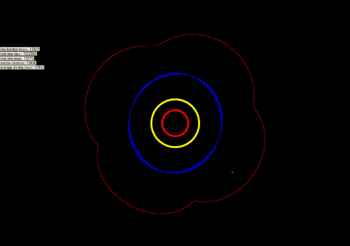
The libration of 2001 XH255. Jupiter in red, Saturn in yellow, and Uranus in blue. Neptune is the white dot at 5 o'clock.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 131697 (2001 XH255)" (last observation: 2006-01-29). Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- 1 2 3 Marc W. Buie. "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 131697" (2006-01-29 using 19 observations). SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2009-02-01.
- 1 2 "MPEC 2009-A63 :Distant Minor Planets (2009 JAN. 29.0 TT)". Minor Planet Center. 2009-01-13. Retrieved 2009-02-01.
- 1 2 Wm. Robert Johnston (22 August 2008). "List of Known Trans-Neptunian Objects". Johnston's Archive. Archived from the original on 13 February 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-01.
- ↑ "AstDys (131697) 2001XH255 Ephemerides". Department of Mathematics, University of Pisa, Italy. Archived from the original on 2009-04-18. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ↑ "MPEC 2006-H30 : 2001 XT254, 2001 XH255". Minor Planet Center. 2006-04-22. Retrieved 2009-02-01.
External links
- Orbital simulation from JPL (Java) / Horizons Ephemeris
- (131697) 2001 XH255 at the JPL Small-Body Database
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/31/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.