79 Eurynome
|
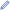
A three-dimensional model of 79 Eurynome based on its light curve. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | James Craig Watson |
| Discovery date | September 14, 1863 |
| Designations | |
Named after | Eurynome |
| Main belt | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch December 31, 2006 (JD 2454100.5) | |
| Aphelion | 435.949 Gm (2.914 AU) |
| Perihelion | 295.538 Gm (1.976 AU) |
| 365.743 Gm (2.445 AU) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.192 |
| 1396.288 d (3.82 a) | |
Average orbital speed | 18.87 km/s |
| 149.498° | |
| Inclination | 4.622° |
| 206.802° | |
| 200.384° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 66.5 km |
| Mass | 3.1×1017 kg |
Mean density | ? g/cm³ |
| 0.0186 m/s² | |
| 0.0352 km/s | |
| ? d | |
| Albedo | 0.262 (geometric)[1] |
| Temperature | ~178 K |
Spectral type | S |
| 9.35 (brightest) | |
| 7.96 | |
|
| |
79 Eurynome (/jʊˈrɪnəmiː/ ew-RIN-ə-mee) is a quite large and bright main-belt asteroid composed of silicate rock. Eurynome was discovered by J. C. Watson on September 14, 1863. It was his first asteroid discovery. It is named after one of the many Eurynomes in Greek mythology.
References
External links
- Orbital simulation from JPL (Java)
- Ephemeris
- 79 Eurynome at the JPL Small-Body Database
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
.png)