April 3, 2012 tornado outbreak
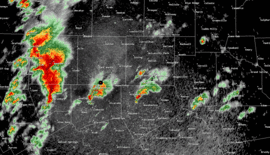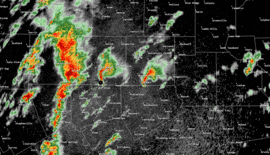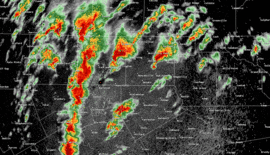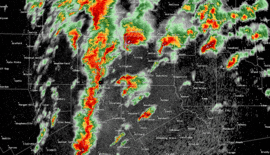 Radar loop of storms affecting Dallas/Fort Worth during the outbreak. | |
| Type | Tornado outbreak |
|---|---|
| Duration | April 3, 2012 |
| Max rating1 | EF3 tornado |
| Duration of tornado outbreak2 | 6 hours, 27 minutes |
| Highest winds |
|
| Largest hail | 3.5 in (89 mm) near Forney |
| Damage | ≥$1 billion[1] (estimated) |
| Casualties | 0 fatalities, 29 injured |
|
1Most severe tornado damage; see Enhanced Fujita scale 2Time from first tornado to last tornado | |
The April 3, 2012 tornado outbreak was a small, albeit localized tornado outbreak that primarily affected the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex.[2] During the morning of April 3, a large low-pressure area and associated frontal boundaries tracked across the Southern US Plains. Initially, environmental conditions did not favor the development of tornadoes. However, an outflow boundary from an area of storms in Oklahoma moved southwards before stalling over the Dallas–Fort Worth area. This allowed the formation of individual supercells, which would produce numerous tornadoes in the region. Many of these tornadoes occurred in the afternoon and evening hours of the day. One of these tornadoes was an EF3 tornado which struck areas of Forney, Texas, damaging homes and businesses; this tornado would be the strongest confirmed during the outbreak. However, the costliest tornado was of EF2 intensity, and struck the counties of Ellis and Dallas, causing roughly $400 million in damages. The same tornado also injured 10 people, but did not cause any damage. Throughout the duration of the outbreak, there were 22 confirmed tornadoes, though 17 of them were rated EF0 – the lowest rating on the Enhanced Fujita Scale.
In conjunction with the tornadoes, numerous hail and wind reports were received by the Storm Prediction Center (SPC) that day, though it is unclear which were directly associated with the storm complex. However, severe weather in Texas resulted in excess of $1 billion in damages, mostly due to the tornadoes. It was estimated that at least 1,100 homes in the metropolitan area were damaged in the outbreak, including at least 349 that were destroyed. Despite hitting heavily populated areas, however, no deaths were reported. However, a total of 29 injuries were confirmed.[3]
Meteorological synopsis

A low pressure system and associated frontal boundaries tracked across the Southern Plains on April 3. The large-scale synoptics were marginal for tornadoes, hence only a slight risk of severe weather was issued by the Storm Prediction Center in Norman, Oklahoma, with large hail the primary threat and tornadoes and damaging winds secondary threats.[4] As a result of the initially perceived low risk, only a severe thunderstorm watch was initially issued for the region at 9:20 am CDT (1420 UTC).[5] Once the small-scale synoptics became more conducive for tornado activity, the watch was upgraded to a tornado watch for North Texas at 12:10 pm CDT (1720 UTC).[6]
What was initially believed to be a wind and hail event from reliable models and forecast unexpectedly developed into a locally significant tornado outbreak as a result of changing mesoscale situations, concentrated on the heavily populated Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex. That development was attributed to an outflow boundary from another area of storms farther north in Oklahoma that tracked southward across the Red River and into the Metroplex where it stalled just south of the Interstate 20 corridor in the southern suburbs, allowing discrete supercells to form along the boundary. The boundary increased low-level wind shear significantly due to easterly winds, allowing for tornadoes to develop. As a result, taking advantage of the highly unstable environment that became much more highly sheared than initially forecasted with high CAPE values, the storms became much more intense than forecasted and quickly became tornadic and intense, resulting in severe damage across the region in heavily populated areas. South of the boundary, shear was much more marginal and tornadoes did not develop.[7] Once the cells tracked eastward towards Louisiana, the atmosphere was much more stable and the cells rapidly weakened.
Tornadoes
| EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
April 3 event
| List of reported tornadoes – Tuesday, April 3, 2012 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | | | | | | Comments/Damage | |
| Texas | |||||||
| EF1 | N of Cleburne | Johnson | 32°21′N 97°24′W / 32.35°N 97.40°W | 1741 – 1743 | 1.16 miles (1.87 km) | 60 yd (55 m) | Several houses were damaged. A barn was completely unroofed by the tornado. A horse trailer was overturned and two lawnmowers sustained damage. Damages totaled $60,000.[8] |
| EF2 | W of Lancaster to NW of Hutchins | Ellis, Dallas | 32°36′N 96°45′W / 32.60°N 96.75°W | 1800 | 13.7 miles (22.0 km) | This tornado was broadcast on WFAA-TV, and is notable for being broadcast live, as several large tractor-trailers were being tossed into the air as it hit a Schneider National truck terminal. An estimated 650 houses were damaged in Lancaster, some of them destroyed. Cars were tossed and trees and power lines were downed. Ten people were injured, two severely.[9][10] | |
| EF0 | ENE of Burleson | Johnson | 32°32′N 97°17′W / 32.54°N 97.28°W | 1808 | 0.3 miles (480 m) | Brief touchdown with no damage. | |
| EF2 | Kennedale to Arlington | Tarrant | 32°38′N 97°13′W / 32.63°N 97.22°W | 1821 | 6.4 miles (10.3 km) | Over 200 homes and businesses were damaged. Some homes lost their entire second stories. Numerous trees were downed and an apartment complex was damaged. The Green Oaks Nursing and Rehabilitation Center suffered severe damage in Arlington before the tornado lifted on the shores of Lake Arlington. Seven people were injured.[11][12] | |
| EF0 | East Dallas | Dallas | 32°47′N 96°41′W / 32.78°N 96.69°W | 1855 | 0.1 miles (0.16 km) | Brief tornado near Skyline High School damaged trees and a few roofs. | |
| EF0 | WNW of Grand Prairie | Tarrant | 32°46′N 97°04′W / 32.77°N 97.06°W | 1858 | 0.4 miles (0.64 km) | Brief tornado in the northern sections of town. A few buildings sustained severe roof damage and power lines were downed. Trees damage occurred and street signs were bent over. | |
| EF0 | NW of Irving | Dallas | 32°52′N 96°59′W / 32.86°N 96.98°W | 1908 | 1.4 miles (2.3 km) | Brief tornado with damage to Townsell Elementary School, where HVAC units were torn off the roof and a gas line was ruptured. Several businesses sustained roof damage as well. Trees and fences were downed, and a road sign was blown over. | |
| EF0 | E of Coppell | Dallas | 32°57′N 96°59′W / 32.95°N 96.99°W | 1923 | 2 miles (3.2 km) | Tornado produced minor damage to several roofs and an awning at a gas station in a narrow, non-continuous path. | |
| EF0 | S of Denton | Denton | 33°10′N 97°08′W / 33.16°N 97.14°W | 1940 | 0.25 miles (0.40 km) | Brief tornado with minor damage. | |
| EF0 | S of Cumby | Hunt | 33°05′N 95°51′W / 33.09°N 95.85°W | 2020 | 0.25 miles (0.40 km) | Tornado occurred over open country with no damage. | |
| EF0 | Mesquite area | Dallas | 32°46′N 96°36′W / 32.77°N 96.60°W | 2022 | 0.3 miles (0.48 km) | Brief tornado near the Mesquite Rodeo Arena. Several trees were downed and houses suffered roof damage. One business was badly damaged. | |
| EF0 | SW of Sulphur Springs | Hopkins | 33°05′N 95°40′W / 33.08°N 95.66°W | 2024 | 0.15 miles (0.24 km) | Brief tornado over open country. | |
| EF3 | Forney area | Kaufman | 32°45′N 96°28′W / 32.75°N 96.47°W | 2033 – 2039 | 7.73 miles (12.44 km) | 150 yd (140 m) | Short-lived tornado of considerable damage in the Forney area, particularly the Diamond Creek Subdivision, and caused seven injuries. At its initial touchdown in downtown Forney, numerous trees were snapped and uprooted. The roof of a fire station was damaged, while shingle and window damage occurred to nearby buildings. An outbuilding was completely destroyed. A dry cleaning business suffered significant damage to its roof and commercial signage. Other industrial buildings saw minor damage. However, once the tornado entered the Diamond Creek subdivision, it quickly intensified. Several homes were completely destroyed, with other unroofed or heavily damaged. The roof of the nearby Crosby Elementary School was damaged, with nearby cars damaged. After exiting the subdivision, the tornado weakened and continued to produce minor damage before dissipating. Damages amounted to $100 million.[13] |
| EF0 | WSW of Poetry | Kaufman | 32°49′N 96°22′W / 32.81°N 96.36°W | 2042 | 0.5 miles (0.80 km) | Brief tornado with no damage. Formed from the same supercell that produced the EF3 Forney tornado. | |
| EF0 | North Sulphur Springs | Hopkins | 33°08′N 95°36′W / 33.13°N 95.60°W | 2054 | 0.5 miles (0.80 km) | Trees and power lines were downed. | |
| EF2 | SE of Royse City | Rockwall, Hunt | 32°55′N 96°20′W / 32.91°N 96.33°W | 2056 | 3.1 miles (5.0 km) | Large wedge tornado. Several homes were badly damaged in a subdivision, and one home of poor construction was completely swept away. Multiple buildings were destroyed at an industrial park. Trees were snapped and uprooted and a gas station was destroyed as well. Other homes were damaged as the tornado crossed into Hunt County. In Hunt County, two mobile homes were damaged and two others were destroyed. Another permanent home was damaged before it dissipated.[14] | |
| EF0 | S of Greenville | Hunt | 33°02′N 96°08′W / 33.04°N 96.14°W | 2127 | 0.5 miles (0.80 km) | Brief touchdown over open country. | |
| EF0 | E of Hagansport | Franklin | 33°21′N 95°08′W / 33.35°N 95.14°W | 2139 | 1.4 miles (2.3 km) | Tornado uprooted trees near the Sulphur River. | |
| EF0 | S of Clarksville | Red River | 33°28′N 95°04′W / 33.46°N 95.06°W | 2141 | 1.6 miles (2.6 km) | Several trees were snapped or uprooted. | |
| EF0 | SW of De Kalb | Bowie | 33°26′N 94°43′W / 33.43°N 94.71°W | 2144 | 2.3 miles (3.7 km) | Several trees were snapped or uprooted. | |
| EF0 | NW of Winnsboro | Hopkins | 33°01′N 95°22′W / 33.01°N 95.36°W | 2236 | 0.5 miles (0.80 km) | Tree damage occurred along the path. | |
| Louisiana | |||||||
| EF0 | ESE of Rodessa | Caddo | 32°58′N 93°59′W / 32.97°N 93.98°W | 0008 | 3.1 miles (5.0 km) | Several trees were snapped or uprooted, some of which fell on buildings. One outbuilding was directly damaged by the tornado. | |
| Sources: SPC Storm Reports for 04/03/12, NWS Dallas/Fort Worth, NWS Shreveport, LA, NCDC Storm Events Database | |||||||
Aftermath
The city of Kennedale was one of the first to declare itself a disaster area on April 3, 2012, just a few hours after one of the first tornados to hit the Dallas-Fort Worth metroplex area struck their town. Kennedale made the disaster declaration official on April 4, 2012.[15] Both Mayor Bryan Lankhorst of Kennedale and Mayor Robert Cluck of Arlington signed disaster declarations for their cities.[16] These declarations paved the way for Texas Governor Rick Perry to declare Dallas, Kaufman, and Tarrant counties disaster areas on Thursday, April 5, 2012.[17]
See also
- Tornadoes of 2012
- Tornadoes of 2006 - From December 29–30, 2006, 22 tornados struck the Dallas-Fort Worth metroplex area and surrounding areas in another outbreak.
- 2000 Fort Worth tornado - On March 28, 2000 two tornados caused massive damage to downtown Fort Worth, as well as damage to the cities of Arlington and Grand Prairie.
- April 1994 tornado outbreak - On April 25, 1994 a tornado outbreak hit the Dallas-Fort Worth area, spawning 25 twisters that day and causing 3 deaths locally in Lancaster
References
- ↑ Jeff Masters (May 11, 2012). "2nd billion-dollar weather disaster of 2012: April 3 severe weather in Texas". Weather Underground. Retrieved May 12, 2012.
- ↑ Jervis, Rick; Rice, Doyle (3 April 2012). "Officials assess damage after tornadoes pummel Dallas area". USA TODAY. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- ↑ Staff, CNN Wire (5 April 2012). "Red Cross: 1,100 homes struck by Texas twisters". CNN. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ↑ Corfidi, Steve; Cohen, Ariel (3 April 2012). "Apr 3, 2012 1300 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook". Storm Prediction Center. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ Mead, Corey (3 April 2012). "Severe Thunderstorm Watch 132". Storm Prediction Center. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ Mead, Corey (3 April 2012). "Tornado Watch 133". Storm Prediction Center. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ National Weather Service Fort Worth (4 April 2012). "Area Forecast Discussion". Archived from the original on 4 April 2012. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ Webmaster, FWD (5 April 2012). "April 3rd 2012 Severe Weather Outbreak:Johnson County Survey". Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ↑ Lancaster/Dallas Tornado, Rated EF-2. National Weather Service. 4 April 2012. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ Paul J. Webber (April 4, 2012). "Tornado-wrecked Dallas begins assessing damage". Associated Press. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved April 4, 2012.
- ↑ WFAA (3 April 2012). "Severe weather blog: North Texas cleanup under way". WFAA News 8 HD (Interview). Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex: American Broadcasting Company. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ Kennedale/Arlington Tornado, Rated EF-2. National Weather Service. 4 April 2012. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ Forney Tornado, Rated EF-3. National Weather Service. 4 April 2012. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ↑ "April 3rd 2012 Severe Weather Outbreak:Rockwall/Hunt County Survey". National Weather Service. 4 April 2012. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ↑ Cirmo, Amethyst (4 April 2012). "Press Release:KENNEDALE - DECLARATION OF DISASTER. CLEANUP UNDERWAY" (PDF). Fort Worth Star-Telegram. Retrieved 6 April 2012.
- ↑ Schrock, Susan; Vaughn, Chris (4 April 2012). "Arlington/Kennedale tornado traveled 4.6 miles, weather service says". Fort Worth Star-Telegram. Retrieved 6 April 2012.
- ↑ "Disaster declaration for 3 counties" (Interview). Austin, Texas: LIN Television of Texas. 5 April 2012. Retrieved 5 April 2012 – via KXAN.
External links
For the latest severe weather information:
Storm Reports: