Detroit People Mover
 | ||||||
 Entering Renaissance Center station | ||||||
| Overview | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | Downtown Detroit | |||||
| Transit type | People mover | |||||
| Number of lines | 1 | |||||
| Number of stations | 13 | |||||
| Daily ridership | 6,000 (2014) | |||||
| Annual ridership | 2,413,414 (2015) | |||||
| Headquarters |
1420 Washington Boulevard Detroit, Michigan 48226 | |||||
| Operation | ||||||
| Began operation | 1987 | |||||
| Operator(s) | Detroit Transportation Corporation | |||||
| Number of vehicles | 12 | |||||
| Technical | ||||||
| System length | 2.94 mi (4.73 km) | |||||
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) | |||||
| Electrification | Third rail | |||||
| ||||||
The Detroit People Mover is a 2.94-mile (4.73 km) automated people mover system which operates on a single track, and encircles Downtown Detroit, Michigan.[2]
The Woodward Avenue Light Rail line, later officially named the "Qline", beginning construction in late July 2014, will serve as a link between the Detroit People Mover and New Center Amtrak station with its current service and proposed SEMCOG Commuter Rail, plus additional access to DDOT and SMART bus routes as part of a comprehensive network of transportation in metropolitan Detroit.[3]
The People Mover uses UTDC ICTS Mark I technology and the cars are driverless. A siding allows the system to be used in a two-way bypass manner when part of the circular track is closed.
History
The Detroit People Mover has its origins in 1966, with Congressional creation of the Urban Mass Transportation Administration (UMTA) to develop new types of transit. In 1975, following the failure to produce any large-scale results and increased pressure to show results, UMTA created the Downtown People Mover Program (DPM) and sponsored a nationwide competition that offered federal funds to cover much of the cost of planning and construction of such a system. UMTA reviewed thirty-five full proposals. From these, they selected proposals from Cleveland, Houston, Los Angeles, and St. Paul. In addition, UMTA decided they would approve proposals from Baltimore, Detroit, and Miami to develop People Mover systems if they could do so with existing grant commitments. Of the seven cities with UMTA approval for their People Mover proposals, only Detroit and Miami persevered to build and operate systems.[4]
The Ford Motor Company was involved in one of the designs of the People Mover and had hired AlScott Service Company to design and build a room size working model of the system. This model was used for Ford's proposals in their attempt to build the system.[5]
The People Mover was intended to be the downtown distributor for a proposed city and metro-wide light rail transit system for Detroit in the early 1980s; however, funding was scaled back.[6] President Gerald Ford had promised 600 million in federal funds. Plans included a subway line along Woodward Avenue that would turn into a street level train at McNichols and eventually go all the way to Pontiac, with additional rail lines running along Gratiot and a commuter line between Detroit and Port Huron. Inability of local leaders to come to an agreement led to the 600 million commitment being withdrawn by the Reagan Administration. Yet the People Mover still moved forward.[7] At the time of planning, the system was projected to have a ridership of 67,700 daily.[8]
The People Mover is owned and operated by the Detroit Transportation Corporation (DTC). The DTC was incorporated in 1985 as a Michigan Public Body Corporate for the purpose of acquiring, owning, constructing, furnishing, equipping, completing, operating, improving, enlarging, and/or disposing of the Central Automated Transit Systems (CATS) in Detroit, Michigan. DTC acquired the CATS project from the Suburban Mobile Authority for Regional Transportation (SMART) formerly known as the Southeastern Michigan Transportation Authority (SEMTA), on October 4, 1985. The DTC was created by the City of Detroit, Michigan pursuant to Act 7 of Public Acts of 1967 and is a component unit of the City of Detroit and accounts its activity as per proprietary funds.[9]
The CATS project, aka the Downtown People Mover (DPM), officially opened to the public on July 31, 1987. Prior to November 18, 1988, the People Mover System was operated and maintained by the primary contractor, Urban Transportation Development Corporation (UTDC) on a month-to-month basis. On November 18, 1988, the DTC assumed the responsibility to operate and maintain the People Mover System.
The system opened in 1987 using the same technology as Vancouver's SkyTrain and Toronto's Scarborough RT line. In the first year, an average of 11,000 riders used the People Mover each day; the one-day record was 54,648.[10]
When the People Mover opened, it ran counter-clockwise. On July 20, 2008, the system was shut down temporarily to replace track on six of the curves along the route. When it reopened in August, the system was run clockwise, as it is still run today, although it can run in either direction when necessary. The change in direction reduced the time required to complete one round-trip. The clockwise direction has one short, relatively steep uphill climb and then coasts downhill for a majority of the ride, allowing the train to use gravity to accelerate. This makes each round-trip slightly faster than running uphill most of the way in the counter-clockwise direction.[11]
On January 22, 2015 at approximately 10:10 PM, one of the cars jumped a rail hitting the rail platform. This prompted the system to be temporarily shut down to allow an investigation to take place. After 17 hours of investigation, the system resumed service. According to a media release given by the inspectors, "A bracket beneath one of the People Mover cars dislodged, catching under the rear car of the train approaching Times Square Station. This caused the rear car to come out of alignment and leave the rail. As a result, the second car scraped the platform, dislodging the door as the train pulled into the station."[12]
Cost-effectiveness and use
.jpg)
The Mover costs $12 million annually in city and state subsidies to run.[13] The cost-effectiveness of the Mover has drawn criticism.[14] In every year between 1997 and 2006, the cost per passenger mile exceeded $3, and was $4.26 in 2009,[15] compared with Detroit bus routes that operate at $0.82[15] (the New York City Subway operates at $0.30 per passenger mile). The Mackinac Center for Public Policy also charges that the system does not benefit locals, pointing out that fewer than 30% of the riders are Detroit residents and that Saturday ridership (likely out-of-towners) dwarfs that of weekday usage.[13] The system was designed to move up to 15 million riders a year. In 2008 it served approximately 2 million riders. This meant the system averaged about 7,500 people per day, about 2.5 percent of its daily peak capacity of 288,000.[16][17] In 2006, the Mover filled less than 10 percent of its seats.[13]
As of 2016, passengers pay $0.75 per trip, with discounts for seniors and multiple rides.[18]
Among the busiest periods was the five days around the 2006 Super Bowl XL, when 215,910 patrons used the service.[19] In addition to major downtown concerts and sporting events, other high ridership times include the week of the annual North American International Auto Show in January and the Youmacon anime convention at the end of October, ever since the convention expanded in 2012 to utilize Cobo Center in addition to the Renaissance Center. The system had 92,384 riders during the 2014 extended con weekend.[20]
As the downtown area has changed, this has impacted service and access to certain stations although the overall route and placement of the stations remains the same. When the J. L. Hudson Department Store building was imploded in October 1998, the nearby part of the track was damaged and forced the system to shut down. Before the track was completely repaired about a year later, limited service went into effect. In 2000, the David Whitney Building closed, cutting off access to the Grand Circus Park Station. The station later reopened without handicapped access as that was inside the David Whitney Building, which eventually reopened in late 2014. During construction of Compuware World Headquarters and parking garage, the Cadillac Center stop was closed as part of the parking structure was built around it. The station remained largely untouched and unmodified although the entrance was slightly expanded to allow a direct walkway to the nearby parking garage staircase and elevator tower.
In 2002, the concrete berms in front of the Renaissance Center were removed to make it more inviting to the rest of downtown. This also required the demolition of the station and tile artwork by George Woodman. Limited service continued but once again, ridership dropped significantly (see graph below) until the station and section of track were rebuilt to restore full circular operations in 2004. To replace the old artwork, Woodman designed a new tile art piece called Path Games.
As part of the restoration of the David Whitney Building, the Grand Circus Park station was closed on August 16, 2014 to complete a facelift which was originally planned to open in January 2015. The improved station will now feature ADA accessibility independently of the David Whitney Building. The project is overseen by Dumas Concepts in Building. The Grand Circus Park station officially reopened on June 13, 2015.[21] Because of the closure, the 2014 ridership level of that station dropped to 72,774 (12 out of the 13 stations). For comparison, the 2013 ridership level at Grand Circus was 136,255.[22]
Expansion
There have been proposals to extend the People Mover northward to the New Center and neighborhoods not within walking distance of the city's downtown. A proposal was put forward by Marsden Burger, former manager of the People Mover, to double the length of the route by extending the People Mover along Woodward Avenue to West Grand Boulevard and into the New Center area.[23] New stops would have included the Amtrak station, Wayne State University and the cultural center, the Detroit Medical Center, and the Henry Ford Hospital. The plan was proposed at a tentative cost of $150–200 million, and would have been paid for by a combination of public and private financing.[24] It was ultimately decided that the system would instead be connected to New Center by a streetcar line following much of the proposed route.
Operations and maintenance
The People Mover is owned and operated by the Detroit Transportation Corporation, an agency of the Detroit city government.
The People Mover system's operations center is located at the Times Square Station. Housed in the same complex is the system's maintenance facility and storage of the cars in an indoor facility.[25] Cars enter south turnout to enter the maintenance facility and exit from the north turn out back onto the main track. Maintenance equipment (work cars, etc...) are lifted up to track level by crane, but not stored with the DPM cars.
Work cars
Work cars are not maintained or owned by DPM, but by contractors:[26]
- three car Loram rail grinding set (8 stone L-Series Specialty Rail Grinders)
Ridership
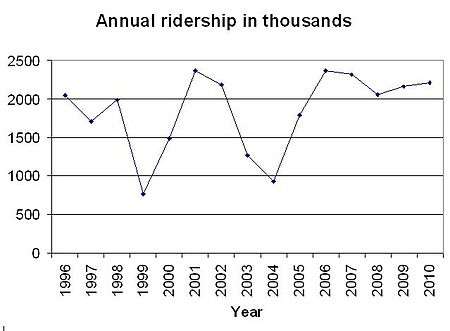
| Year | Calendar Year Ridership (Jan. 1- Dec. 31) | Fiscal Year Ridership (July 1- June 30) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2,369,915 | 2,104,832 | DTC[27] |
| 2002 | 1,837,807 | 2,186,526 | DTC[27] |
| 2003 | 1,017,243 | 1,267,927 | DTC[27] |
| 2004 | 953,753 | 922,644 | DTC[27] |
| 2005 | 1,792,924 | 1,339,646 | DTC[27] |
| 2006 | 2,368,361 | 2,307,909 | DTC[27] |
| 2007 | 2,320,433 | 2,307,774 | DTC[27] |
| 2008 | 2,059,714 | 2,315,395 | DTC[27] |
| 2009 | 2,161,436 | 1,941,501 | DTC[27] |
| 2010 | 2,216,800 | 2,181,440 | DTC[27] |
| 2011 | 2,285,358 | 2,408,131 | DTC[27] |
| 2012 | 2,085,487 | 2,046,444 | DTC[27] |
| 2013 | 2,207,333 | 2,118,301 | DTC[27] |
| 2014 | 2,357,520 | 2,140,066 | DTC[27] |
| 2015 | 2,413,414 | 2,442,031 | DTC[27] |
Stations
| Detroit People Mover | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The DPM stops at 13 stations, eight of which were built into existing buildings. As the system is single tracked, the stations only have a single platform setup. Originally, the 13 stations were planned not to have any distinctive features. However, in 1984 after construction had recently begun, Irene Walt assembled a volunteer committee to persuade the project agency to include artwork in each station. Called the Downtown Detroit People Mover Art Commission (later known as Art in the Stations), they raised $2 million to finance the project. As a result, there are 18 new original pieces of art spread throughout the stations, plus a piece from 1903 that had previously been in storage, on permanent loan from the Detroit Institute of Arts. The commissions efforts and art installation were documented in a 30-minute film by Sue Marx and Pamela Conn, who had recently won an Academy Award for the short documentary Young at Heart. Art in the Stations premiered at the Detroit Institute of Arts in 1989. In 2004, the book Art in the Stations was published, with photographs by Balthazar Korab, containing information on all the station artwork and the artists who created them.
| Station | Location |
|---|---|
| Broadway Station | Broadway and John R. Street (downtown YMCA) |
| Grand Circus Park Station | Park Street & Woodward Avenue (David Whitney Building) |
| Times Square Station | Grand River Avenue & Times Square |
| Michigan Avenue Station | Michigan Avenue & Cass Avenue |
| Fort/Cass Station | Fort Street & Cass Avenue |
| Cobo Center Station | Cass Street & Congress Street (inside Cobo Hall) |
| Joe Louis Arena Station | 3rd Street & Jefferson Avenue (Joe Louis Arena) |
| Financial District Station | Larned Street & Shelby Street (150 West Jefferson) |
| Millender Center Station | Randolph & Jefferson Avenue (inside Milender Center) |
| Renaissance Center Station | Renaissance Center |
| Bricktown Station | Beaubien Street & East Fort Street |
| Greektown Station | Beaubien Street between Monroe & East Lafayette Street (Greektown Historic District) |
| Cadillac Center Station | Gratiot Avenue & Library Street |
Public art
Each station displays artwork created by various artists. Art was completed with the system opening in 1987 unless otherwise noted:
- Times Square
- In Honor of W. Hawkins Ferry (Artist: Tom Phardel / Pewabic Pottery - glazed tile)
- Untitled (1993) (Artist: Anat Shiftan / Pewabic Pottery - tile mural)
- Michigan Ave
- Voyage (Artist: Allie McGhee - tile mural)
- On the Move (Artist: Kirk Newman - cast bronze shape on tile)
- Fort/Cass
- Untitled (Artist: Farley Tobin - tile mural)
- Progression II (1993) (Artist: Sandra jo Osip - bronze sculpture)
- Cobo Center
- Calvacade of Cars (1988) (Artist: Larry Ebel/Linda Cianciolo Scarlett - mural)
- Joe Louis Arena
- Voyage (Artist: Gerome Kamrowski - venetian glass mosaic)
- Financial District
- 'D' for Detroit (Artist: Joyce Kozloff - hand painted ceramic mural)
- Millender Center
- Detroit New Morning (Artist: Alvin D. Loving Jr. - painted glazed tiles
- Renaissance Center
- Siberian Ram (1993) (Artist: Marshall Fredericks - cast bronze sculpture)
- Path Games (2004) (Artist: George Woodman - ceramic tile mural)
- Dreamers and Voyagers Come to Detroit (1987-2002) (Artist: George Woodman - ceramic tile mural, destroyed with station demolition)
- Bricktown
- Beaubien Passage (Artist: Glen Michaels - bas relief on porcelain panels)
- Greektown
- Neon for the Greektown Station (Artist: Stephen Antonakos - free form neon light display)
- Cadillac Center
- In Honour of Mary Chase Stratton (Artist: Diana Kulisek Pancioli/Pewabic Pottery - tile mural interspersed with bronze plaque by Carlo Romanelli 1903)
- Broadway
- The Blue Nile (Artist: Charles McGee - painted mural panels)
- Untitled (Artist: Jun Kaneko - tile)
- Grand Circus Park
- Catching Up (Artist: J. Seward Johnson Jr - bronze statue)
Rolling stock
- Manufacturer: Urban Transportation Development Corporation (now Bombardier Transportation)
- Type: ICTS Mark I
- Number of cars: 12
- Maximum speed: 56 mph[2]
The system operates in two-car pairs.
See also
- Art on the Move
- List of rapid transit systems
- List of United States rapid transit systems by ridership
- Metromover
- Transportation in metropolitan Detroit
References
- ↑ Detroit Transportation Corporation (2015). "System Map" (Map). Station to Station Guide (PDF). Scale not given. Detroit Transportation Corporation. pp. 12–13. Retrieved June 9, 2015.
- 1 2 "The Detroit People Mover - Overview". Thepeoplemover.com. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ↑ Ann Arbor - Detroit Regional Rail Project SEMCOG. Retrieved on February 4, 2010.
- ↑ "The Downtown People Mover Program". Faculty.washington.edu. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ↑ AlScott Service company, Detroit Michigan
- ↑ Phillipp Oswalt. "Shrinking Cities," (PDF). p. 93. Retrieved 2009-09-07.
- ↑ Ryan Felton. "How Detroit ended up with the worst public transit". Retrieved 2014-12-14.
- ↑ Wendell Cox. "Analysis of the Proposed Las Vegas LLC Monorail" (PDF). p. 14. Retrieved 2007-09-20.
- ↑ "Summary of Significant Account Policies" (PDF). p. 12.
- ↑ "Detroit downtown peoplemover, advanced automated urban transit". Faculty.washington.edu. 2008-06-29. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ↑ "Detroit People Mover Reopens and Makes Changes". Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ↑ "People Mover Resumes Service". 2015-01-24. Retrieved 2015-01-25.
- 1 2 3 People Mover grows up
- ↑ Braun, Ken (2007-12-11). "The Detroit People Mover Still Serves as "a Rich Folks' Roller Coaster" [Michigan Capitol Confidential]". Mackinac.org. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- 1 2 "Pricey pensions for Detroit's roller-coaster for rich people". Speroforum.com. 2011-02-27. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ↑
- ↑ Luczak, Marybeth (1998). "Is there people-mover in your future?". Railway AgeIn fiscal year 1999-2000 the city was spending $3 for every $0.50 rider fare, according to The Detroit News'.
- ↑ "Detroit People Mover Proposed Fare Structure" (PDF). Detroit Transportation Corporation. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
- ↑ Detroit Transportation Corporation
- ↑ Alexander, Ericka (2015-10-13). "DPM is the Place to Be for Youmacon 2015 - Find out why!"". DTC Marketing. Retrieved 2015-10-22.
- ↑ "People Mover's Grand Circus Park Station Reopens". CBS Detroit. 2015-06-13. Retrieved 2015-08-27.
- ↑ Lawrence, Eric D (2015-06-24). "People Mover's Grand Circus Station back in service". Detroit Free Press. Retrieved 2015-08-27.
- ↑ "DetroitPeopleMover2". Drcurryassociates.net. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ↑ Detroit News
- ↑ "Times Square(Detroit People Mover)". The SubwayNut. 2011-10-28. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ↑ http://www.thepeoplemover.com/resource/attach/28/DTCrailgrindingtechSpecMar102of3.doc
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 "About Ridership".
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Detroit People Mover. |
