Financial economics
| Economics |
|---|
_Per_Capita_in_2015.svg.png) |
|
|
| By application |
|
| Lists |
|
Financial economics is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on both sides of a trade".[1] Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as prices, interest rates and shares, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus: asset pricing (or "investment theory") and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of capital and the second of users of capital.
The subject is concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment".[2] It therefore centers on decision making under uncertainty in the context of the financial markets, and the resultant economic and financial models and principles, and is concerned with deriving testable or policy implications from acceptable assumptions. It is built on the foundations of microeconomics and decision theory.
Financial econometrics is the branch of financial economics that uses econometric techniques to parameterise these relationships. Mathematical finance is related in that it will derive and extend the mathematical or numerical models suggested by financial economics. Note though that the emphasis there is mathematical consistency, as opposed to compatibility with economic theory.
Financial economics is usually taught at the postgraduate level; see Master of Financial Economics. Recently, specialist undergraduate degrees are offered in the discipline.[3]
Note that this article provides an overview and survey of the field: for derivations and more technical discussion, see the specific articles linked.
Underlying economics
| JEL classification codes |
| In the Journal of Economic Literature classification codes, Financial Economics is one of the 19 primary classifications, at JEL: G. It follows Monetary and International Economics and precedes Public Economics. Detailed subclassifications are linked in the following footnote.[4]
The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics (2008, 2nd ed.) also uses the JEL codes to classify its entries in v. 8, Subject Index, including Financial Economics at pp. 863–64. The corresponding footnotes below have links to entry abstracts of The New Palgrave Online for each primary or secondary JEL category (10 or fewer per page, similar to Google searches):
|
As above, the discipline essentially explores how rational investors would apply decision theory to the problem of investment. The subject is thus built on the foundations of microeconomics and decision theory, and derives several key results for the application of decision making under uncertainty to the financial markets.
Present value, expectation and utility
Underlying all of financial economics are the concepts of present value and expectation.[11] Calculating their present value allows the decision-maker to aggregate the cashflows (or other returns) to be produced by an asset in the future, to a single value at the date in question, and so to compare two opportunities; this concept is the starting point for financial decision-making. Financial economics can be said to date from a book on compound interest by Richard Witt ("Arithmetical Questions" (1613)), and these ideas were further developed by Johan de Witt and Edmond Halley.
An immediate extension is to combine probabilities with present value, leading to the expected value criterion which sets asset value as a function of the sizes of the expected payouts and the probabilities of their occurrence. These ideas originate with Blaise Pascal and Pierre de Fermat.
So far this does not consider risk aversion: since individuals receive greater utility from each extra dollar when they are poor than when comparatively rich. To allow for this, one can adjust the weights assigned to each of the possible outcomes ("states") accordingly in order to maximise the expected utility. (Some investors may in fact be risk seeking as opposed to risk averse, but the same logic would apply.) More formally, the expected utility hypothesis states that, if certain axioms are satisfied, the subjective value associated with a gamble by an individual is that individual's statistical expectation of the valuations of the outcomes of that gamble. The impetus for these ideas arose from various inconsistencies observed under the expected value framework, such as the St. Petersburg paradox (see also Ellsberg paradox). The development here originally due to Daniel Bernoulli, and later formalized by John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern.
Arbitrage-free pricing and equilibrium
The concepts of arbitrage-free "rational" pricing and equilibrium are then coupled with the above to derive "classical" financial economics. Rational pricing is the assumption that asset prices (and hence asset pricing models) will reflect the arbitrage-free price of the asset, as any deviation from this price will be "arbitraged away". This assumption is useful in pricing fixed income securities, particularly bonds, and is fundamental to the pricing of derivative instruments.
Economic equilibrium is, in general, a state in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences these equilibrium values of economic variables will not change. General equilibrium deals with the behavior of supply, demand, and prices in a whole economy with several or many interacting markets, by seeking to prove that a set of prices exists that will result in an overall equilibrium. (This is in contrast to partial equilibrium, which only analyzes single markets.)
The two concepts are linked as follows: where market prices do not allow for profitable arbitrage, i.e. they comprise an arbitrage-free market, then these prices are also said to constitute an "arbitrage equilibrium". Intuitively, this may be seen by considering that where an arbitrage opportunity does exist, then prices can be expected to change, and are therefore not in equilibrium.[12] An arbitrage equilibrium is thus a precondition for a general economic equilibrium.
The immediate, and formal, extension of this idea, the Fundamental theorem of asset pricing, shows that where markets are as above - and are additionally (implicitly and correspondingly) complete - we may then make financial decisions by constructing a risk neutral probability measure corresponding to the market. "Complete" here means that there is a price for every asset in every possible state of the world, and that the complete set of possible bets on future states-of-the-world can therefore be constructed with existing assets (assuming no friction), essentially solving simultaneously for n probabilities corresponding to n prices. The formal derivation will proceed by arbitrage arguments.[11][12] For a worked example see Rational pricing#Risk neutral valuation, where, in a simplified environment, the market has only two possible states - up and down - and where p and (1-p) are the two corresponding (i.e. implied) probabilities, and in turn, the derived distribution (or "measure").
With this measure in place, the expected, i.e. required, return of any security (or portfolio) will then equal the riskless return, plus an "adjustment for risk",[11] i.e. a security-specific risk premium, compensating for the extent to which the cashflows are unpredictable. All pricing models are then essentially variants of this, given specific assumptions and/or conditions.[11][13] This approach is consistent with the above, but with the expectation based on "the market" (i.e. arbitrage-free, and, per the theorem, therefore in equilibrium) as opposed to individual preferences.
Thus, continuing the example, to value a specific security, its forecasted cashflows in the up- and down-states are multiplied through by p and (1-p) respectively, and are then discounted at the risk-free interest rate plus an appropriate premium. In general, this premium may be derived by the CAPM (or extensions) as will be seen under #Uncertainty. In corporate finance and accounting contexts, it is the most likely (i.e. "average") cashflows which are forecasted overall, as opposed to those state by state, see John Burr Williams' proposal below; the discounting methodology is unchanged.
State prices
With the above relationship established, the further specialized Arrow–Debreu model may be derived. This important result suggests that, under certain economic conditions, there must be a set of prices such that aggregate supplies will equal aggregate demands for every commodity in the economy. The analysis here is often undertaken assuming a Representative agent.
The Arrow–Debreu model applies to economies with maximally complete markets, in which there exists a market for every time period and forward prices for every commodity at all time periods. A direct extension, then, is the concept of a state price security (also called an Arrow-Debreu security), a contract that agrees to pay one unit of a numeraire (a currency or a commodity) if a particular state occurs ("up" and "down" in the simplified example above) at a particular time in the future and pays zero numeraire in all the other states. The price of this security is the state price of this particular state of the world. In the above example, the state prices would equate to the present values of $p and $(1-p): i.e. what one would pay today, respectively, for the up- and down-state securities. The state price vector is the vector of state prices for all states.
State prices find immediate application in Financial Economics, as will be seen below: for example, any derivatives contract whose settlement value is a function of an underlying whose value is uncertain at contract date can be decomposed as a linear combination of its Arrow-Debreu securities, and thus as a weighted sum of its state prices. In the above example, the price of a derivative today would be [up-state-price * up-state-payoff + down-state-price * down-state-payoff]; see below regrading the absence of any risk premium here. For a continuous random variable indicating a continuum of possible states, the value is found by integrating over the state price density; see Stochastic discount factor. These concepts are extended to Martingale pricing and the related Risk-neutral measure.
Resultant models
| The capital asset pricing model (CAPM)
|

| The Black–Scholes equation
|
| The Black–Scholes formula for the value of a call option:
|
Applying the preceding economic concepts, we may then derive various economic- and financial models and principles. As above, the two usual areas of focus are Asset Pricing and Corporate Finance, the first being the perspective of providers of capital, the second of users of capital. Here, and for (almost) all other financial economics models, the questions addressed are typically framed in terms of "time, uncertainty, options, and information",[1] as will be seen below.
- Time: money now is traded for money in the future.
- Uncertainty (or risk): The amount of money to be transferred in the future is uncertain.
- Options: one party to the transaction can make a decision at a later time that will affect subsequent transfers of money.
- Information: knowledge of the future can reduce, or possibly eliminate, the uncertainty associated with future monetary value (FMV).
Applying this framework, with the above concepts, leads to the required models. This derivation begins with the assumption of "no uncertainty" and is then expanded to incorporate the other considerations. (This division sometimes denoted "deterministic" and "random",[14] or "stochastic".)
Certainty
A starting point here is “Investment under certainty". The Fisher separation theorem, asserts that the objective of a corporation will be the maximization of its present value, regardless of the preferences of its shareholders. Related is the Modigliani-Miller theorem, which shows that, under certain conditions, the value of a firm is unaffected by how that firm is financed, and depends neither on its dividend policy nor its decision to raise capital by issuing stock or selling debt. The proof here proceeds using arbitrage arguments, and acts as a benchmark for evaluating the effects of factors outside the model that do affect value.
The mechanism for determining (corporate) value is provided by The Theory of Investment Value (John Burr Williams), which proposes that the value of an asset should be calculated using “evaluation by the rule of present worth”. Thus, for a common stock, the intrinsic, long-term worth is the present value of its future net cashflows, in the form of dividends. What remains to be determined is the appropriate discount rate. Later developments show that, "rationally", i.e. in the formal sense, the appropriate discount rate here will (should) depend on the asset's riskiness relative to the overall market, as opposed to its owners' preferences; see below. (Net present value (NPV), a direct extension of these ideas, was first formally applied to Corporate Finance decisioning by Joel Dean in 1951).
Bond valuation, in that cashflows (coupons and return of principal) are deterministic, may proceed in the same fashion.[14] An immediate extension, Arbitrage-free bond pricing, discounts each cashflow at the market derived rate — i.e. at each coupon's corresponding zero-rate — as opposed to an overall rate. Note that in many treatments bond valuation precedes equity valuation, where cashflows (dividends) are not "known" per se: Williams and onward allow for forecasting assumptions - based on historic ratios or published policy - as to these, and cashflows are then treated as deterministic. (See comments under Financial modeling#Accounting, as well as Corporate finance#Quantifying uncertainty.)
These "certainty" results are all commonly employed under corporate finance; uncertainty is the focus of "asset pricing models", as follows.
Uncertainty
For "choice under uncertainty", the twin assumptions of rationality and market efficiency lead to modern portfolio theory (MPT) with its Capital asset pricing model (CAPM) — an equilibrium-based result — and to the Black–Scholes–Merton theory (BSM; often, simply Black-Scholes) for option pricing — an arbitrage-free result.
Briefly, and intuitively - and consistent with #Arbitrage-free pricing and equilibrium above - the linkage is as follows.[15] Given the ability to profit from private information, self-interested traders are motivated to acquire and act on their private information. In doing so, traders contribute to more and more efficient market prices: the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH). The EMH (implicitly) assumes that average expectations constitute an "optimal forecast", i.e. prices using all available information, are identical to the best guess of the future: the assumption of rational expectations. (Note that the EMH does allow that when faced with new information, some investors may overreact and some may underreact, but what is required, however, is that investors' reactions follow a normal distribution - so that the net effect on market prices cannot be reliably exploited to make an abnormal profit.) In the competitive limit, market prices will reflect all available information and prices can only move in response to news:[16] the random walk hypothesis. Thus, if prices of financial assets are (broadly) correct, i.e. efficient, then deviations from these (equilibrium) values could not last for long.
Under these conditions investors can then be assumed to act rationally: their investment decision must be calculated or a loss is sure to follow. Also, where an arbitrage opportunity presents itself, then investors will exploit it, reinforcing this equilibrium. Here, as under the certainty-case above, the specific assumption as to pricing is that prices are calculated as the present value of expected future dividends,[13][16] as based on currently available information. What is required though is a theory for determining the appropriate discount rate given this uncertainty: this is provided by the MPT and its CAPM. Relatedly, rationality — in the sense of arbitrage-exploitation — gives rise to Black-Scholes; option values here ultimately consistent with the CAPM.
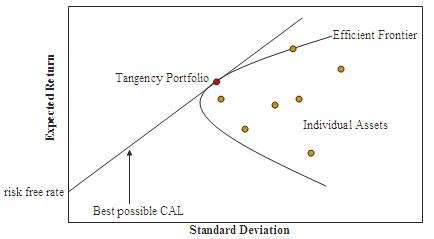
In general, then, while portfolio theory studies how investors should balance risk and return when investing in many assets or securities, the CAPM is more focused, describing how, in equilibrium, markets set the prices of assets in relation to how risky they are. The theory demonstrates that if one can construct an efficient frontier — i.e. each combination of assets offering the best possible expected level of return for its level of risk, see diagram — then mean-variance efficient portfolios can be formed simply as a combination of holdings of the risk-free asset and the "market portfolio" (the Mutual fund separation theorem), with the combinations here plotting as the capital market line, or CML. Then given this CML, the theory shows that the required return on risky securities will be independent of the investor's utility function, and solely determined by their covariance with aggregate, i.e. market, risk (“beta”). As seen in the formula aside, this result is consistent with the preceding, equaling the riskless return plus an adjustment for risk.[13] Note an important implication here: under the assumptions of MPT, an asset may be priced without reference to the investor's level of risk aversion, thus providing a readily determined discount rate for corporate finance decision makers as above.[17] (The efficient frontier was introduced by Harry Markowitz. The CAPM was derived by Jack Treynor (1961, 1962), William F. Sharpe (1964), John Lintner (1965) and Jan Mossin (1966) independently.)
Black-Scholes provides a mathematical model of a financial market containing derivative instruments, and the resultant formula for the price of European-styled options. The model is expressed as the Black–Scholes equation, a partial differential equation describing the changing price of the option over time; it is derived assuming log-normal, geometric Brownian motion. The key financial insight behind the model is that one can perfectly hedge the option by buying and selling the underlying asset in just the right way and consequently "eliminate risk", absenting the risk adjustment from the pricing (, the value, or price, of the option, grows at , the risk-free rate; see Black–Scholes equation#Financial interpretation).[11][13] This hedge, in turn, implies that there is only one right price — in an arbitrage-free sense — for the option. And this price is returned by the Black–Scholes option pricing formula. (The formula, and hence the price, is consistent with the equation, since the formula is the solution to the equation.) Since the formula is without reference to the share's expected return, Black-Scholes entails (assumes) risk neutrality, consistent with the "elimination of risk" here. Relatedly, therefore, the pricing formula may also be derived directly via risk neutral expectation; see Brownian model of financial markets. (BSM is consistent with "previous versions of the formula" of Louis Bachelier and Edward O. Thorp.[18])
As mentioned, it can be shown that the two models are consistent; then, as is to be expected, "classical" financial economics is thus unified. Here, the Black Scholes equation may alternatively be derived from the CAPM, and the price obtained from the Black-Scholes model is thus consistent with the expected return from the CAPM.[19] The Black-Scholes theory, although built on Arbitrage-free pricing, is therefore consistent with the equilibrium based capital asset pricing. Both models, in turn, are ultimately consistent with the Arrow-Debreu theory, and may be derived via state-pricing,[11] further explaining, and if required demonstrating, this unity.
Extensions
More recent work further generalizes and / or extends these models.
Portfolio theory
- See also: Post-modern portfolio theory; Mathematical finance#Risk and portfolio management: the P world.
The majority of developments here relate to required return, extending the basic CAPM. Multi-factor models such as the Fama–French three-factor model and the Carhart four-factor model, propose factors other than market return as relevant in pricing. The Intertemporal CAPM and Consumption-based CAPM similarly extend the model. With intertemporal portfolio choice, the investor now repeatedly optimizes her portfolio; while the inclusion of consumption (in the economic sense) then incorporates all sources of wealth, and not just market-based investments, into the investor's calculation of required return.
Whereas the above extend the CAPM, the single-index model is a more simple model. It assumes, only, a correlation between security and market returns, without (numerous) other economic assumptions. It is useful in that it simplifies the estimation of correlation between securities, significantly reducing the inputs for building the correlation matrix required for portfolio optimization. The arbitrage pricing theory (APT) similarly differs as regards its assumptions. Instead of assuming equilibrium, it returns the required (expected) return of a financial asset as a linear function of various macro-economic factors, and assumes that arbitrage should bring incorrectly priced assets back into line.
As regards Portfolio optimization, the Black–Litterman model departs from the original Markowitz approach of constructing portfolios via an efficient frontier. Black–Litterman instead starts with an equilibrium assumption, and is then modified to take into account the 'views' (i.e., the specific opinions about asset returns) of the investor in question to arrive at a bespoke asset allocation. The universal portfolio algorithm (Thomas M. Cover) applies machine learning to asset selection, learning adaptively from historical data. See also Portfolio optimization#Improving portfolio optimization for other techniques and / or objectives.
Derivative pricing
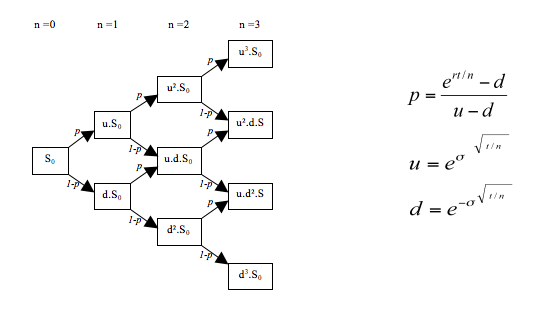
As regards derivative pricing, the binomial options pricing model provides a discretized version of Black-Scholes, useful for the valuation of American styled options; discretized models of this type are built using state-prices (as above), while exotic derivatives although modeled in continuous time via Monte Carlo methods for option pricing are also priced using risk neutral expected value. Various other numeric techniques have also been developed. The theoretical framework too has been extended such that martingale pricing is now the standard approach. Since the work of Breeden and Litzenberger in 1978,[20] a large number of researchers have used options to extract Arrow–Debreu prices for a variety of applications in financial economics. Developments relating to complexities in return and / or volatility are discussed below.
Drawing on these techniques, derivative models for various other underlyings and applications have also been developed, all based on the same logic. Real options valuation allows that option holders can influence the option's underlying; models for employee stock option valuation explicitly assume non-rationality on the part of option holders; Credit derivatives allow that payment obligations / delivery requirements might not be honored. Exotic derivatives are now routinely valued.
Similarly, beginning with Oldrich Vasicek, various short rate models, as well as the HJM and BGM forward rate-based techniques, allow for an extension of these to fixed income- and interest rate derivatives. (The Vasicek and CIR models are equilibrium-based, while Ho–Lee and subsequent models are based on arbitrage-free pricing.) Bond valuation is relatedly extended: the Stochastic calculus approach, employing these methods, allows for rates that are "random" (while returning a price that is arbitrage free, as above); Lattice models for Hybrid Securities allow for non-deterministic cashflows (and stochastic rates).
As above, (OTC) derivative pricing has relied on the BSM risk neutral pricing framework, under the assumptions of funding at the risk free rate and the ability to perfectly replicate derivatives so as to fully hedge. Post the financial crisis of 2008 issues such as counterparty credit risk, funding costs and costs of capital are considered in the valuation.[21] The purpose of these inclusions is twofold: primarily to hedge for possible losses due to counterparty default; but also, to determine (and hedge) the amount of capital required under Basel III. There are two (emergent) techniques. When the deal is collateralized then the “fair-value” is computed as before, but using the Overnight Index Swap (OIS) curve for discounting. (The OIS is chosen here as it reflects the rate for overnight unsecured lending between banks, and is thus considered a good indicator of the interbank credit markets.) When the deal is not collateralized then a CVA (Credit Valuation Adjustment) is added to this value.[22] The CVA reflects the market value of counterparty credit risk, while other Valuation Adjustments for Debit, Funding, regulatory Capital and Margin (DVA, FVA, KVA and MVA) may also be added. These are collectively referred to as xVA.
Swap pricing is relatedly and further modified. Previously, swaps were valued off a single interest rate curve such that the two legs (fixed and floating for interest rate swaps) had the same value at initiation; see further under Rational pricing. Post crisis, to accommodate credit risk, valuation is now under a two-curve framework, where one curve (OIS) is used for discounting, and a curve that matches the maturity of the underlying floating rate is used for the projection of forward rates. Further, since the basis spread between LIBOR rates of different maturities widened during the crisis, forecast curves are often constructed for each LIBOR tenor used in floating rate derivative legs, with the various curves best fitted to observed swap prices. This approach is then referred to as a “multi-curve” framework.[23] Currency basis will require additional curves.
Corporate finance theory
Corporate finance theory has also been extended: mirroring the above developments, asset-valuation and decisioning no longer need assume "certainty". As discussed above, Monte Carlo methods in finance, introduced by David B. Hertz in 1964, allow financial analysts to construct "stochastic" or probabilistic corporate finance models, as opposed to the traditional static and deterministic models; see Corporate finance#Quantifying uncertainty. Relatedly, Real Options theory, as discussed, allows for owner - i.e. managerial - actions that impact underlying value; by incorporating option pricing logic, these actions are then applied to a distribution of future outcomes, changing with time, which then determine the "project's" valuation today.
Other extensions here include [24] agency theory, which analyses the difficulties in motivating corporate management (the "agent") to act in the best interests of shareholders (the "principal"), rather than in their own interests. Clean surplus accounting and the related residual income valuation provide a model that returns price as a function of earnings, expected returns, and change in book value, as opposed to dividends. This approach, to some extent, arises due to the implicit contradiction of seeing value as a function of dividends, while also holding that dividend policy cannot influence value per Modigliani and Miller’s “Irrelevance principle”; see Dividend policy#Irrelevance of dividend policy.
Challenges and criticism
- See also: Financial mathematics#Criticism; Financial engineering#Criticisms; Financial Modelers' Manifesto; Unreasonable ineffectiveness of mathematics#Economics and finance; Physics envy; as well as.[25]
As above, there is a very close link between the random walk hypothesis, with the associated expectation that price changes should follow a normal distribution, on the one hand, and market efficiency and rational expectations, on the other. Note, however, that (wide) departures from these are commonly observed, and there are thus, respectively, two main sets of challenges presented here.
Departures from normality
- See also: Capital asset pricing model#Problems of CAPM; Modern portfolio theory#Criticisms; Black–Scholes model#Criticism.
The first set of challenges: As discussed, the assumptions that market prices follow a random walk and / or that asset returns are normally distributed are fundamental. Empirical evidence, however, suggests that these assumptions may not hold (see Kurtosis risk, Skewness risk, Long tail) and that in practice, traders, analysts and particularly risk managers frequently modify the "standard models" (see Model risk). In fact, Benoît Mandelbrot had discovered already in the 1960s that changes in financial prices do not follow a Gaussian distribution, the basis for much option pricing theory, although this observation was slow to find its way into mainstream financial economics.
Financial models with long-tailed distributions and volatility clustering have been introduced to overcome problems with the realism of the above “classical” financial models; while jump diffusion models allow for (option) pricing incorporating "jumps" in the spot price. Risk managers, similarly, complement (or substitute) the standard value at risk models with historical simulations, mixture models, principal component analysis, extreme value theory, as well as models for volatility clustering.[26] For further discussion see Fat-tailed distribution#Applications in economics, and Value at risk#Criticism.
Closely related is the volatility smile, where implied volatility - the volatility corresponding to the BSM price - is observed to differ as a function of strike price (i.e. moneyness), true only if the price-change distribution is non-normal, unlike that assumed by BSM. The term structure of volatility describes how (implied) volatility differs for related options with different maturities. An implied volatility surface is then a three-dimensional surface plot of volatility smile and term structure. These empirical phenomena negate the assumption of constant volatility — and log-normality— upon which Black-Scholes is built;[18] see Black–Scholes model#The volatility smile.
Approaches developed here in response include local volatility and stochastic volatility (the Heston, SABR and CEV models, amongst others). Alternatively, implied-binomial and -trinomial trees instead of directly modelling volatility, return a lattice consistent with — in an arbitrage-free sense — (all) observed prices, facilitating the pricing of other, i.e. non-quoted, strike/maturity combinations. Edgeworth binomial trees allow for a specified (i.e. non-Gaussian) skew and kurtosis in the spot price. Priced here, options with differing strikes will return differing implied volatilities, and the tree can thus be calibrated to the smile if required.[27] Similarly purposed closed-form models include: Jarrow and Rudd (1982); Corrado and Su (1996); Backus, Foresi, and Wu (2004).[28]
As above, additional to log-normality in returns, BSM assumes the ability to perfectly replicate derivatives so as to fully hedge, and hence to discount at the risk-free rate. This, in turn, is built on the assumption of a credit-risk-free environment. The post crisis reality, however, differs, necessitating the various xVA adjustments to the derivative valuation, as described. Note that these adjustments are additional to any smile or surface effect. This is valid as the smile is built on price data relating to fully collateralized positions, and there is therefore no "double counting" of credit risk (etc.) when including xVA.
Departures from rationality
| Market anomalies and Economic puzzles |
- See also: Efficient-market hypothesis#Criticism and behavioral finance; Rational expectations#Criticisms.
The second set of challenges: As seen, a common assumption is that financial decision makers act rationally; see Homo economicus. Recently, however, researchers in experimental economics and experimental finance have challenged this assumption empirically. These assumptions are also challenged theoretically, by behavioral finance, a discipline primarily concerned with the limits to rationality of economic agents.
Consistent with, and complementary to these findings, various persistent market anomalies have been documented, these being price and/or return distortions - e.g. size premiums - which appear to contradict the efficient-market hypothesis; calendar effects are the best known group here. Related to these are various of the economic puzzles, concerning phenomena similarly contradicting the theory. The equity premium puzzle, as one example, arises in that the difference between the observed returns on stocks as compared to government bonds is consistently higher than the risk premium rational equity investors should demand, an "abnormal return". For further context see Random walk hypothesis#A non-random walk hypothesis, and sidebar for specific instances.
More generally, and particularly following the financial crisis of 2007–2010, financial economics and mathematical finance have been subjected to deeper criticism; notable here is Nassim Nicholas Taleb, who claims that the prices of financial assets cannot be characterized by the simple models currently in use, rendering much of current practice at best irrelevant, and, at worst, dangerously misleading; see Black swan theory, Taleb distribution. A topic of general interest studied in recent years has thus been financial crises,[29] and the failure of financial economics to model these.
Areas of research attempting to explain (or at least model) these phenomena, and crises, include noise trading, market microstructure, and Heterogeneous agent models. The latter is extended to agent-based computational economics, where price is treated as an emergent phenomenon, resulting from the interaction of the various market participants (agents). The noisy market hypothesis argues that prices can be influenced by speculators and momentum traders, as well as by insiders and institutions that often buy and sell stocks for reasons unrelated to fundamental value; see Noise (economic). The adaptive market hypothesis is an attempt to reconcile the efficient market hypothesis with behavioral economics, by applying the principles of evolution to financial interactions. An information cascade, alternatively, shows market participants engaging in the same acts as others ("herd behavior"), despite contradictions with their private information. See also Hyman Minsky's "financial instability hypothesis", as well as George Soros' approach, #Reflexivity, financial markets, and economic theory.
Note however, that on the obverse, various studies have shown that despite these departures from efficiency, asset prices do typically exhibit a random walk and that one cannot therefore consistently outperform market averages.[30] The practical implication, therefore, is that passive investing (e.g. via low-cost index funds) should, on average, serve better than any other active strategy.[31] Burton Malkiel's A Random Walk Down Wall Street - first published in 1973, and in its 12th edition as of 2015 - is a widely read popularization of these arguments. (See also John C. Bogle’s Common Sense on Mutual Funds; but compare Warren Buffett's The Superinvestors of Graham-and-Doddsville.) Note also that institutionally inherent limits to arbitrage — as opposed to factors directly contradictory to the theory — are sometimes proposed as an explanation for these departures from efficiency.
See also
- Category:Finance theories
- Category:Financial economists
- Deutsche Bank Prize in Financial Economics
- Financial modeling
- Fischer Black Prize
- List of unsolved problems in economics#Financial economics
- Outline of economics
- Outline of finance
References
- 1 2 William F. Sharpe, "Financial Economics". Stanford.edu. Retrieved 2009-08-06.
- ↑ "Robert C. Merton - Nobel Lecture" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-08-06.
- ↑ e.g.: Kent; City London; UC Riverside; Leicester; Toronto; UMBC
- ↑ JEL classification codes — Financial economics JEL: G Subcategories
- ↑ All entries under JEL: G: http://www.dictionaryofeconomics.com/search_results?,q=&field=content&edition=all&topicid=G
- ↑ The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics Online: Search results
- ↑ The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics Online: Search results
- ↑ The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics Online: Search results
- ↑ The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics Online: Search results
- ↑ In particular by clicking to Advanced searches from http://www.dictionaryofeconomics.com/, which brings up http://www.dictionaryofeconomics.com/advanced_search, drilling to the secondary category, then to the tertiary category, followed by clicking the Search button at the bottom. For example, from secondary code JEL: G0, http://www.dictionaryofeconomics.com/search_results?,q=&field=content&edition=all&topicid=G0, then to the JEL: G00, then pressing the Search button to bring up the entry links at http://www.dictionaryofeconomics.com/search_results?q=&field=content&edition=all&topicid=G00.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Rubinstein, Mark. (2005). “Great Moments in Financial Economics: IV. The Fundamental Theorem (Part I)”, Journal of Investment Management, Vol. 3, No. 4, Fourth Quarter 2005; ~ (2006). Part II, Vol. 4, No. 1, First Quarter 2006. See under "External links".
- 1 2 Freddy Delbaen and Walter Schachermayer. (2004). "What is... a Free Lunch?" (pdf). Notices of the AMS 51 (5): 526–528
- 1 2 3 4 Christopher L. Culp and John H. Cochrane. (2003). "Equilibrium Asset Pricing and Discount Factors: Overview and Implications for Derivatives Valuation and Risk Management," in Modern Risk Management : A History. Peter Field, ed. London: Risk Books, 2003. ISBN 1904339050
- 1 2 See Luenberger's Investment Science, under Bibliography.
- ↑ For a more formal treatment, see, for example: Eugene F. Fama. 1965. Random Walks in Stock Market Prices. Financial Analysts Journal, September/October 1965, Vol. 21, No. 5: 55-59.
- 1 2 Shiller, Robert J. (2003). "From Efficient Markets Theory to Behavioral Finance" (PDF). Journal of Economic Perspectives. 17 (1 (Winter 2003)): 83–104. doi:10.1257/089533003321164967.
- ↑ Jensen, Michael C. and Smith, Clifford W., "The Theory of Corporate Finance: A Historical Overview". In: The Modern Theory of Corporate Finance, New York: McGraw-Hill Inc., pp. 2-20, 1984.
- 1 2 Haug, E.G. and Taleb, N.N. (2008): Why We Have Never Used the Black-Scholes-Merton Option Pricing Formula, Wilmott Magazine 1/2008
- ↑ Don M. Chance. Option Prices and Expected Returns
- ↑ Breeden, Douglas T.; Litzenberger, Robert H. (1978). "Prices of State-Contingent Claims Implicit in Option Prices". Journal of Business. 51 (4): 621–651. doi:10.1086/296025. JSTOR 2352653.
- ↑ Post-Crisis Pricing of Swaps using xVAs, Christian Kjølhede & Anders Bech, Master thesis, Aarhus University
- ↑ Derivatives Pricing after the 2007-2008 Crisis: How the Crisis Changed the Pricing Approach, Didier Kouokap Youmbi, Bank of England – Prudential Regulation Authority
- ↑ Multi-Curve Valuation Approaches and their Application to Hedge Accounting according to IAS 39, Dr. Dirk Schubert, KPMG
- ↑ See Jensen and Smith under "External links", as well as Rubinstein under "Bibliography".
- ↑ "What We Do Not Know: 10 Unsolved Problems in Finance", by Brealey, Myers and Allen, under "External Links"
- ↑ III.A.3 in Carol Alexander, ed. The Professional Risk Managers' Handbook:A Comprehensive Guide to Current Theory and Best Practices. PRMIA Publications (January 2005). ISBN 978-0976609704
- ↑ See for example Pg 217 of: Jackson, Mary; Mike Staunton (2001). Advanced modelling in finance using Excel and VBA. New Jersey: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-49922-6.
- ↑ See: Emmanuel Jurczenko, Bertrand Maillet & Bogdan Negrea, 2002. "Revisited multi-moment approximate option pricing models: a general comparison (Part 1)". Working paper, London School of Economics and Political Science.
- ↑ From The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, Online Editions, 2011, 2012, with abstract links:
• "regulatory responses to the financial crisis: an interim assessment" by Howard Davies
• "Credit Crunch Chronology: April 2007–September 2009" by The Statesman's Yearbook team
• "Minsky crisis" by L. Randall Wray
• "euro zone crisis 2010" by Daniel Gros and Cinzia Alcidi.
• Carmen M. Reinhart and Kenneth S. Rogoff, 2009. This Time Is Different: Eight Centuries of Financial Folly, Princeton. Description, ch. 1 ("Varieties of Crises and their Dates," pp. 3-20), and chapter-preview links. - ↑ William F Sharpe, "The Arithmetic of Active Management"
- ↑ William F. Sharpe, Indexed Investing: A Prosaic Way to Beat the Average Investor. May 1, 2002. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
Bibliography
Financial economics
- Roy E. Bailey (2005). The Economics of Financial Markets. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521612802.
- Marcelo Bianconi (2013). Financial Economics, Risk and Information (2nd Edition). World Scientific. ISBN 9814355135.
- Zvi Bodie, Robert C. Merton and David Cleeton (2008). Financial Economics (2nd Edition). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0131856154.
- James Bradfield (2007). Introduction to the Economics of Financial Markets. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-531063-4.
- Jakša Cvitanić and Fernando Zapatero (2004). Introduction to the Economics and Mathematics of Financial Markets. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0262033206.
- George M. Constantinides, Milton Harris, René M. Stulz (editors) (2003). Handbook of the Economics of Finance. Elsevier. ISBN 0444513639.
- Keith Cuthbertson; Dirk Nitzsche (2004). Quantitative Financial Economics: Stocks, Bonds and Foreign Exchange. Wiley. ISBN 0470091711.
- Jean-Pierre Danthine, John B. Donaldson (2005). Intermediate Financial Theory (2nd Edition). Academic Press. ISBN 0123693802.
- Louis Eeckhoudt, Christian Gollier, Harris Schlesinger (2005). Economic and Financial Decisions Under Risk. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-12215-1.
- Jürgen Eichberger; Ian R. Harper (1997). Financial Economics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198775407.
- Frank J. Fabozzi, Edwin H. Neave and Guofu Zhou (2011). Financial Economics. Wiley. ISBN 0470596201.
- Christian Gollier (2004). The Economics of Risk and Time (2nd Edition). MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-57224-8.
- Thorsten Hens and Marc Oliver Rieger (2010). Financial Economics: A Concise Introduction to Classical and Behavioral Finance. Springer. ISBN 3540361464.
- Chi-fu Huang and Robert H. Litzenberger (1998). Foundations for Financial Economics. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0135006538.
- Jonathan E. Ingersoll (1987). Theory of Financial Decision Making. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0847673596.
- Robert A. Jarrow (1988). Finance theory. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0133148653.
- Chris Jones (2008). Financial Economics. Routledge. ISBN 0415375851.
- Brian Kettell (2002). Economics for Financial Markets. Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-5384-8.
- Yvan Lengwiler (2006). Microfoundations of Financial Economics: An Introduction to General Equilibrium Asset Pricing. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691126313.
- Stephen F. LeRoy; Jan Werner (2000). Principles of Financial Economics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521586054.
- Leonard C. MacLean; William T. Ziemba (2013). Handbook of the Fundamentals of Financial Decision Making. World Scientific. ISBN 9814417343.
- Frederic S. Mishkin (2012). The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets (3rd Edition). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0132961970.
- Harry H. Panjer, ed. (1998). Financial Economics with Applications. Actuarial Foundation. ISBN 0938959484.
- Geoffrey Poitras (Editor) (2007). Pioneers of Financial Economics, Volume I. Edward Elgar Publishing. ISBN 978-1845423810.; Volume II ISBN 978-1845423827.
- Richard Roll (series editor) (2006). The International Library of Critical Writings in Financial Economics. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing. External link in
|title=(help)
Asset pricing
- Kerry E. Back (2010). Asset Pricing and Portfolio Choice Theory. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195380614.
- Tomas Björk (2009). Arbitrage Theory in Continuous Time (3rd Edition). Oxford University Press. ISBN 019957474X.
- John H. Cochrane (2005). Asset Pricing. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691121370.
- Darrell Duffie (2001). Dynamic Asset Pricing Theory (3rd Edition). Princeton University Press. ISBN 069109022X.
- Edwin J. Elton, Martin J. Gruber, Stephen J. Brown, William N. Goetzmann (2014). Modern Portfolio Theory and Investment Analysis (9th Edition). Wiley. ISBN 1118469941.
- Robert A. Haugen (2000). Modern Investment Theory (5th Edition). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0130191701.
- Mark S. Joshi, Jane M. Paterson (2013). Introduction to Mathematical Portfolio Theory. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 1107042313.
- David G. Luenberger (2013). Investment Science (2nd Edition). Oxford University Press. ISBN 0199740089.
- Harry M. Markowitz (1991). Portfolio Selection: Efficient Diversification of Investments (2nd Edition). Wiley. ISBN 1557861080.
- Frank Milne (2003). Finance Theory and Asset Pricing (2nd Edition). Oxford University Press. ISBN 0199261075.
- George Pennacchi (2007). Theory of Asset Pricing. Prentice Hall. ISBN 032112720X.
- Mark Rubinstein (2006). A History of the Theory of Investments. Wiley. ISBN 0471770566.
- William F. Sharpe (1999). Portfolio Theory and Capital Markets: The Original Edition. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071353208.
Corporate finance
- Jonathan Berk; Peter DeMarzo (2013). Corporate Finance (3rd Edition). Pearson. ISBN 0132992477.
- Richard Brealey; Stewart Myers; Franklin Allen (2013). Principles of Corporate Finance. Mcgraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0078034763.
- Aswath Damodaran (1996). Corporate Finance: Theory and Practice. Wiley. ISBN 978-0471076803.
- João Amaro de Matos (2001). Theoretical Foundations of Corporate Finance. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691087948.
- Joseph Ogden; Frank C. Jen; Philip F. O'Connor (2002). Advanced Corporate Finance. Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0130915689.
- Pascal Quiry; Yann Le Fur; Antonio Salvi; Maurizio Dallochio; Pierre Vernimmen (2011). Corporate Finance: Theory and Practice (3rd Edition). Wiley. ISBN 978-1119975588.
- Stephen Ross, Randolph Westerfield, Jeffrey Jaffe (2012). Corporate Finance (10th Edition). Mcgraw-Hill. ISBN 0078034779.
- Joel M. Stern, ed. (2003). The Revolution in Corporate Finance (4th Edition). Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 9781405107815.
- Jean Tirole (2006). The Theory of Corporate Finance. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691125562.
- Ivo Welch (2014). Corporate Finance (3rd Edition). ISBN 978-0-9840049-1-1.
External links
Theory
- The History of Finance: An Eyewitness Account. Merton H. Miller
- Great Moments in Financial Economics I, II, III, IVa, IVb (archived, 2007-06-27). Prof. Mark Rubinstein, Haas School of Business
- The Scientific Evolution of Finance (archived, 2003-04-03). Prof. Don Chance, Louisiana State University, Prof. Pamela Peterson James Madison University
- The Theory of Corporate Finance: A Historical Overview, Michael C. Jensen and Clifford W. Smith.
- Microfoundations of Financial Economics Prof. André Farber, Solvay Business School
- An introduction to investment theory, Prof. William Goetzmann, Yale School of Management
- Macro-Investment Analysis. Prof. William F. Sharpe, Stanford Graduate School of Business
- Finance Theory (MIT OpenCourseWare). Prof. Andrew Lo, MIT.
- Financial Theory (Open Yale Courses). Prof. John Geanakoplos, Yale University.
- The Theory of Investment at the Wayback Machine (archived June 21, 2012). Prof. G.L. Fonseca, New School for Social Research
- An Overview of Modern Financial Economics. Chi-fu Huang, MIT Working paper
- Introduction to Financial Economics. Gordan Zitkovi, University of Texas at Austin
- An Introduction to Asset Pricing Theory, Junhui Qian, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
- What We Do Know: The Seven Most Important Ideas in Finance; What We Do Not Know: 10 Unsolved Problems in Finance, Richard A. Brealey, Stewart Myers and Franklin Allen.
Links and portals
- Financial Economics Links on WebEc
- JEL Classification Codes Guide
- Financial Economics Links on RFE
- SSRN Financial Economics Network
- Financial Economics listings on economicsnetwork.ac.uk
- Financial Economics Resources on QFINANCE (archived 2014-03-13).
- Financial Economists Roundtable
Actuarial resources
- Models for Financial Economics (MFE), Society of Actuaries
- Financial Economics (CT8), Institute and Faculty of Actuaries
- A Primer In Financial Economics, S.F. Whelan, D.C. Bowie and A.J. Hibbert. British Actuarial Journal, Volume 8, Issue 01, April 2002, pp 27–65.
- Pension Actuary's Guide to Financial Economics. Gordon Enderle, Jeremy Gold, Gordon Latter and Michael Peskin. Society of Actuaries and American Academy of Actuaries.