Herbimycin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
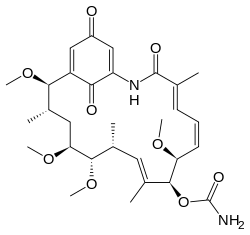
| IUPAC names
[(2R,3S,5S,6R,7S,8E,10R,11S,12E,14E)- 2,5,6,11-tetramethoxy-3,7,9,15-tetramethyl- 16,20,22-trioxo-17-azabicyclo[16.3.1] docosa-8,12,14,18,21-pentaen-10-yl] carbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 70563-58-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1159659 |
| ChemSpider | 10272738 |
| PubChem | 6436247 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H42N2O9 | |
| Molar mass | 574.66 g/mol |
| Solubility | hygroscopic |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | toxic |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Herbimycin is a benzoquinone ansamycin antibiotic that binds to Hsp90 (Heat Shock Protein 90) and alters its function. HSP90 client proteins play important roles in the regulation of the cell cycle, cell growth, cell survival, apoptosis, angiogenesis and oncogenesis.
It was originally found by its herbicidal activity, and thus named. The most recent herbimycins to be discovered, herbimycins D-F, were isolated from a Streptomyces isolated from thermal vents associated with the Ruth Mullins coal fire in Appalachian Kentucky.[1]
Synonyms
- Antibiotic Tan 420F
- Herbimycin A
Biological activity
Herbimycin induces the degradation of proteins that are mutated in tumor cells such as v-Src, Bcr-Abl and p53 preferentially over their normal cellular counterparts. This effect is mediated via HSP90.
References
- ↑ Shaaban, KA; Wang, X; Elshahawi, SI; Ponomareva, LV; Sunkara, M; Copley, GC; Hower, JC; Morris, AJ; Kharel, MK; Thorson, JS (27 September 2013). "Herbimycins D-F, ansamycin analogues from Streptomyces sp. RM-7-15.". Journal of Natural Products. 76 (9): 1619–26. doi:10.1021/np400308w. PMID 23947794.
See also
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/18/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.