Lobules of testis
| Lobules of testis | |
|---|---|
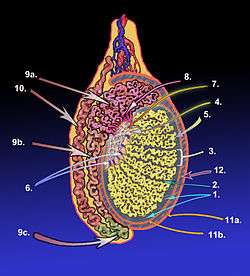 A diagram of the major components of an adult human testicle, including the following numbered items: 1. Tunica albuginea, 2. Septula testis, 3. Lobulus testis, 4. Mediastinum testis, 5. Tubuli seminiferi contorti, 6. Tubuli seminiferi recti, 7. Rete testis, 8. Ductuli efferentes testis, 9a. Head of epididymis, 9b. Body of epididymis, 9.c Tail of epididymis,10. Vas deferens, 11a. Tunica vaginalis (parietal lamina), 11b. Tunica vaginalis (visceral lamina), and 12. Cavity of tunica vaginalis. | |
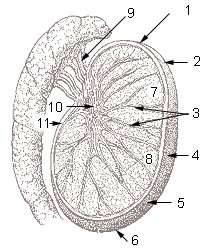 1: Head or upper pole of testis, 2: Tunica albuginea, 3: Testicular septa, 4: Anterior margin (free margin), 5: Lateral surface, 6: Tail or lower pole of testis, 7: Testicular lobules, 8: Parenchyma of testis, 9: Efferent ductules, 10: Mediastinum testis, 11: Posterior margin | |
| Details | |
| Latin | lobuli testis |
The glandular structure of the testis consists of numerous lobules.
Their number, in a single testis, is estimated by Berres at 250, and by Krause at 400.[1] Anatomic studies have demonstrated figures of 250-290 for the same.[2]
They differ in size according to their position, those in the middle of the gland being larger and longer.
The lobules are conical in shape, the base being directed toward the circumference of the organ, the apex toward the mediastinum testis.
Each lobule is contained in one of the intervals between the fibrous septa which extend between the mediastinum testis and the tunica albuginea, and consists of from one to three, or more, minute convoluted tubes, the tubuli seminiferi.
Additional images
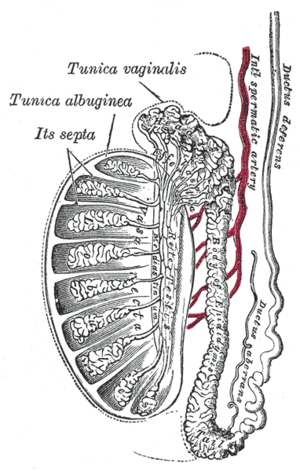 Vertical section of the testis, to show the arrangement of the ducts.
Vertical section of the testis, to show the arrangement of the ducts.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Basu, SC. (2011). Male Reproductive Dysfunction. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. p. 16. ISBN 978-93-5025-703-6.
- ↑ Countouris, N; Holstein, AF (Nov–Dec 1985). "[How many testicular lobules does a human testicle contain? Reexamination of an old problem].". Andrologia (in German). 17 (6): 525–31. PMID 4083540.
External links
- Anatomy photo:36:st-1401 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Inguinal Region, Scrotum and Testes: Testis"