Gilgit-Baltistan
| Gilgit-Baltistan گلگت بلتستان | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative Territory of Pakistan[1] | |||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
| Nickname(s): GB | |||||||
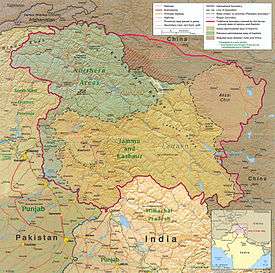
_(claims_hatched).svg.png) Gilgit-Baltistan is shown in red. Rest of Pakistan is shown in white. The Indian administered state of Jammu and Kashmir is shown by hatching. | |||||||
| Coordinates: 35°21′N 75°54′E / 35.35°N 75.9°ECoordinates: 35°21′N 75°54′E / 35.35°N 75.9°E | |||||||
| Country |
| ||||||
| Established | 1 July 1970 | ||||||
| Capital | Gilgit | ||||||
| Largest city | Skardu[2] | ||||||
| Government | |||||||
| • Type | Self-governing territory of Pakistan | ||||||
| • Body | Legislative assembly | ||||||
| • Governor | Mir Ghanzafar Ali[3] | ||||||
| • Chief Minister | Hafeezur Rahman[4] | ||||||
| Area | |||||||
| • Total | 72,971 km2 (28,174 sq mi) | ||||||
| [5] | |||||||
| Population (2015) | |||||||
| • Total | 1,800,000[6] | ||||||
| Time zone | PKT (UTC+5) | ||||||
| ISO 3166 code | PK-GB | ||||||
| Main languages | Balti, Shina, Burushaski | ||||||
| Assembly seats | 33[7] | ||||||
| Districts | 10 | ||||||
| Towns | 9 | ||||||
| Website |
gilgitbaltistan | ||||||
Gilgit-Baltistan (Urdu: گلگت بلتستان), formerly known as the Northern Areas,[8] is the northernmost administrative territory of Pakistan.[9]
It borders Azad Kashmir to the south, the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the west, the Wakhan Corridor of Afghanistan to the north, Xinjiang, PR China, to the east and northeast and Jammu and Kashmir (India) to the southeast. The region has been declared disputed by India and Pakistan together with Azad Kashmir, Aksai Chin, the Shakshagam Valley of China and Jammu and Kashmir, between India, China and Pakistan.[9][10][11]
The territory of present-day Gilgit-Baltistan became a separate administrative unit in 1970 under the name "Northern Areas". It was formed by the amalgamation of the former Gilgit Agency, the Baltistan district and several small former princely states, the larger of which being Hunza and Nagar.[6] In 2009, it was granted limited autonomy and renamed to Gilgit-Baltistan via the Self-Governance Order signed by Pakistan president Asif Ali Zardari, which also aimed to empower the people of Gilgit Baltistan. However, scholars state that the real power rests with the governor and not with chief minister or elected assembly.[12][13] The Pakistan government has rejected Gilgit-Baltistani calls for integration with Pakistan on the grounds that it would jeopardise its demands for the whole Kashmir issue to be resolved according to UN resolutions.[14]
Gilgit-Baltistan covers an area of over 72,971 km² (28,174 sq mi)[5] and is highly mountainous. It had an estimated population of 1,800,000 in 2015.[6] Its capital city is Gilgit (population 216,760 est).
Gilgit-Baltistan is home to five of the "eight-thousanders" and to more than fifty peaks above 7,000 metres (23,000 ft). Three of the world's longest glaciers outside the polar regions are found in Gilgit-Baltistan. Tourism is mostly in trekking and mountaineering, and this industry is growing in importance.
History
Early history

The rock carving found in various places of Gilgit-Baltistan specially those found in Passu village of Hunza suggests the human presence in 2000 BC.[16] Probably within the next few centuries after the human settlement in Tibetan plateau This region was inhabited by Tibetan from east and had shape Balti people of Baltistan though through coming from ladakh these Monpas also racially penetrated in valleys like Hunzas but today Baltistan is more similar to ladakh by physically and cuturally (not religiously) and The Aryan group Dard inhabited mainly the western parts those people are Shina people of Gilgit, Chilas,Astore and diamir while in Hunza and in upper regions are Brushaski and Khowar and the are dard too. who find mention in the works of Herodotus,[lower-alpha 1] Nearchus, Megasthenes, Pliny,[lower-alpha 2] Ptolemy,[lower-alpha 3] and the geographical lists of the Puranas.[17] In 1st century People of this regions were the followers of Bon religion while in almost in 2nd century this was replaced by Budhism.
Between 399 and 414, the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim Faxian (Fa-hsien) visited Gilgit-Baltistan,[18] while in the 6th century Somana Palola (greater Gilgit-Chilas) was ruled by an unknown king. Between 627 and 645, the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim Xuanzang (Hsüan-tsang) travelled through this region. From 644 to 655, 671, Navasurendrādityanandi was King of Palola (Gilgit ). In 706/707, Jayamaṅgalavikramādityanandi became king of Palola. It is said that in the year 717, a delegation of a ruler of great Palola, named Su-fu-she-li-ji-li-ni according to the transcription of Chinese characters, reached the Chinese imperial court. In 719, Su-fu-she-li-ji-li-ni, King of Palola, sent a second delegation to the Chinese Imperial court.[19] At least in 719/720, Ladakh (Mard) was part of the Tibetan Empire. About 720 Buddhism is practiced in Baltistan and Sanskrit was the written language. It is unknown if Baltistan temporarily belonged at that time to Palolo. 720: Delegation of Sou-lin-t'o i che (= Surendrāditya), King of Palola, to the Chinese imperial court. The Emperor gives the ruler of Cashmere "Tchen-fo-lo-pi-li (Chandrāpīḍa)" the title of "King of Cashmere".At least 721/722: Baltistan is part of the Tibetan Empire.[20] 721/722: The conquest of Little Palola or Bru-zha (Yasin) by the Tibetan army fails. Mo-ching-mang (Mo-kin-mang) is King of Palola. With 723 727/28: The Korean Buddhist pilgrim Hyecho (Huichao) reached Palola. In 737/738 Tibetan troops under the leadership of Minister sKyes-bzang ldong-tsab conquer Little Palola. 740/41: The Tibetan Princess Khri-ma-lod was sent as a bride of Su-shih-li-chi, the Rje (ruler) of Little Palola. 747: Reconquest of Palola by a Chinese army under the leadership of the ethnic-Korean commander Gao Xianzhi (Kao Hsien-chih).[21] 753: Conquest of Great Palola by a Chinese army under the military Governor Feng Changqing until 755, when due to the An Lushan rebellion the Chinese lost supremacy in Central Asia and in the regions around Gilgit Baltistan.[22]
Turkic tribes practicing zoroastrianism arrived in Gilgit during the 7th century, and founded the Trakhan dynasty in Gilgit. During 8th century, Tibetans were known to live in Baltistan. Rulers of Gilgit formed an alliance with the Chinese T'ang Dynasty and forced Arabs back with their help.[23]

Medieval History
In 14th century the Muslim Sufi preachers from Persia and central Asia introduced Islam in Baltistan amongst them Mir Sayyid Ali Hamadani was famous who came from Kashmir[24] while in Gilgit region Islam entered in the same century by Turkic Tarkhan rulers.
Gilgit-Baltistan was ruled by many local rulers, amongst whom the Maqpon dynasty of Skardu and the Rajas of Hunza were famous. The Maqpons of Skardu unfied Gilgit Baltistan with Chitral and Ladakh specially in the era of Ali Sher Khan Anchan[25] who had a friendly relation with the Mughal court.[26] Anchan reign brought prosperity in art, sport, and variety in architecture He introduce polo in Gilgit region and in Chitral he sent group of musician in Delhi to learn Indian music and due relation with Mughals; the Mughal architecture influenced Architecture of the region as well.[27]
Later Anchan in his successors Abdal Khan had great influence though In the popular literature of Baltistan he is still alive as dark figure by the nickname "Mizos" "man-eater". The last Maqpons Raja, Ahmed Shah, ruled 1811–1840 all Baltistan. The areas of Gilgit, Chitral and Hunza get independence of Maqpons long before.
Before the demise of Shribadat, a group of Shin people migrated from Gilgit Dardistan and settled in the Dras and Kharmang areas. The descendants of those Dardic people can be still found today, and are believed to have maintained their Dardic culture and Shina language up to the present time.
Modern History

- November 1839: Beginning of the campaign of Zorawar Singh against Baltistan.[28]
- 1839/1840: Conquest of Skardu and capture of Ahmad Shah. Ahmad Shah was forced to accompany Zorawar Singh on his raid into Western Tibet. Appointment of Baghwan Singh as administrator (Thanadar) in Skardu.
- 1841: Successful uprising against the Dogras in Baltistan led by Ali Khan of Rondu, Haidar Khan of Shigar and Daulat Ali Khan from Khaplu. Capture of the Dogra commander Baghwan Singh in Skardu.[29]
- 1842: The second conquest of Baltistan by the Dogra Commander Wasir Lakhpat with the active support of Ali Sher Khan (III) from lKartaksho. Bloody capture of the fortress of Kharphocho. Haidar Khan from Shigar, one of the leaders of the uprising against the Dogra,[30] was imprisoned and died in captivity. Gosaun was appointed as administrator (Thanadar) for Baltistan and till 1860, the entire region of Gilgit-Baltistan was conquered by the Sikhs and the Dogras. It was the Dogras who incorporated Gilgit-Baltistan into Kashmir although the people of the region are more closely related to those of Ladakh and Chitral.[31][32]
After the defeat of the Sikhs in the First Anglo-Sikh War, the region became a part of the princely state with the name Jammu and Kashmir in 1846 under the rule of the Dogras for more than a century. It remained so till a rebellion, organized by commander Major William Brown of the Gilgit Scouts mutiny, overthrew Ghansara Singh, the Governor administering the region on behalf of the Maharaja of Jammu and Kashmir on 1 November 1947.
After Pakistan's independence, Jammu and Kashmir initially remained an independent state. Later On 22 October 1947, Tribal militias backed by Pakistan crossed the border in Jammu and Kashmir with the claim that they needed to suppress a rebellion on the southeast of the kingdom.[33][34] Local tribal militias and the Pakistani armed forces moved to take Srinagar but on reaching Uri they encountered defensive forces. Hari Singh made a plea to India for assistance and signed the Instrument of Accession.
Gilgit's population did not favour the State's accession to India.[35] Sensing their discontent, Major William Brown, the Maharaja's commander of the Gilgit Scouts, mutinied on 1 November 1947, overthrowing the Governor Ghansara Singh. The bloodless coup d'etat was planned by Brown to the last detail under the code name Datta Khel, which was also joined by a rebellious section of the Jammu and Kashmir 6th Infantry under Mirza Hassan Khan. Brown ensured that the treasury was secured and minorities were protected. A provisional government (Aburi Hakoomat) was established by the Gilgit locals with Raja Shah Rais Khan as the president and Mirza Hassan Khan as the commander-in-chief. However, Major Brown had already telegraphed Khan Abdul Qayyum Khan asking Pakistan to take over. The Pakistani political agent, Khan Mohammad Alam Khan, arrived on 16 November and took over the administration of Gilgit.[36][37] According to Brown,
Alam replied [to the locals],: 'you are a crowd of fools led astray by a madman. I shall not tolerate this nonsense for one instance... And when the Indian Army starts invading you there will be no use screaming to Pakistan for help, because you won't get it.'... The provisional government faded away after this encounter with Alam Khan...[38]
The provisional government lasted 16 days. Scholar Yaqoob Khan Bangash states that the people of Gilgit as well as those of Chilas, Koh Ghizr, Ishkoman, Yasin, Punial, Hunza and Nagar joined Pakistan by choice.[39]
After taking control of Gilgit, the Gilgit Scouts along with Azad irregulars moved towards Baltistan and Ladakh and captured Skardu by May 1948. They successfully blocked the Indian reinforcements and subsequently captured Dras and Kargill as well, cutting off the Indian communications to Leh in Ladakh. The Indian forces mounted an offensive in Autumn 1948 and recaptured all of Kargil district. Baltistan region, however, came under Gilgit control.[40][41]
On 1 January 1948, India took the issue of Jammu and Kashmir to the United Nations Security Council. In April 1948, the Council passed a resolution calling for Pakistan to withdraw from all of Jammu and Kashmir and India to reduce its forces to the minimum level, following which a plebiscite would be held to ascertain the people's wishes.[42] However, no withdrawal was ever carried out, India insisting that Pakistan had to withdraw first and Pakistan contending that there was no guarantee that India would withdraw afterwards.[43] Gilgit-Baltastan and a western portion of the state called Azad Jammu and Kashmir have remained under the control of Pakistan since then.[44]
Inside Pakistan
For a short period after joining Pakistan, Gilgit-Baltistan was governed by Azad Kashmir if only "theoretically, but not practically" through its claim of being an alternative government for Jammu and Kashmir.[45] However, on 29 April 1949, Azad Kashmir was made to sign the Karachi Agreement, through which it ceded all control over Gilgit-Baltistan (then called "Northern Areas") to Pakistan's Ministry of Kashmir Affairs. This is seen as an effort by Pakistan to legitimize its rule over Gilgit-Baltistan.[46] The Karachi Agreement is highly unpopular in Gilgit-Baltistan because Gilgit-Baltistan was not a party to it even while its fate was being decided upon.[47]
From then until 1990s, Gilgit-Baltistan was governed through the colonial-era Frontier Crimes Regulations, which treated tribal people as "barbaric and uncivilised," levying collective fines and punishments.[48][49] People had no right to legal representation or a right to appeal.[50][49] Members of tribes had to obtain prior permission from the police to travel to any location and had to keep the police informed about their movements.[51][52]
There was no democratic set-up for Gilgit-Baltistan during this period. All political and judicial powers remained in the hands of the Ministry of Kashmir Affairs and Northern Areas (KANA). The people of Gilgit-Baltistan had no rights and privileges as citizens of either Pakistan or Azad Kashmir.[53]
In 1970 the two parts of the territory, viz., the Gilgit Agency and Baltistan, were merged into a single administrative unit, and given the name "Northern Areas".[9] The Shaksgam tract was ceded by Pakistan to China following the signing of the Sino-Pakistani Frontier Agreement in 1963.[54][55]
In 1969, a Northern Areas Advisory Council (NAAC) was created, later renamed to Northern Areas Council (NAC) in 1974 and Northern Areas Legislative Council (NALC) in 1994. But it was devoid of legislative powers. All law-making was concentrated in the KANA Ministry of Pakistan. In 1994, a Legal Framwork Order (LFO) was created by the KANA Ministry to serve as the de facto constitution for the region.[56][57]
In late 1990s, the President of Al-Jihad Trust filed a petition in the Supreme Court of Pakistan to determine the legal status of Gilgit-Baltistan. In its judgement of 28 May 1999, the Court directed the Government of Pakistan to ensure the provision of equal rights to the people of Gilgit-Baltistan, and gave it six months to do so. This introduced a flurry of reforms, but largely cosmetic. A position of 'Deputy Chief Executive' was created to act the local administrator, but the real powers still rested with the 'Chief Executive', who was the Federal Minister of KANA. "The secretaries were more powerful than the concerned advisors," in the words of one commentator. In spite of various reforms packages over the years, the situation is essentially unchanged.[58]
Meanwhile, public rage in Gilgit-Baltistan is "growing alarmingly." Prominent "antagonist groups" have mushroomed protesting the absence of civic rights and democracy.[59] Pakistan government has been debating the grant of a provincial status to Gilgit-Baltastan.[60]
Government
The territory of present-day Gilgit-Baltistan became a separate administrative unit in 1970 under the name "Northern Areas". It was formed by the amalgamation of the former Gilgit Agency, the Baltistan District of the Ladakh Wazarat, and the hill states of Hunza and Nagar. It presently consists of nine districts, has a population approaching one million, an area of approximately 28,000 square miles (73,000 km2), and shares borders with Pakistan, China, Afghanistan, and India. In 1993, an attempt was made by the High Court of Azad Jammu and Kashmir to annex Gilgit-Baltistan but was quashed by the Supreme Court of Pakistan after protests by the locals of Gilgit-Baltistan, who feared domination by the Kashmiris.[14]
Government of Pakistan abolished State Subject Rule in Gilgit-Baltistan in 1974, which resulted in demographic changes in the territory.[61][62] While administratively controlled by Pakistan since the First Kashmir War, Gilgit-Baltistan has never been formally integrated into the Pakistani state and does not participate in Pakistan's constitutional political affairs.[63][64] On 29 August 2009, the Gilgit-Baltistan Empowerment and Self-Governance Order 2009, was passed by the Pakistani cabinet and later signed by the then President of Pakistan Asif Ali Zardari.[65] The order granted self-rule to the people of Gilgit-Baltistan, by creating, among other things, an elected Gilgit-Baltistan Legislative Assembly and Gilgit-Baltistan Council. Gilgit-Baltistan thus gained a de facto province-like status without constitutionally becoming part of Pakistan.[63][66] Currently Gilgit Baltistan is neither a province nor a state. It has a semi provincial entity of government.[67] Officially, The Pakistan government has rejected Gilgit-Baltistani calls for integration with Pakistan on the grounds that it would jeopardise its demands for the whole Kashmir issue to be resolved according to UN resolutions.[14] Some Kashmiri nationalist groups, such as the Jammu and Kashmir Liberation Front, claim Gilgit-Baltistan as part of a future independent state to match what existed in 1947.[14] India, on the other hand, maintains that Gilgit-Baltistan is a part of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir that is "an integral part of the country [India]."[68]

Regions
- Administrative divisions
Gilgit-Baltistan is administratively divided into three divisions[69] which, in turn, are divided into ten districts, consisting of the four Baltistan districts of Skardu, Shigar, Kharmang, and Ghanche, and the six Gilgit districts of Gilgit, Ghizer, Diamer, Astore, Hunza and Nagar, of which Astore and Diamer are part of Diamer Division.[70][71] The principal administrative centers are the towns of Gilgit and Skardu.
| Division | District | Area (km²) | Capital | Population (2013)[72] | Divisional Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baltistan | Ghanche | 4,052 | Khaplu | 108,000 | Skardu |
| Shigar | 8,500 | Shigar | - | ||
| Kharmang | 5,500 | Kharmang | - | ||
| Skardu | 8,700 | Skardu | 305,000* | ||
| Gilgit | Gilgit | 14,672 | Gilgit | 222,000 | Gilgit |
| Ghizer | 9,635 | Gahkuch | 190,000 | ||
| Hunza | 7,900 | Aliabad | 70,000 (2015)[73] | ||
| Nagar | 5,000 | Nagar | 51,387 (1998)[72] | ||
| Diamer | Diamer | 10,936 | Chilas | 214,000 | ---- |
| Astore | 5,092 | Eidghah | 114,000 |
* - Combined population of Skardu, Shigar and Kharmang Districts. Shigar and Kharmang Districts were carved out of Skardu District after 1998. The estimated population of Gilgit-Baltistan was about 1.8 million in 2015[6] and the overall population growth rate between 1998 and 2011 was 63.1% making it 4.85% annually.[74][75]
Geography and climate





Gilgit-Baltistan borders Pakistan's Khyber Pukhtunkhwa province to the west, a small portion of the Wakhan Corridor of Afghanistan to the north, China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region to the northeast, the Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir to the southeast, and the Pakistani-administered state of Azad Jammu and Kashmir to the south.
Gilgit-Baltistan is home to five of the "eight-thousanders" and to more than fifty peaks above 7,000 metres (23,000 ft). Gilgit and Skardu are the two main hubs for expeditions to those mountains. The region is home to some of the world's highest mountain ranges. The main ranges are the Karakoram and the western Himalayas. The Pamir Mountains are to the north, and the Hindu Kush lies to the west. Amongst the highest mountains are K2 (Mount Godwin-Austen) and Nanga Parbat, the latter being one of the most feared mountains in the world.
Three of the world's longest glaciers outside the polar regions are found in Gilgit-Baltistan: the Biafo Glacier, the Baltoro Glacier, and the Batura Glacier. There are, in addition, several high-altitude lakes in Gilgit-Baltistan:
- Sheosar Lake in the Deosai Plains, skardu
- Naltar lakes in the Naltar Valley, Gilgit
- Satpara Tso Lake in Skardu, Baltistan
- Katzura Tso Lake in Skardu, Baltistan
- Zharba Tso Lake in Shigar, Baltistan
- Phoroq Tso Lake in Skardu, Baltistan
- Lake Kharfak in Gangche, Baltistan
- Byarsa Tso Lake in Gultari, Astore
- Borith Lake in Gojal, upper Hunza, Gilgit
- Rama Lake near Astore
- Rush Lake near Nagar, Gilgit
- Kromber Lake at Kromber Pass Ishkoman Valley, Ghizer District
- Barodaroksh Lake in Bar Valley, Nagar
- Ghorashi Lake in Ghandus Valley, Kharmang
The Deosai Plains, are located above the tree line and constitute the second-highest plateau in the world at 4,115 metres (14,500 feet) after Tibet. The plateau lies east of Astore, south of Skardu and west of Ladakh. The area was declared as a national park in 1993. The Deosai Plains cover an area of almost 5,000 square kilometres (1,900 sq mi). For over half the year (between September and May), Deosai is snow-bound and cut off from rest of Astore and Baltistan in winters. The village of Deosai lies close to Chilum chokki and is connected with the Kargil district of Ladakh through an all-weather road.
Rock art and petroglyphs
There are more than 50,000 pieces of rock art (petroglyphs) and inscriptions all along the Karakoram Highway in Gilgit-Baltistan, concentrated at ten major sites between Hunza and Shatial. The carvings were left by invaders, traders, and pilgrims who passed along the trade route, as well as by locals. The earliest date back to between 5000 and 1000 BCE, showing single animals, triangular men and hunting scenes in which the animals are larger than the hunters. These carvings were pecked into the rock with stone tools and are covered with a thick patina that proves their age.
The ethnologist Karl Jettmar has pieced together the history of the area from inscriptions and recorded his findings in Rock Carvings and Inscriptions in the Northern Areas of Pakistan[77] and the later-released Between Gandhara and the Silk Roads — Rock Carvings Along the Karakoram Highway.[78] Many of these carvings and inscriptions will be inundated and/or destroyed when the planned Basha-Diamir dam is built and the Karakoram Highway is widened.
Climate
The climate of Gilgit-Baltistan varies from region to region, surrounding mountain ranges creates sharp variations in weather. The eastern part has the moist zone of the western Himalayas, but going toward Karakoram and Hindu Kush, the climate dries considerably.[79]
There are towns like Gilgit and Chilas that are very hot during the day in summer yet cold at night and valleys like Astore, Khaplu, Yasin, Hunza, and Nagar, where the temperatures are cold even in summer.[80]
Economy and resources
The economy of the region is primarily based on a traditional route of trade, the historic Silk Road. The China Trade Organization forum led the people of the area to actively invest and learn modern trade know-how from its Chinese neighbor Xinjiang. Later, the establishment of a chamber of commerce and the Sust dry port (in Gojal Hunza) are milestones. The rest of the economy is shouldered by mainly agriculture and tourism. Agricultural products are wheat, corn (maize), barley, and fruits. Tourism is mostly in trekking and mountaineering, and this industry is growing in importance.[81][82]
In early September 2009, Pakistan signed an agreement with the People's Republic of China for a major energy project in Gilgit-Baltistan which includes the construction of a 7,000-megawatt dam at Bunji in the Astore District.[83]
Mountaineering


Gilgit-Baltistan is home to more than 20 peaks of over 20,000 feet (6,100 m), including K-2 the second highest mountain on Earth.[85] Other well known peaks include Masherbrum (also known as K1), Broad Peak, Hidden Peak, Gasherbrum II, Gasherbrum IV, and Chogolisa, situated in Khaplu Valley. The following peaks have so far been scaled by various expeditions:
| Name of Peak | Photos | Height | Date of Conquest | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.K-2 |  | (28,250Ft) | 31 Jul 1954 | Karakoram |
| 2. Nanga Parbat |  | (26,660 Ft) | 3 Jul 1953 | Himalaya |
| 3. Gasherbrum I |  | (26,360Ft) | 7 Jul 1956 | Karakoram |
| 4. Broad Peak |  | (26,550Ft) | 9 Jun 1957 | Karakoram |
| 5. Muztagh Tower |  | (23,800Ft) | 6 Aug 1956 | Karakoram |
| 6. Gasherbrum II |  |
(26,120Ft) | 4 Jul 1958 | Karakoram |
| 7. Hidden Peak |  | (26,470Ft) | 4 Jul 1957 | Karakoram |
| 8. Khunyang Chhish | | (25,761 Ft) | 4 July 1971 | Karakoram |
| 9. Masherbrum |  | (25,659 Ft) | 4 Aug 1960 | Karakoram |
| 10. Saltoro Kangri |  | (25,400Ft) | 4 June 1962 | Karakoram |
| 11. Chogolisa |  |
(25,148 Ft) | 4 Aug 1963 | Karakoram |
Sports
Every year, many tourists visit to enjoy polo in Gilgit-Baltistan. "Polo" is a Persian word which means "ball".
Other games such as cricket, tuksori of Nagar, gulli danda, kabbadi, and volleyball are also played.[86]

Transport
Before 1978, Gilgit-Baltistan was cut off from the rest of the Pakistan and the world due to the harsh terrain and the lack of accessible roads. All of the roads to the south opened toward the Pakistan-administered state of Azad Kashmir and to the southeast toward the present-day Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir. During the summer, people could walk across the mountain passes to travel to Rawalpindi. The fastest way to travel was by air, but air travel was accessible only to a few privileged local people and to Pakistani military and civilian officials. Then, with the assistance of the Chinese government, Pakistan began construction of the Karakoram Highway (KKH), which was completed in 1978.
The Karakoram Highway connects Islamabad to Gilgit and Skardu, which are the two major hubs for mountaineering expeditions in Gilgit-Baltistan. The journey from Rawalpindi/Islamabad to Gilgit takes approximately 20 to 24 hours. Landslides on the Karakoram Highway are very common. The Karakoram Highway connects Gilgit to Tashkurgan Town, Kashgar, China via Sust, the customs and health-inspection post on the Gilgit-Baltistan side, and the Khunjerab Pass, the highest paved international border crossing in the world at 4,693 metres (15,397 ft).
Northern Areas Transport Corporation (NATCO) offers bus and jeep transport service to the two hubs and several other popular destinations, lakes, and glaciers in the area.
In March 2006, the respective governments announced that, commencing on 1 June 2006, a thrice-weekly bus service would begin across the boundary from Gilgit to Kashgar and road-widening work would begin on 600 kilometres (370 mi) of the Karakoram Highway. There would also be one daily bus in each direction between the Sust and Taxkorgan border areas of the two political entities.[87]
Pakistan International Airlines used to fly a Fokker F27 Friendship daily between Gilgit Airport and Benazir Bhutto International Airport. The flying time was approximately 50 minutes, and the flight was one of the most scenic in the world, as its route passed over Nanga Parbat, a mountain whose peak is higher than the aircraft's cruising altitude. However, the Fokker F27 was retired after a crash at Multan in 2006. Currently, flights are being operated by PIA to Gilgit on the brand-new ATR 42-500, which was purchased in 2006. With the new plane, the cancellation of flights is much less frequent. Pakistan International Airlines also offers regular flights of a Boeing 737 between Skardu and Islamabad. All flights are subject to weather clearance; in winter, flights are often delayed by several days.
A railway through the region has been proposed; see Khunjerab Railway for details.
Population
Demographics
At the last census (1998), the population of Gilgit-Baltistan was 870,347.[88] Approximately 14% of the population was urban.[89] The estimated population Gilgit-Baltistan in 2013 is over 2 million. The population of Gilgit-Baltistan consists of many diverse linguistic, ethnic, and religious sects, due in part to the many isolated valleys separated by some of the world's highest mountains. The ethnic groups include Shins, Yashkuns, Kashmiris, Kashgaris,Pamiris, Pathans, and Kohistanis.[90] A significant number of people from Gilgit-Baltistan are resident in other parts of Pakistan mainly in Punjab and Karachi. The literacy rate of Gilgit-Baltistan is approximately 72%.
Languages
Gilgit Baltistan is a multi lingual region where Urdu being a national and official language serves as the lingua franca for inter ethnic communications. English is co-official and also used in education, while Arabic is used for religious purposes. The table below shows a break up of Gilgit Baltistan first language speakers.
| Rank | Language | 1998 census, | Detail [91][92][93][94][95][96][97][98] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shina | 38% | It is spoken by majority in six Tehsils (Gilgit, Diamir/Chilas, Darel/Tangir, Astore, Puniyal/Gahkuch and Rondu). It is a Dardic Language whose syntax and structure resembles Punjabi language.[99] |
| 2 | Balti | 28% | It is spoken by majority in five Tehsils (Skardu/Shigar,Kharmang, Gultari, Khaplu and Mashabrum). It is from the Tibetan language family and has Urdu borrowings. |
| 3 | Burushaski | 12% | It is spoken by majority in four Tehsils (Nagar 1,Hunza/Aliabad,Nagar II, and Yasin). It is a language isolate that has borrowed considerable Urdu vocabulary. |
| 4 | Khowar | 12% | It is spoken by majority in two Tehsils (Gupis and Ishkomen but also spoken in Yasin and Puniyal/Gahkuch Tehsils). Like Shina, it is a Dardic language. |
| 5 | Wakhi | 6% | It is spoken by majority in one Tehsil (Gojal but also spoken in Ishkomen and Yasin Tehsils). It is classified as eastern Iranian/ Pamiri language. |
| Others | 7% | Pashto, Kashmiri, Domaaki (spoken by musician clans in the region) and Gojri languages are also spoken by a significant population of the region. |
Religion
The population of Gilgit-Baltistan is Muslim belonging to different sects of Islam, the Shia sect being the most common. Gilgit-Baltistan is the only Shia majority area in Sunni majority Pakistan.[101] People belonging to Shia sect of Islam are in majority in Skardu district, while Diamir and Astore have Sunni majority, Ghanche have Noorbakhshi and Ghizar have Ismaili majority which is a subsection of Shia Islam.[102] Gilgit and Hunza Nagar districts have a population belonging to a mix of all these sects.[100]
In 1948, the Shias and Ismailis constituted about 85% of the population. The proportion was brought down by General Zia ul-Haq through a conscious policy of demographic change by encouraging the migration of Sunnis from other provinces and the Federally Administered Tribal Areas. The policy is said to have been motivated by a desire to counter the growing sectarian consciousness of the Shias after the Iranian Revolution in 1979.[103]
Culture
| Provincial animal | Yak | |
|---|---|---|
| Provincial bird | Shaheen falcon | |
| Provincial tree | Quercus ilex | |
| Provincial flower | Aquilegia pubiflora (common) |  |
Gilgit-Baltistan is home of diversified cultures, ethnic groups, languages and backgrounds. It is home to people belonging to all regions of Gilgit-Baltistan as well as other areas of Pakistan.[104] Major Cultural events include:[104]
- Shandoor Polo Festival
- Babusar Polo Festival
- Jashn-e-Baharan / Harvest Time Festival (Navroz)
Following are the dances of Gilgit-Baltistan:[104]
- Old Man Dance: In this dance more than one person wears old-style dresses.
- Cow Boy Dance (Payaloo): In this dance a person wears old style dress, long leather shoes and a stick in hand.
- Sword Dance: In this unique dance the participants show taking one sword in right and shield in left. One to six participants as pair can dance.
See also
Notes
- ↑ He mentions twice a people called Dadikai, first along with the Gandarioi, and again in the catalogue of king Xerxes's army invading Greece. Herodotus also mentions the gold-digging ants of Central Asia.
- ↑ In the 1st century, Pliny repeats that the Dards were great producers of gold.
- ↑ Ptolemy situates the Daradrai on the upper reaches of the Indus
References
- ↑ http://gbtribune.files.wordpress.com/2012/09/self-governance-order-2009.pdf
- ↑ "Skardu". Skardu. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- ↑ "Pir Karam Ali Shah appointed GB Governor". The News. 2011-01-26. Retrieved 2011-01-28.
- ↑ "In the saddle: New CM has a vision for Gilgit-Baltistan". The Express Tribune. 30 June 2015. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- 1 2 "UNPO: Gilgit Baltistan: Impact Of Climate Change On Biodiversity". unpo.org. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Shahid Javed Burki 2015.
- ↑ Legislative Assembly will have directly elected 24 members, besides six women and three technocrats. "Gilgit Baltistan: New Pakistani Package or Governor Rule" 3 September 2009, The Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO)
- ↑ Hinman, Bonnie (15 September 2011), We Visit Pakistan, Mitchell Lane Publishers, Inc., p. 41, ISBN 978-1-61228-103-2
- 1 2 3 Weightman, Barbara A. (2 December 2005). Dragons and Tigers: A Geography of South, East, and Southeast Asia (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 193. ISBN 978-0-471-63084-5.
- ↑ Gilgit-Baltistan: Disputed or victim of Kashmir dispute?
- ↑ The Myth of Gilgit-Baltistan's Linkage with Jammu & Kashmir
- ↑ In Pakistan-controlled Kashmir, residents see experiment with autonomy as 'illusion', Christian Science Monitor, 28 November 2011
- ↑ Sering, Senge H., "Constitutional Impasse in Gilgit-Baltistan (Jammu and Kashmir): The Fallout", Strategic Analysis, 34 (3): 354–358, doi:10.1080/09700161003658998, (subscription required (help)),
Instead of the chief minister, the order rests all administrative, political and judicial authority with the governor, which makes him the supreme authority and portrays the assembly as a toothless tiger. At best, the order legitimises Pakistan's occupation and claims political rights for the locals without changing the power equation.
- 1 2 3 4 Schofield, Victoria (2000). Kashmir in Conflict: India, Pakistan, and the Unending War. I.B. Tauris. pp. 180–181.
- ↑ "Episode 1: A Window to Gilgit-Baltistan".
- ↑ By Ian Hibbert. Alpamayo to Everest: It's Not About the Summit.
- ↑ Petech, Luciano (1977). The Kingdom of Ladakh c. 950–1842 A.D. Istituto Italiano per il media ed Estremo Oriente.
- ↑ By Rafi U. Samad. The Grandeur of Gandhara: The Ancient Buddhist Civilization of the Swat ...
- ↑ "Baltistan". tibetan incyclopedia.
- ↑ August Hermann Francke. Antiquities of Indian Tibet, Part 1.
- ↑ René Grousset. The Rise and Splendour of the Chinese Empire. p. 160.
- ↑ By Angela Falco Howard. Chinese Sculpture. p. 313.
- ↑ Robert W. Bradnock (1994). South Asian Handbook. Trade & Travel Publications. p. 1168.
- ↑ By Henry Osmaston, Philip Denwood. Recent Research on Ladakh 4 & 5: Proceedings of the Fourth and Fifth ...
- ↑ P. Stobdan,. The last colony: Muzaffarabad-Gilgit-Baltistan.
- ↑ International Council on Archives, National Archives of Pakistan. Guide to the Sources of Asian History: National archives, Provincial archives, District archives.
- ↑ Philippe Fabry, Yousuf Shahid. Wandering with the Indus.
- ↑ By S.R. Bakshi. Kashmir: History and People.
- ↑ By Sanjeev Kumar Bhasin. Amazing Land Ladakh: Places, People, and Culture.
- ↑ By Shridhar Kaul, H. N. Kaul. Ladakh Through the Ages, Towards a New Identity.
- ↑ Varieties of Secularism in Asia: Anthropological Explorations of Religion ...
- ↑ By Peter Berger, Frank Heidemann. The Modern Anthropology of India: Ethnography, Themes and Theory.
- ↑ "Quick guide: Kashmir dispute". BBC News. 29 June 2006. Retrieved 14 June 2009.
- ↑ "Who changed the face of '47 war?". Times of India. 14 August 2005. Retrieved 14 August 2005.
- ↑ Bangash 2010, p. 128: [Ghansara Singh] wrote to the prime minister of Kashmir: 'in case the State accedes to the Indian Union, the Gilgit province will go to Pakistan', but no action was taken on it, and in fact Srinagar never replied to any of his messages.
- ↑ Schofield 2003, pp. 63–64.
- ↑ Bangash 2010
- ↑ Bangash 2010, p. 133.
- ↑ Gilgit-Baltistan — part of Pakistan by choice, The Express Tribune, 9 January 2016.
- ↑ Schofield 2003, p. 66.
- ↑ Bajwa, Farooq (2013), From Kutch to Tashkent: The Indo-Pakistan War of 1965, Hurst Publishers, pp. 22–24, ISBN 978-1-84904-230-7
- ↑ Bose, Tapan K. (2004). Raṇabīra Samāddāra, ed. Peace Studies: An Introduction To the Concept, Scope, and Themes. Sage. p. 324. ISBN 978-0-7619-9660-6.
- ↑ Varshney, Ashutosh (1992), "Three Compromised Nationalisms: Why Kashmir has been a Problem" (PDF), in Raju G. C. Thomas, Perspectives on Kashmir: the roots of conflict in South Asia, Westview Press, p. 212, ISBN 978-0-8133-8343-9
- ↑ Warikoo, Kulbhushan (2008). Himalayan Frontiers of India: Historical, Geo-Political and Strategic Perspectives (1st ed.). Routledge. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-415-46839-8.
- ↑ Snedden 2013, p. 91.
- ↑ Sahni 2009, p. 73.
- ↑ International Crisis Group 2007, p. 5.
- ↑ Bansal 2007, p. 60.
- 1 2 From the fringes: Gilgit-Baltistanis silently observe elections, Dawn, 1 May 2013.
- ↑ Priyanka Singh 2013, p. 16.
- ↑ Raman 2009, p. 87.
- ↑ Behera 2007, p. 180.
- ↑ Ershad Mahmud 2008, p. 25.
- ↑ Chellaney, Brahma (2011). Water: Asia's New Battleground. Georgetown University Press. p. 249. ISBN 978-1-58901-771-9.
- ↑ "China's Interests in Shaksgam Valley". Sharnoff's Global Views.
- ↑ International Crisis Group 2007, pp. 8–9.
- ↑ Ershad Mahmud 2008, pp. 28–29.
- ↑ Ershad Mahmud 2008, pp. 26–27.
- ↑ Ershad Mahmud 2008, p. 32.
- ↑ Ershad Mahmud, Gilgit-Baltistan: A province or not, The News on Sunday, 24 January 2016.
- ↑ "Pakistan abolished State Subject Rule in Gilgit-Baltistan in 1974-Those Troubled Peaks".
- ↑ "GB's aspirations".
- 1 2 "Gilgit-Baltistan: A question of autonomy". Indian Express. September 21, 2009. Retrieved 2013-02-23.
- ↑ Shigri, Manzar. "Pakistan's disputed Northern Areas go to polls". Reuters.com. Retrieved 2013-02-23.
- ↑ "Pakistani president signs Gilgit-Baltistan autonomy order _English_Xinhua". News.xinhuanet.com. 2009-09-07. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ "Gilgit-Baltistan autonomy". Dawn. 2009-09-09. Retrieved 2013-02-23.
- ↑ www.skardu.pk. Skardu.pk http://www.skardu.pk/gilgit-baltistan-the-jewel-of-pakistan/.
|first1=missing|last1=in Authors list (help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ "Gilgit-Baltistan part of Jammu and Kashmir: India". Times of India. Press Trust of India. March 10, 2006.
- ↑ "Gilgit-Baltistan divided into three divisions - The Express Tribune". tribune.com.pk. 1 February 2012. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "Mehdi Shah announces formation of 2 Divisions, 2 sub-divisions and 4 Tehsils in Gilgit – Baltistan - PAMIR TIMES - Voices of the Mountain Communities". pamirtimes.net. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "Wrangling over new Astore district headquarters". Dawn Newspaper Internet Edition. Retrieved 2006-11-17.
- 1 2 "Gilgit-Baltistan: Districts & Places - Population Statistics in Maps and Charts". citypopulation.de. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ Shafqat Hussain 2015.
- ↑ "Pak population increased by 46.9% between 1998 and 2011". The Times of India. Retrieved 27 January 2016.
- ↑ "Statistical Booklet on Gilgit-Baltistan" (PDF). Government of Gilgit-Baltistan, 2014. Retrieved 2014-12-11.
- ↑ Tropical Bryology
- ↑ "Rock Carvings and Inscriptions along the Karakorum Highway (Pakistan) –- a brief introduction".
- ↑ "Between gandhara and the silk roads".
- ↑ WWF Pakistan. "Climate of Gilgit-Baltistan (formerly Northern Areas)". WWF Pakistan. Retrieved 2009-06-11.
- ↑ http://gilgit-baltistan.com/weather/
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica. "Baltistan (region, Northern Areas, Kashmir, Pakistan) – Britannica Online Encyclopedia". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica. "Gilgit (Kashmir region, Indian subcontinent) – Britannica Online Encyclopedia". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ "Pakistan | Gilgit-Baltistan autonomy". Dawn.Com. 2009-09-09. Archived from the original on September 12, 2009. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ "Welcome to PAKISTANALPINE.COM". pakistanalpine.com. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ Baltistan in History, Banat Gul Afridi
- ↑ Sports and games of the 18th and … – Google Books. Books.google.co.nz. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ↑ "Kashgar-Gilgit bus service planned". Dawn Newspaper Internet Edition. Retrieved 2006-11-17.
- ↑ "Administrative Divisions and Population of the Northern Areas (1998)". Northern Areas Management Information System. Retrieved 2006-11-17.
- ↑ "Population, poverty and environment" (PDF). Northern Areas Strategy for Sustainable Development. Retrieved 2006-11-17.
- ↑ "Pakistan's Fragile Foundations". Council on Foreign Relations. 2009-03-12.
- ↑ "International Programs".
- ↑ "Khowar - South Asia Blog".
- ↑ Katy, Gardner (1999). Leif O. Manger, ed. Muslim diversity: local Islam in global contexts. Routledge. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-7007-1104-8.
- ↑ "Election : Gilgit-Baltistan - 8 Languages, 10 Ethnic Groups, 6 Districts, 4 Religious sects - 24 National Assembly Seats ! - GILGIT BALTISTAN (GB)".
- ↑ Colin P. Masica (1993), The Indo-Aryan Languages, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-29944-6,
... he agreed with Grierson in seeing Rajasthani influence on Pahari and 'Dardic' influence on (or under) the whole Northwestern group + Pahari [...] Sindhi and including 'Lahnda', Dardic, Romany and West Pahari, there has been a tendency to transfer of 'r' from medial clusters to a position after the initial consonant ...
- ↑ S. Munshi, Keith Brown (editor), Sarah Ogilvie (editor) (2008), Concise encyclopedia of languages of the world, Elsevier, ISBN 0-08-087774-5, retrieved 2010-05-11,
Based on historical sub-grouping approximations and geographical distribution, Bashir (2003) provides six sub-groups of the Dardic languages ...
- ↑ Amar Nath Malik (1995), The phonology and morphology of Panjabi, Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers, ISBN 81-215-0644-1, retrieved 2010-05-26,
... drakhat 'tree' ...
- ↑ electricpulp.com. "DARDESTĀN".
- ↑ "The Record News".
- 1 2 "Sectarian conflict in Gilgit-Baltistan" (PDF). pildat. May 2011. Retrieved 24 June 2013.
- ↑ Naumann & Fischer-Tahir 2013, p. 87.
- ↑ Spencer C. Tucker & Priscilla Roberts 2008, p. 917.
- ↑ Raman 2009, p. 79.
- 1 2 3 "Culture and Heritage of Gilgit". visitgilgitbaltistan.gov.pk. Gov.Pk. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
Bibliography
- Pakistan Trekking Guide, by Isobel and Ben Shaw, 1993.
- Wang, S. (2004). "Of Rivers and Human Rights: the Northern Areas, Pakistan's Forgotten Colony in Jammu and Kashmir". International Journal on Minority and Group Rights. 11: 187. doi:10.1163/1571811041631272.
- Matthias Naumann; Andrea Fischer-Tahir (12 January 2013), Peripheralization: The Making of Spatial Dependencies and Social Injustice, Springer Science & Business Media, ISBN 978-3-531-19018-1
- Spencer C. Tucker; Priscilla Roberts (12 May 2008), The Encyclopedia of the Arab-Israeli Conflict: A Political, Social, and Military History [4 volumes]: A Political, Social, and Military History, ABC-CLIO, ISBN 978-1-85109-842-2
- Bangash, Yaqoob Khan (2010), "Three Forgotten Accessions: Gilgit, Hunza and Nagar", The Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History, 38 (1): 117–143, doi:10.1080/03086530903538269, (subscription required (help))
- Bansal, Alok (2007), "In Pursuit of Forced Assimilation: Sectarian and Ethnic Marginalisation in Gilgit-Baltistan", India Quarterly: A Journal of International Affairs, 63 (2): 56–80, doi:10.1177/097492840706300203, (subscription required (help))
- Burki, Shahid Javed (2015), Historical Dictionary of Pakistan, Rowman & Littlefield, p. 228, ISBN 978-1-4422-4148-0
- Behera, Navnita Chadha (2007), Demystifying Kashmir, Pearson Education India, ISBN 81-317-0846-2
- Bouzas, Antia Mato (12 January 2013), "Securitization and Development as Modes of Peripheralization in North-Eastern Pakistan", in Matthias Naumann; Andrea Fischer-Tahir, Peripheralization: The Making of Spatial Dependencies and Social Injustice, Springer Science & Business Media, pp. 77–98, ISBN 978-3-531-19018-1
- Hussain, Shafqat (2015), Remoteness and Modernity: Transformation and Continuity in Northern Pakistan, Yale University Press, p. 14, ISBN 978-0-300-20555-8
- International Crisis Group (2007), Discord in Pakistan's Northern Areas (PDF), Brussels: International Crisis Group
- Mahmud, Ershad (2008), "The Gilgit-Baltistan Reforms Package 2007: Background, Phases and Analysis", Policy Perspectives, 5 (1): 23–40, JSTOR 42909184
- Raman, B. (2009), "The Northern Areas of Jammu and Kashmir", in K. Warikoo, Himalayan Frontiers of India: Historical, Geo-Political and Strategic Perspectives, Routledge, pp. 78–88, ISBN 978-1-134-03294-5
- Schofield, Victoria (2003) [First published in 2000], Kashmir in Conflict, London and New York: I. B. Taurus & Co, ISBN 1-86064-898-3
- Sahni, Sat Paul (2009), "The Ceasefire Line and Line of Control in Jammu and Kashmir: Evolution of a border", in K. Warikoo, Himalayan Frontiers of India: Historical, Geo-Political and Strategic Perspectives, Routledge, pp. 67–77, ISBN 978-1-134-03294-5
- Singh, Priyanka (2013), Gilgit Baltistan: Between Hope and Despair, New Delhi: Institute for Defence Studies and Analyses, ISBN 978-93-82169-13-0
- Snedden, Christopher (2013) [first published as The Untold Story of the People of Azad Kashmir, 2012], Kashmir: The Unwritten History, HarperCollins India, ISBN 93-5029-898-8
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gilgit-Baltistan. |
- Official Website of the Gilgit-Baltistan Council
- Official Website of the Government of Gilgit-Baltistan
- Official Tourism Website of the Government of Gilgit-Baltistan
- Official Website of Ministry of Kashmir & Gilgit Baltistan
- Gilgit-Baltistan at DMOZ
 Gilgit-Baltistan travel guide from Wikivoyage
Gilgit-Baltistan travel guide from Wikivoyage
 |
|
 | ||
| |
|
| ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| |
|
.jpg)
.jpg)