Rabies
| Rabies | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A dog with rabies in the paralytic (post-furious) stage | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| ICD-10 | A82 |
| DiseasesDB | 11148 |
| MedlinePlus | 001334 |
| eMedicine | med/1374 eerg/493 ped/1974 |
| Patient UK | Rabies |
| MeSH | D011818 |
| Orphanet | 770 |
Rabies is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the brain in humans and other mammals.[1] Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure.[1] These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: violent movements, uncontrolled excitement, fear of water, an inability to move parts of the body, confusion, and loss of consciousness.[1] Once symptoms appear, the result is nearly always death.[1] The time period between contracting the disease and the start of symptoms is usually one to three months; however, this time period can vary from less than one week to more than one year.[1] The time is dependent on the distance the virus must travel to reach the central nervous system.[2]
Rabies is caused by lyssaviruses, including rabies virus and Australian bat lyssavirus.[3] Rabies is spread when an infected animal scratches or bites another animal or human.[1] Saliva from an infected animal can also transmit rabies if the saliva comes into contact with the eyes, mouth, or nose.[1] Globally, dogs are the most common animal involved.[1] More than 99% of rabies cases in countries where dogs commonly have the disease are caused by dog bites.[4] In the Americas, bat bites are the most common source of rabies infections in humans, and less than 5% of cases are from dogs.[1][4] Rodents are very rarely infected with rabies.[4] The rabies virus travels to the brain by following the peripheral nerves. The disease can only be diagnosed after the start of symptoms.[1]
Animal control and vaccination programs have decreased the risk of rabies from dogs in a number of regions of the world.[1] Immunizing people before they are exposed is recommended for those who are at high risk. The high-risk group includes people who work with bats or who spend prolonged periods in areas of the world where rabies is common.[1] In people who have been exposed to rabies, the rabies vaccine and sometimes rabies immunoglobulin are effective in preventing the disease if the person receives the treatment before the start of rabies symptoms.[1] Washing bites and scratches for 15 minutes with soap and water, povidone iodine, or detergent may reduce the number of viral particles and may be somewhat effective at preventing transmission.[1][5] Only five people have survived a rabies infection after showing symptoms, and this was with extensive treatment known as the Milwaukee protocol.[6][7]
Rabies causes about 24,000 to 60,000 deaths worldwide per year.[8][9] More than 95% of human deaths caused by rabies occur in Africa and Asia.[1] Rabies is present in more than 150 countries and on all continents but Antarctica.[1] More than 3 billion people live in regions of the world where rabies occurs.[1] A number of countries, including Australia, Canada, Japan, and the United States, and Western Europe, do not have rabies among dogs.[10][11] Many small island nations do not have rabies at all.[12]
Signs and symptoms

The period between infection and the first symptoms (incubation period) is typically 1–3 months in humans.[8] Incubation periods as short as four days and longer than six years have been documented, depending on the location and severity of the contaminated wound and the amount of virus introduced.[8] Initial signs and symptoms of rabies are often nonspecific such as fever and headache.[8] As rabies progresses and causes inflammation of the brain and/or meninges, signs and symptoms can include slight or partial paralysis, anxiety, insomnia, confusion, agitation, abnormal behavior, paranoia, terror, and hallucinations, progressing to delirium, and coma.[2][8] The person may also have hydrophobia.[1]
Death usually occurs 2 to 10 days after first symptoms. Survival is rare once symptoms have presented,[8] even with the administration of proper and intensive care.[13] Jeanna Giese, who in 2004 was the first patient treated with the Milwaukee protocol,[14] became the first person ever recorded to have survived rabies without receiving successful post-exposure prophylaxis. An intention-to-treat analysis has since found this protocol has a survival rate of about 8%.[15]
Hydrophobia

Hydrophobia ("fear of water") is the historic name for rabies.[16] It refers to a set of symptoms in the later stages of an infection in which the person has difficulty swallowing, shows panic when presented with liquids to drink, and cannot quench his or her thirst. Any mammal infected with the virus may demonstrate hydrophobia.[17]
Saliva production is greatly increased, and attempts to drink, or even the intention or suggestion of drinking, may cause excruciatingly painful spasms of the muscles in the throat and larynx. This can be attributed to the fact that the virus multiplies and assimilates in the salivary glands of the infected animal for the purpose of further transmission through biting. The ability to transmit the virus would decrease significantly if the one infected could swallow saliva and water.[18]
Hydrophobia is commonly associated with furious rabies, which affects 80% of the infected people. The remaining 20% may experience a paralytic form of rabies that is marked by muscle weakness, loss of sensation, and paralysis; this form of rabies does not usually cause fear of water.[17]
Cause
Rabies is caused by a number of lyssaviruses including: rabies virus and Australian bat lyssavirus.[3]
The rabies virus is the type species of the Lyssavirus genus, in the family Rhabdoviridae, order Mononegavirales. Lyssavirions have helical symmetry, with a length of about 180 nm and a cross-section of about 75 nm.[19] These virions are enveloped and have a single-stranded RNA genome with negative sense. The genetic information is packed as a ribonucleoprotein complex in which RNA is tightly bound by the viral nucleoprotein. The RNA genome of the virus encodes five genes whose order is highly conserved: nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), matrix protein (M), glycoprotein (G), and the viral RNA polymerase (L).[20]
Once within a muscle or nerve cell, the virus undergoes replication. The trimeric spikes on the exterior of the membrane of the virus interact with a specific cell receptor, the most likely one being the acetylcholine receptor. The cellular membrane pinches in a procession known as pinocytosis and allows entry of the virus into the cell by way of an endosome. The virus then uses the acidic environment, which is necessary, of that endosome and binds to its membrane simultaneously, releasing its five proteins and single strand RNA into the cytoplasm.[21]
The L protein then transcribes five mRNA strands and a positive strand of RNA all from the original negative strand RNA using free nucleotides in the cytoplasm. These five mRNA strands are then translated into their corresponding proteins (P, L, N, G and M proteins) at free ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Some proteins require post-translative modifications. For example, the G protein travels through the rough endoplasmic reticulum, where it undergoes further folding, and is then transported to the Golgi apparatus, where a sugar group is added to it (glycosylation).[21]
Where there are enough proteins, the viral polymerase will begin to synthesize new negative strands of RNA from the template of the positive strand RNA. These negative strands will then form complexes with the N, P, L and M proteins and then travel to the inner membrane of the cell, where a G protein has embedded itself in the membrane. The G protein then coils around the N-P-L-M complex of proteins taking some of the host cell membrane with it, which will form the new outer envelope of the virus particle. The virus then buds from the cell.[21]
From the point of entry, the virus is neurotropic, traveling quickly along the neural pathways into the central nervous system. The virus usually first infects muscle cells close to the site of infection, where they are able to replicate without being 'noticed' by the host's immune system. Once enough virus has been replicated, they begin to bind to acetyl choline receptors (p75NR) at the neuromuscular junction.[22] The virus then travels through the nerve cell axon via retrograde transport, as its P protein interacts with dynein, a protein present in the cytoplasm of nerve cells. Once the virus reaches the cell body it travels rapidly to the Central Nervous System (CNS), replicating in motor neurons and eventually reaching the brain.[2] After the brain is infected, the virus travels centrifugally to the peripheral and autonomic nervous systems, eventually migrating to the salivary glands, where it is ready to be transmitted to the next host.[23]:317
Transmission
All warm-blooded species, including humans, may become infected with the rabies virus and develop symptoms. Birds were first artificially infected with rabies in 1884; however, infected birds are largely if not wholly asymptomatic, and recover.[24] Other bird species have been known to develop rabies antibodies, a sign of infection, after feeding on rabies-infected mammals.[25][26]
The virus has also adapted to grow in cells of poikilothermic ("cold-blooded") vertebrates.[27][28] Most animals can be infected by the virus and can transmit the disease to humans. Infected bats,[29][30] monkeys, raccoons, foxes, skunks, cattle, wolves, coyotes, dogs, mongooses (normally yellow mongoose)[31] and cats present the greatest risk to humans.
Rabies may also spread through exposure to infected bears, domestic farm animals, groundhogs, weasels, and other wild carnivorans. Lagomorphs, such as hares and rabbits, and small rodents such as chipmunks, gerbils, guinea pigs, hamsters, mice, rats, and squirrels, are almost never found to be infected with rabies and are not known to transmit rabies to humans.[32] Bites from mice, rats, or squirrels rarely require rabies prevention because these rodents are typically killed by any encounter with a larger, rabid animal, and would, therefore, not be carriers.[33] The Virginia opossum is resistant but not immune to rabies.[34]
The virus is usually present in the nerves and saliva of a symptomatic rabid animal.[35][36] The route of infection is usually, but not always, by a bite. In many cases, the infected animal is exceptionally aggressive, may attack without provocation, and exhibits otherwise uncharacteristic behavior.[37] This is an example of a viral pathogen modifying the behavior of its host to facilitate its transmission to other hosts.
Transmission between humans is extremely rare. A few cases have been recorded through transplant surgery.[38] The only well-documented cases of rabies caused by human-to-human transmission occurred among eight recipients of transplanted corneas and among three recipients of solid organs.[39] In addition to transmission from cornea and organ transplants, bite and non-bite exposures inflicted by infected humans could theoretically transmit rabies, but no such cases have been documented, since infected humans are usually hospitalized and necessary precautions taken. Casual contact, such as touching a person with rabies or contact with non-infectious fluid or tissue (urine, blood, feces) does not constitute an exposure and does not require post-exposure prophylaxis. Additionally, as the virus is present in sperm or vaginal secretions, spread through sex may be possible.[40]
After a typical human infection by bite, the virus enters the peripheral nervous system. It then travels along the afferent nerves toward the central nervous system.[41] During this phase, the virus cannot be easily detected within the host, and vaccination may still confer cell-mediated immunity to prevent symptomatic rabies. When the virus reaches the brain, it rapidly causes encephalitis, the prodromal phase, which is the beginning of the symptoms. Once the patient becomes symptomatic, treatment is almost never effective and mortality is over 99%. Rabies may also inflame the spinal cord, producing transverse myelitis.[42][43]
Diagnosis
Rabies can be difficult to diagnose, because, in the early stages, it is easily confused with other diseases or with aggressiveness.[44] The reference method for diagnosing rabies is the fluorescent antibody test (FAT), an immunohistochemistry procedure, which is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO).[45] The FAT relies on the ability of a detector molecule (usually fluorescein isothiocyanate) coupled with a rabies-specific antibody, forming a conjugate, to bind to and allow the visualisation of rabies antigen using fluorescent microscopy techniques. Microscopic analysis of samples is the only direct method that allows for the identification of rabies virus-specific antigen in a short time and at a reduced cost, irrespective of geographical origin and status of the host. It has to be regarded as the first step in diagnostic procedures for all laboratories. Autolysed samples can, however, reduce the sensitivity and specificity of the FAT.[46] The RT PCR assays proved to be a sensitive and specific tool for routine diagnostic purposes,[47] particularly in decomposed samples[48] or archival specimens.[49] The diagnosis can be reliably made from brain samples taken after death. The diagnosis can also be made from saliva, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid samples, but this is not as sensitive and reliable as brain samples.[46] Cerebral inclusion bodies called Negri bodies are 100% diagnostic for rabies infection but are found in only about 80% of cases.[19] If possible, the animal from which the bite was received should also be examined for rabies.[50]
Cheaper rabies diagnosis will become possible for low-income settings: accurate rabies diagnosis can be done at a tenth of the cost of traditional testing using basic light microscopy techniques.[51] In Germany as of July 2016, rabies test strips, made by 6 companies, had high false-negative, suggesting that some manufacturers had poor quality control. The kits were made by companies in China, Germany, India, South Korea and the United States, and cost $3 to $11.[52]
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis in a case of suspected human rabies may initially include any cause of encephalitis, in particular infection with viruses such as herpesviruses, enteroviruses, and arboviruses such as West Nile virus. The most important viruses to rule out are herpes simplex virus type one, varicella zoster virus, and (less commonly) enteroviruses, including coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, polioviruses, and human enteroviruses 68 to 71.[53]
New causes of viral encephalitis are also possible, as was evidenced by the 1999 outbreak in Malaysia of 300 cases of encephalitis with a mortality rate of 40% caused by Nipah virus, a newly recognized paramyxovirus.[54] Likewise, well-known viruses may be introduced into new locales, as is illustrated by the outbreak of encephalitis due to West Nile virus in the eastern United States.[55] Epidemiologic factors, such as season, geographic location, and the patient's age, travel history, and possible exposure to bites, rodents, and ticks, may help direct the diagnosis.
Prevention
Almost all human cases of rabies were fatal until a vaccine was developed in 1885 by Louis Pasteur and Émile Roux. Their original vaccine was harvested from infected rabbits, from which the virus in the nerve tissue was weakened by allowing it to dry for five to ten days.[56] Similar nerve tissue-derived vaccines are still used in some countries, as they are much cheaper than modern cell culture vaccines.[57]
The human diploid cell rabies vaccine was started in 1967. Less expensive purified chicken embryo cell vaccine and purified vero cell rabies vaccine are now available.[50] A recombinant vaccine called V-RG has been used in Belgium, France, Germany, and the United States to prevent outbreaks of rabies in undomesticated animals.[58] Immunization before exposure has been used in both human and nonhuman populations, where, as in many jurisdictions, domesticated animals are required to be vaccinated.[59]
The number of recorded human deaths from rabies in the United States has dropped from 100 or more annually in the early 20th century to one or two per year due to widespread vaccination of domestic dogs and cats and the development of human vaccines and immunoglobulin treatments. Most deaths now result from bat bites, which may go unnoticed by the victim and hence untreated.[60]
The Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services Communicable Disease Surveillance 2007 Annual Report states the following can help reduce the risk of contracting rabies:[61]
- Vaccinating dogs, cats, and ferrets against rabies
- Keeping pets under supervision
- Not handling wild animals or strays
- Contacting an animal control officer upon observing a wild animal or a stray, especially if the animal is acting strangely
- If bitten by an animal, washing the wound with soap and water for 10 to 15 minutes and contacting a healthcare provider to determine if post-exposure prophylaxis is required
September 28 is World Rabies Day, which promotes the information, prevention, and elimination of the disease.[62]
Treatment
Treatment after exposure can prevent the disease if administered promptly, generally within 10 days of infection.[19] Thoroughly washing the wound as soon as possible with soap and water for approximately five minutes is effective in reducing the number of viral particles.[63] Povidone-iodine or alcohol is then recommended to reduce the virus further.[64]
In the US, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends people receive one dose of human rabies immunoglobulin (HRIG) and four doses of rabies vaccine over a 14-day period.[65] The immunoglobulin dose should not exceed 20 units per kilogram body weight. HRIG is expensive and constitutes most of the cost of post exposure treatment, ranging as high as several thousand dollars.[66] As much as possible of this dose should be injected around the bites, with the remainder being given by deep intramuscular injection at a site distant from the vaccination site.[21]
The first dose of rabies vaccine is given as soon as possible after exposure, with additional doses on days three, seven and 14 after the first. Patients who have previously received pre-exposure vaccination do not receive the immunoglobulin, only the postexposure vaccinations on days 0 and 3.[67]
The pain and side effects of modern cell-based vaccines are similar to flu shots. The old nerve-tissue-based vaccinations that require multiple painful injections into the abdomen with a large needle are inexpensive, but are being phased out and replaced by affordable World Health Organization intradermal-vaccination regimens.[50]
Intramuscular vaccination should be given into the deltoid, not the gluteal area, which has been associated with vaccination failure due to injection into fat rather than muscle. In infants, the lateral thigh is recommended.[68]
Awakening to find a bat in the room, or finding a bat in the room of a previously unattended child or mentally disabled or intoxicated person, is regarded as an indication for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP). The recommendation for the precautionary use of PEP in occult bat encounters where no contact is recognized has been questioned in the medical literature, based on a cost–benefit analysis.[69] However, a 2002 study has supported the protocol of precautionary administering of PEP where a child or mentally compromised individual has been alone with a bat, especially in sleep areas, where a bite or exposure may occur without the victim being aware.[70] Begun with little or no delay, PEP is 100% effective against rabies.[14] In the case in which there has been a significant delay in administering PEP, the treatment should be administered regardless, as it may still be effective.[21]
Induced coma
In 2004, American teenager Jeanna Giese survived an infection of rabies unvaccinated. She was placed into an induced coma upon onset of symptoms and given ketamine, midazolam, ribavirin, and amantadine. Her doctors administered treatment based on the hypothesis that detrimental effects of rabies were caused by temporary dysfunctions in the brain and could be avoided by inducing a temporary partial halt in brain function that would protect the brain from damage while giving the immune system time to defeat the virus. After 31 days of isolation and 76 days of hospitalization, Giese was released from the hospital.[71] She survived with all higher level brain functions, but an inability to walk and balance.[72] On a podcast of NPR's Radiolab, Giese recounted: "I had to learn how to stand and then to walk, turn around, move my toes. I was really, after rabies, a new born baby who couldn't do anything. I had to relearn that all...mentally I knew how to do stuff but my body wouldn't cooperate with what I wanted it to do. It definitely took a toll on me psychologically. You know I'm still recovering. I'm not completely back. Stuff like balance, and I can't run normally."[73]
Giese's treatment regimen became known as the Milwaukee protocol, which has since undergone revision with the second version omitting the use of ribavirin. Two of 25 patients survived when treated under the first protocol. A further 10 patients have been treated under the revised protocol, with a further two survivors.[15]
On June 12, 2011, Precious Reynolds, an eight-year-old girl from Humboldt County, California, became the third reported person in the United States to have recovered from rabies without receiving PEP.[74]
Prognosis
In unvaccinated humans, rabies is almost always fatal after neurological symptoms have developed.[75]
Vaccination after exposure, PEP, is highly successful in preventing the disease if administered promptly, in general within 6 days of infection. Begun with little or no delay, PEP is 100% effective against rabies.[14] In the case of significant delay in administering PEP, the treatment still has a chance of success.[21]
Five of the first 43 patients (12%) treated with the Milwaukee protocol survived, and those receiving treatment survived longer than those not receiving the treatment.[76]
Epidemiology

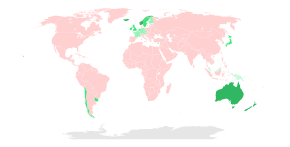
rabies eliminated before 1990
rabies eliminated in or after 1990
year of rabies elimination unknown
In 2010, an estimated 26,000 people died from rabies, down from 54,000 in 1990.[77] The majority of the deaths occurred in Asia and Africa.[75] India has the highest rate of human rabies in the world, primarily because of stray dogs,[78] whose number has greatly increased since a 2001 law forbade the killing of dogs.[79] Effective control and treatment of rabies in India is also hindered by a form of mass hysteria known as puppy pregnancy syndrome (PPS). Dog bite victims with PPS (both male and female) become convinced that puppies are growing inside them, and often seek help from faith healers rather than from conventional medical services. In cases where the bite was from a rabid dog, this decision can prove fatal. Dr. Nitai Kishore Marik, former district medical officer of West Midnapur, states "I have seen scores of cases of rabies that reached our hospitals very late because of the intervention of faith healers. We could not save those lives."[80] An estimated 20,000 people die every year from rabies in India — more than a third of the global toll.[79] As of 2015, China had the second-highest number of cases (approximately 6,000), followed by the Democratic Republic of the Congo (5,600).[81]
The rabies virus survives in widespread, varied, rural animal reservoirs. Despite Australia's official rabies-free status,[82] Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV), discovered in 1996, is a strain of rabies prevalent in native bat populations. There have been three human cases of ABLV in Australia, all of them fatal.
In Asia and in parts of the Americas and Africa, dogs remain the principal host. Mandatory vaccination of animals is less effective in rural areas. Especially in developing countries, pets may not be privately kept and their destruction may be unacceptable. Oral vaccines can be safely distributed in baits, a practice that has successfully reduced rabies in rural areas of Canada, France, and the United States. In Montréal, Quebec, Canada, baits are successfully used on raccoons in the Mont-Royal Park area. Vaccination campaigns may be expensive, and cost-benefit analysis suggests baits may be a cost-effective method of control.[83] In Ontario, a dramatic drop in rabies was recorded when an aerial bait-vaccination campaign was launched.[84]
Rabies is common among wild animals in the US. Bats, raccoons, skunks and foxes account for almost all reported cases (98% in 2009). Rabid bats are found in all 48 contiguous states. Other reservoirs are more limited geographically; for example, the raccoon rabies virus variant is only found in a relatively narrow band along the East Coast. Due to a high public awareness of the virus, efforts at vaccination of domestic animals and curtailment of feral populations, and availability of postexposure prophylaxis, incidents of rabies in humans are very rare. A total of 49 cases of the disease was reported in the country between 1995 and 2011; of these, 11 are thought to have been acquired abroad. Almost all domestically acquired cases are attributed to bat bites.[85]
In Switzerland, the disease has been virtually eliminated after scientists placed chicken heads laced with live attenuated vaccine in the Swiss Alps.[84] The foxes of Switzerland, proven to be the main source of rabies in the country, ate the chicken heads and immunized themselves.[84]
Italy, after being declared rabies-free from 1997 to 2008, has witnessed a reemergence of the disease in wild animals in the Triveneto regions (Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Veneto and Friuli-Venezia Giulia), due to the spreading of an epidemic in the Balkans that hit Austria too. An extensive wild animals vaccination campaign eliminated the virus from Italy again, and it regained the rabies-free country status in 2013, the last reported case of rabies being reported in a red fox in early 2011.[86][87]
History

Rabies has been known since around 2000 B.C.[88] The first written record of rabies is in the Mesopotamian Codex of Eshnunna (circa 1930 BC), which dictates that the owner of a dog showing symptoms of rabies should take preventive measure against bites. If another person were bitten by a rabid dog and later died, the owner was heavily fined.[89]
Ineffective folk remedies abounded in the medical literature of the ancient world. The physician Scribonius Largus prescribed a poultice of cloth and hyena skin; Antaeus recommended a preparation made from the skull of a hanged man.[90]
Rabies appears to have originated in the Old World, the first epizootic in the New World occurring in Boston in 1768.[91] It spread from there, over the next few years, to various other states, as well as to the French West Indies, eventually becoming common all across North America.
Rabies was considered a scourge for its prevalence in the 19th century. In France and Belgium, where Saint Hubert was venerated, the "St Hubert's Key" was heated and applied to cauterize the wound. By an application of magical thinking, dogs were branded with the key in hopes of protecting them from rabies. The fear of rabies was almost irrational, due to the insignificant number of vectors (mostly rabid dogs) and the absence of any efficacious treatment. It was not uncommon for a person bitten by a dog but merely suspected of being rabid, to commit suicide or to be killed by others.[92] This gave Louis Pasteur ample opportunity to test postexposure treatments from 1885.[8] In ancient times, the attachment of the tongue (the lingual frenulum, a mucous membrane) was cut and removed as this is where rabies was thought to originate. This practice ceased with the discovery of the actual cause of rabies.[23]
In modern times, the fear of rabies has not diminished, and the disease and its symptoms, particularly agitation has served as an inspiration for several works of zombie or similarly-themed fiction, often portraying rabies as having mutated into a stronger virus which fills humans with murderous rage or uncurable illness, bringing about a devastating, widespread pandemic.[93]
Etymology
The term is derived from the Latin rabies, "madness".[94] This, in turn, may be related to the Sanskrit rabhas, "to do violence".[95] The Greeks derived the word lyssa, from lud or "violent"; this root is used in the name of the genus of rabies Lyssavirus.[92]
Other animals
Rabies is infectious to mammals; three stages are recognized. The first stage is a one- to three-day period characterized by behavioral changes and is known as the prodromal stage. The second is the excitative stage, which lasts three to four days. This stage is often known as "furious rabies" for the tendency of the affected animal to be hyper-reactive to external stimuli and bite at anything near. The third is the paralytic stage and is caused by damage to motor neurons. Incoordination is seen, owing to rear limb paralysis, and drooling and difficulty swallowing is caused by paralysis of facial and throat muscles. Death is usually caused by respiratory arrest.[96]
Research
Rabies has the advantage over other pseudotyping methods for gene delivery in that the cell-targeting (tissue tropism) is more specific for difficult-to-reach sites, such as the central nervous system without invasive delivery methods, as well as being capable of retrograde tracing (i.e., going against the flow of information at synapses) in neuronal circuits.[97]
Evidence indicates artificially increasing the permeability of the blood–brain barrier, which normally does not allow most immune cells across, promotes viral clearance.[98][99]
See also
- Global Alliance for Rabies Control
- Neglected tropical diseases
- Rabies in popular culture
- World Rabies Day
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 "Rabies Fact Sheet N°99". World Health Organization. July 2013. Retrieved 28 February 2014.
- 1 2 3 Cotran RS, Kumar V, Fausto N (2005). Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (7th ed.). Elsevier/Saunders. p. 1375. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- 1 2 "Rabies, Australian bat lyssavirus and other lyssaviruses". The Department of Health. Dec 2013. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- 1 2 3 Tintinalli, Judith E. (2010). Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (Emergency Medicine (Tintinalli)). McGraw-Hill. pp. Chapter 152. ISBN 0-07-148480-9.
- ↑ William H. Wunner (2010). Rabies: Scientific Basis of the Disease and Its Management. Academic Press. p. 556. ISBN 9780080550091.
- ↑ Hemachudha T, Ugolini G, Wacharapluesadee S, Sungkarat W, Shuangshoti S, Laothamatas J (May 2013). "Human rabies: neuropathogenesis, diagnosis, and management.". Lancet neurology. 12 (5): 498–513. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(13)70038-3. PMID 23602163.
- ↑ "UC Davis Children's Hospital patient becomes third person in U.S. to survive rabies". UC Davis Medical Center. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Giesen, A; Gniel, D; Malerczyk, C (March 2015). "30 Years of rabies vaccination with Rabipur: a summary of clinical data and global experience". Expert Review of Vaccines (Review). 14 (3): 351–67. doi:10.1586/14760584.2015.1011134. PMID 25683583.
- ↑ GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (10 January 2015). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet (London, England). 385 (9963): 117–71. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604
 . PMID 25530442.
. PMID 25530442. - ↑ WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies : second report. (PDF) (2 ed.). Geneva: WHO. 2013. p. 3. ISBN 9789241209823.
- ↑ "Penang on rabies alert". The Star. September 17, 2015. Retrieved 19 September 2015.
- ↑ "Rabies-Free Countries and Political Units". CDC. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- ↑ Rupprecht CE, Willoughby R, Slate D (2006). "Current and future trends in the prevention, treatment and control of rabies". Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy. 4 (6): 1021–38. doi:10.1586/14787210.4.6.1021. PMID 17181418.
- 1 2 3 Jordan Lite (2008-10-08). "Medical Mystery: Only One Person Has Survived Rabies without Vaccine—But How?". Scientific American. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- 1 2 Willoughby RE (2009). "Are we getting closer to the treatment of rabies?: medical benchmarks". Future Virology. MedScape. 4 (6): 563–70. doi:10.2217/fvl.09.52.
- ↑ Smallman-Raynor, Andrew Cliff, Peter Haggett, Matthew (2004). World atlas of epidemic diseases. London: Arnold. p. 51. ISBN 9780340761717.
- 1 2 "Symptoms of rabies". NHS.uk. June 12, 2012. Retrieved 3 September 2014.
- ↑ "Rabies". AnimalsWeCare.com.
- 1 2 3 Drew WL (2004). "Chapter 41: Rabies". In Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 597–600. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
- ↑ Finke S, Conzelmann KK (August 2005). "Replication strategies of rabies virus". Virus Res. 111 (2): 120–31. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.004. PMID 15885837.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Rabies Post-Exposure Prophylaxis". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2009-12-23. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- ↑ Gluska, Shani & Zahavi, Eitan Erez & Chein, Michael & Gradus, Tal & Bauer, Anja & Finke, Stefan & Perlson, Eran (August 28, 2014). "Rabies Virus Hijacks and Accelerates the p75NTR Retrograde Axonal Transport Machinery". PLOS Pathogens. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004348.
- 1 2 Baer, George (1991). The Natural History of Rabies. CRC Press. ISBN 9780849367601. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ↑ Shannon LM, Poulton JL, Emmons RW, Woodie JD, Fowler ME (April 1988). "Serological survey for rabies antibodies in raptors from California". J. Wildl. Dis. 24 (2): 264–7. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-24.2.264. PMID 3286906.
- ↑ Gough PM, Jorgenson RD (1976). "Rabies antibodies in sera of wild birds". Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 12 (3): 392–5. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-12.3.392. PMID 16498885.
- ↑ Jorgenson RD, Gough PM (July 1976). "Experimental rabies in a great horned owl". J. Wildl. Dis. 12 (3): 444–7. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-12.3.444.
- ↑ Wong, Derek. "Rabies". Wong's Virology. Retrieved 19 Mar 2009.
- ↑ Campbell, James B.; Charlton, K.M. (1988). Developments in Veterinary Virology: Rabies. Springer. p. 48. ISBN 0-89838-390-0.
- ↑ Pawan JL (1959). "The transmission of paralytic rabies in Trinidad by the vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus murinus Wagner". Caribbean Medical Journal. 21: 110–36. PMID 13858519.
- ↑ Pawan JL (1959). "Rabies in the vampire bat of Trinidad, with special reference to the clinical course and the latency of infection". Caribbean Medical Journal. 21: 137–56. PMID 14431118.
- ↑ Taylor PJ (December 1993). "A systematic and population genetic approach to the rabies problem in the yellow mongoose (Cynictis penicillata)". The Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research. 60 (4): 379–87. PMID 7777324.
- ↑ "Rabies. Other Wild Animals: Terrestrial carnivores: raccoons, skunks and foxes.". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC). Retrieved 2010-12-23.
- ↑ Anderson, Janet & Frey, Rebecca (2006). "Rabies". Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine (3rd ed.).
- ↑ McRuer DL, Jones KD (May 2009). "Behavioral and nutritional aspects of the Virginian opossum (Didelphis virginiana)". The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Exotic Animal Practice. 12 (2): 217–36, viii. doi:10.1016/j.cvex.2009.01.007. PMID 19341950.
- ↑ The Merck Manual (11th ed.). 1983. p. 183.
- ↑ The Merck manual of Medical Information (Second Home ed.). 2003. p. 484.
- ↑ Turton, Jenny (2000). "Rabies: a killer disease". National Department of Agriculture.
- ↑ Srinivasan A, Burton EC, Kuehnert MJ, Rupprecht C, Sutker WL, Ksiazek TG, Paddock CD, Guarner J, Shieh WJ, Goldsmith C, Hanlon CA, Zoretic J, Fischbach B, Niezgoda M, El-Feky WH, Orciari L, Sanchez EQ, Likos A, Klintmalm GB, Cardo D, LeDuc J, Chamberland ME, Jernigan DB, Zaki SR (March 2005). "Transmission of rabies virus from an organ donor to four transplant recipients" (PDF). N Engl J Med. 352 (11): 1103–11. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043018. PMID 15784663.
- ↑ "Exposure to the Virus".
- ↑ RabiesAlliance.org
- ↑ Jackson, Alan C.; Wunner, William H. (2002). Rabies. Academic Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-12-379077-4.
- ↑ Lynn DJ, Newton HB, Rae-Grant AD (2012). The 5-Minute Neurology Consult. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 414–. ISBN 978-1-4511-0012-9.
- ↑ Davis, Larry Ernest & King, Molly K. & Schultz, Jessica L. (June 15, 2005). Fundamentals of neurologic disease. Demos Medical Publishing. p. 73. ISBN 978-1-888799-84-2.
- ↑ Cynthia M.; Kahn, BA, eds. (2010). The Merck Veterinary Manual (10th ed.). Kendallville, Indiana: Courier Kendallville, Inc. p. 1193. ISBN 0-911910-93-X.
- ↑ Dean, D.J.; Abelseth, M.K. (1973). "Ch. 6: The fluorescent antibody test". In Kaplan, M.M.; Koprowski, H. Laboratory techniques in rabies. Monograph series. 23 (3rd ed.). World Health Organization. p. 73.
- 1 2 Fooks AR, Johnson N, Freuling CM, Wakeley PR, Banyard AC, McElhinney LM, Marston DA, Dastjerdi A, Wright E, Weiss RA, Müller T (2009). "Emerging technologies for the detection of rabies virus: challenges and hopes in the 21st century". PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 3 (9): e530. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000530. PMC 2745658
 . PMID 19787037.
. PMID 19787037. - ↑ Tordo, N; Bourhy, H; Sacramento, D (1994). "Ch. 10: PCR technology for lyssavirus diagnosis". In Clewley, J.P. The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for Human Viral Diagnosis. CRC Press. pp. 125–145. ISBN 978-0-8493-4833-4.
- ↑ David D, Yakobson B, Rotenberg D, Dveres N, Davidson I, Stram Y (2002). "Rabies virus detection by RT-PCR in decomposed naturally infected brains". Veterinary Microbiology. 87 (2): 111–8. doi:10.1016/s0378-1135(02)00041-x. PMID 12034539.
- ↑ Biswal M, Ratho R, Mishra B (September 2007). "Usefulness of reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for detection of rabies RNA in archival samples". Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases. 60 (5): 298–9. PMID 17881871.
- 1 2 3 Ly S, Buchy P, Heng NY, Ong S, Chhor N, Bourhy H, Vong S (2009). Carabin H, ed. "Rabies situation in Cambodia" (PDF). PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 3 (9): e511. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000511. PMC 2731168
 . PMID 19907631. e511.
. PMID 19907631. e511. - ↑ Dürr S, Naïssengar S, Mindekem R, Diguimbye C, Niezgoda M, Kuzmin I, Rupprecht CE, Zinsstag J (2008). Cleaveland S, ed. "Rabies diagnosis for developing countries" (PDF). PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2 (3): e206. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000206. PMC 2268742
 . PMID 18365035. e206.
. PMID 18365035. e206. - ↑ http://www.nytimes.com/2016/07/05/health/rabies-test-strips.html?_r=0
- ↑ "Rabies: Differential Diagnoses & Workup". eMedicine Infectious Diseases. 2008-10-03. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- ↑ Taylor DH, Straw BE, Zimmerman JL, D'Allaire S (2006). Diseases of swine. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 463–5. ISBN 0-8138-1703-X. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- ↑ Minagar, Alireza; J. Steven Alexander (2005). Inflammatory Disorders Of The Nervous System: Pathogenesis, Immunology, and Clinical Management. Humana Press. ISBN 1-58829-424-2.
- ↑ Geison GL (April 1978). "Pasteur's work on rabies: Reexamining the ethical issues". Hastings Center Report. 8 (2): 26–33. doi:10.2307/3560403. JSTOR 3560403. PMID 348641.
- ↑ Srivastava AK, Sardana V, Prasad K, Behari M (March 2004). "Diagnostic dilemma in flaccid paralysis following anti-rabies vaccine". Neurol India. 52 (1): 132–3. PMID 15069272.
- ↑ Reece JF, Chawla SK (2006). "Control of rabies in Jaipur, India, by the sterilisation and vaccination of neighbourhood dogs". Vet Rec. 159 (12): 379–83. doi:10.1136/vr.159.12.379. PMID 16980523.
- ↑ "Compendium of Animal Rabies Prevention and Control" (PDF). National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians. 2007-12-31. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑ "Rabies in the U.S.". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). April 22, 2011. Retrieved December 31, 2011.
- ↑ 2007 Annual Report (PDF) (Report). Bureau of Communicable Disease Control and Prevention. 2007.
- ↑ "World Rabies Day". World Health Organization (WHO).
- ↑ "Rabies & Australian bat lyssavirus information sheet". Health.vic.gov.au. Retrieved 2012-01-30.
- ↑ National Center for Disease Control (2014). "National Guidelines on Rabies Prophylaxis" (pdf). Retrieved 5 September 2014.
- ↑ "Use of a Reduced (4-Dose) Vaccine Schedule for Postexposure Prophylaxis to Prevent Human Rabies". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- ↑ "Cost of Rabies Prevention".
- ↑ Park's textbook of Community medicine,22nd edition,2013,p 254
- ↑ "Rabies". www.who.int. World Health Organization. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- ↑ De Serres G, Skowronski DM, Mimault P, Ouakki M, Maranda-Aubut R, Duval B (2009). "Bats in the bedroom, bats in the belfry: Reanalysis of the rationale for rabies post-exposure prophylaxis". Clin Infect Dis. 48 (11): 1493–9. doi:10.1086/598998. PMID 19400689.
- ↑ Despond O, Tucci M, Decaluwe H, Grégoire MC, S Teitelbaum J, Turgeon N (March 2002). "Rabies in a nine-year-old child: The myth of the bite". Can J Infect Dis. 13 (2): 121–5. PMC 2094861
 . PMID 18159381.
. PMID 18159381. - ↑ Willoughby RE, Tieves KS, Hoffman GM, Ghanayem NS, Amlie-Lefond CM, Schwabe MJ, Chusid MJ, Rupprecht CE (June 2005). "Survival after treatment of rabies with induction of coma" (PDF). New England Journal of Medicine. 352 (24): 2508–14. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050382. PMID 15958806.
- ↑ Hu WT, Willoughby RE, Dhonau H, Mack KJ (August 2007). "Long-term follow-up after treatment of rabies by induction of coma" (PDF). New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (9): 945–6. doi:10.1056/NEJMc062479. PMID 17761604.
- ↑ "Rodney Versus Death". Radiolab. 13 August 2013.
- ↑ "UC Davis Children's Hospital patient becomes third person in US to survive rabies". Health News. 2011-06-12. Retrieved 2011-06-12.
- 1 2 "Rabies". World Health Organization (WHO). September 2011. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ↑ "Rabies Registry". Medical College of Wisconsin. 2005. Retrieved 29 December 2009.
- ↑ Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R et al. (Dec 15, 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010.". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. PMID 23245604.
- ↑ Dugan, Emily (2008-04-30). "Dead as a dodo? Why scientists fear for the future of the Asian vulture". The Independent. London. Retrieved 2008-10-11.
India now has the highest rate of human rabies in the world.
- 1 2 Harris, Gardiner (6 August 2012). "Where Streets Are Thronged With Strays Baring Fangs". New York Times. Retrieved 6 August 2012.
- ↑ Medicine challenges Indian superstition | Asia | DW.DE | 31.12.2012
- ↑ Hampson, Katie; Coudeville, Laurent; Lembo, Tiziana; Sambo, Maganga; Kieffer, Alexia; Attlan, Michaël; Barrat, Jacques; Blanton, Jesse D.; Briggs, Deborah J.; Cleaveland, Sarah; Costa, Peter; Freuling, Conrad M.; Hiby, Elly; Knopf, Lea; Leanes, Fernando; Meslin, François-Xavier; Metlin, Artem; Miranda, Mary Elizabeth; Müller, Thomas; Nel, Louis H.; Recuenco, Sergio; Rupprecht, Charles E.; Schumacher, Carolin; Taylor, Louise; Vigilato, Marco Antonio Natal; Zinsstag, Jakob; Dushoff, Jonathan (2015). "Estimating the Global Burden of Endemic Canine Rabies". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 9 (4): e0003709. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0003709. PMC 4400070
 . PMID 25881058.
. PMID 25881058. - ↑ "Essential rabies maps". World Health Organization (WHO).
- ↑ Meltzer MI (October–December 1996). "Assessing the costs and benefits of an oral vaccine for raccoon rabies: a possible model". Emerg Infect Dis. 2 (4): 343–9. doi:10.3201/eid0204.960411. PMC 2639934
 . PMID 8969251.
. PMID 8969251. - 1 2 3 Grambo, Rebecca L (1995). The World of the Fox. Vancouver: Greystone Books. pp. 94–5. ISBN 0-87156-377-0.
- ↑ "Rabies Surveillance Data in the United States". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- ↑ http://www.izsvenezie.com/rabies-in-africa-the-resolab-network/
- ↑ http://www.quotidianosanita.it/governo-e-parlamento/articolo.php?articolo_id=13650
- ↑ Adamson PB (1977). "The spread of rabies into Europe and the probable origin of this disease in antiquity". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 2 (2): 140–4. doi:10.1017/S0035869X00133829. JSTOR 25210880. PMID 11632333.
- ↑ Dunlop, Robert H; Williams, David J (1996). Veterinary Medicine: An Illustrated History. Mosby. ISBN 0-8016-3209-9.
- ↑ Barrett, Alan D.T.; Stanberry, Lawrence R. (2009). Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases. Academic Press. p. 612. ISBN 9780080919027. Retrieved 2016-01-08.
- ↑ The Natural History of Rabies
The first major epizootic in North America was reported in 1768, continuing until 1771 when foxes and dogs carried the disease to swine and domestic animals. The malady was so unusual that it was reported as a new disease - 1 2 Rotivel, Yolande. "Introduction". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved 2009-04-25.
- ↑ Than, Ker. ""Zombie Virus" Possible via Rabies-Flu Hybrid?". National Geographic. National Geographic. Retrieved 13 September 2015.
- ↑ Simpson DP (1979). Cassell's Latin Dictionary (5 ed.). London: Cassell. p. 883. ISBN 0-304-52257-0.
- ↑ Dalfardi, Behnam; Esnaashary, Mohammad Hosein; Yarmohammadi, Hassan (2014-02-17). "Rabies in medieval Persian literature – the Canon of Avicenna (980–1037 AD)". Infectious Diseases of Poverty. 3: 7. doi:10.1186/2049-9957-3-7. ISSN 2049-9957. PMC 3933285
 .
. - ↑ Ettinger, Stephen J; Feldman, Edward C (1995). Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine (4th ed.). W.B. Saunders Company. ISBN 0-7216-6795-3.
- ↑ Carpentier DC, Vevis K, Trabalza A, Georgiadis C, Ellison SM, Asfahani RI, Mazarakis ND (8 September 2011). "Enhanced pseudotyping efficiency of HIV-1 lentiviral vectors by a rabies/vesicular stomatitis virus chimeric envelope glycoprotein". Gene Therapy. 19 (7): 761–74. doi:10.1038/gt.2011.124. PMID 21900965.
- ↑ Roy A, Hooper DC (2007). "Lethal silver-haired bat rabies virus infection can be prevented by opening the blood–brain barrier". J. Virol. 81 (15): 7993–8. doi:10.1128/JVI.00710-07. PMC 1951307
 . PMID 17507463.
. PMID 17507463. - ↑ Roy A, Phares TW, Koprowski H, Hooper DC (2007). "Failure to open the blood–brain barrier and deliver immune effectors to central nervous system tissues leads to the lethal outcome of silver-haired bat rabies virus infection". J. Virol. 81 (3): 1110–8. doi:10.1128/JVI.01964-06. PMC 1797506
 . PMID 17108029.
. PMID 17108029.
Further reading
- George M. Baer, ed. (1991). The Natural History of Rabies (2 ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-0849367601.
- Jackson, Alan C.; William H. Wunner (2007). Rabies, Second Edition: Scientific Basis of the Disease and Its Management. London, UK: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0123693662.
- Murphy, Monica; Bill Wasik (26 July 2012). "Undead: The Rabies Virus Remains a Medical Mystery". Wired. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- "Rabies". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2 August 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- Wasik, Bill; Monica Murphy (2012). Rabid: A Cultural History of the World's Most Diabolical Virus. Viking. ISBN 978-0670023738.
- George M. Baer (2 December 2012). THE NATURAL HISTORY OF RABIES. Elsevier. p. 335. ISBN 978-0-323-13970-0.
- "Latent Rabies". N Engl J Med. 324: 1890–1891. June 27, 1991. doi:10.1056/NEJM199106273242611.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rabies. |
| Look up rabies in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Rabies at DMOZ
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR): Rhabdoviridae
- World Rabies Day
- OIE's Rabies Portal
- Aerophobia and Hydrophobia in Rabies Videos
- "Rabies virus". NCBI Taxonomy Browser. 11292.