Alphavirus
| Alphavirus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group IV ((+)ssRNA) |
| Order: | Unassigned |
| Family: | Togaviridae |
| Genus: | Alphavirus |
| Type species | |
| Sindbis virus | |
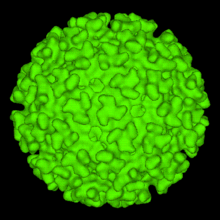
In biology and immunology, an alphavirus belongs to the group IV Togaviridae family of viruses, according to the system of classification based on viral genome composition introduced by David Baltimore in 1971. Alphaviruses, like all other group IV viruses, have a positive sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are thirty alphaviruses able to infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses as well as invertebrates. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes making the alphaviruses a contributor to the collection of Arboviruses – or Arthropod-Borne Viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical (although slightly pleomorphic), and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.
Genome
| Alpha_E1_glycop | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 crystal structure of the homotrimer of fusion glycoprotein e1 from semliki forest virus. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Alpha_E1_glycop | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01589 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002548 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1rer | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1rer | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.G | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 117 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1rer | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Alpha_E2_glycop | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
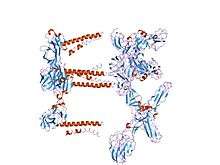 mapping the e2 glycoprotein of alphaviruses | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Alpha_E2_glycop | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00943 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000936 | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.G | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 117 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 2yew | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Alpha_E3_glycop | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Alpha_E3_glycop | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01563 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002533 | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.G | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 117 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The alphaviruses are small, spherical, enveloped viruses with a genome of a single positive sense strand RNA. The total genome length ranges between 11,000 and 12,000 nucleotides, and has a 5’ cap, and 3’ poly-A tail. The four non-structural protein genes are encoded in the 5′ two-thirds of the genome, while the three structural proteins are translated from a subgenomic mRNA colinear with the 3′ one-third of the genome.
There are two open reading frames (ORF’s) in the genome, non-structural and structural. The first is non structural and encodes proteins (nsP1–nsP4) necessary for transcription and replication of viral RNA. The second encodes three structural proteins: the core nucleocapsid protein C, and the envelope proteins P62 and E1 that associate as a heterodimer. The viral membrane-anchored surface glycoproteins are responsible for receptor recognition and entry into target cells through membrane fusion.
Structural proteins
The proteolytic maturation of P62 into E2 and E3 causes a change in the viral surface. Together the E1, E2, and sometimes E3, glycoprotein "spikes" form an E1/E2 dimer or an E1/E2/E3 trimer, where E2 extends from the centre to the vertices, E1 fills the space between the vertices, and E3, if present, is at the distal end of the spike.[1] Upon exposure of the virus to the acidity of the endosome, E1 dissociates from E2 to form an E1 homotrimer, which is necessary for the fusion step to drive the cellular and viral membranes together. The alphaviral glycoprotein E1 is a class II viral fusion protein, which is structurally different from the class I fusion proteins found in influenza virus and HIV. The structure of the Semliki Forest virus revealed a structure that is similar to that of flaviviral glycoprotein E, with three structural domains in the same primary sequence arrangement.[2] The E2 glycoprotein functions to interact with the nucleocapsid through its cytoplasmic domain, while its ectodomain is responsible for binding a cellular receptor. Most alphaviruses lose the peripheral protein E3, but in Semliki viruses it remains associated with the viral surface.
Non structural proteins
Four nonstructural proteins (nsP1-4) which are produced as a single polyprotein constitute the virus' replication machinery.[3] The processing of the polyprotein occurs in a highly regulated manner, with cleavage at the P2/3 junction influencing RNA template use during genome replication. This site is located at the base of a narrow cleft and is not readily accessible. Once cleaved nsP3 creates a ring structure that encircles nsP2. These two proteins have an extensive interface.
Mutations in nsP2 that produce noncytopathic viruses or a temperature sensitive phenotypes cluster at the P2/P3 interface region. P3 mutations opposite the location of the nsP2 noncytopathic mutations prevent efficient cleavage of P2/3. This in turn affects RNA infectivity altering viral RNA production levels.
Virology
The nucleocapsid, 40 nanometers in diameter, contains 240 copies of the capsid protein and has a T = 4 icosahedral symmetry. The E1 and E2 viral glycoproteins are embedded in the lipid bilayer. Single E1 and E2 molecules associate to form heterodimers. The E1-E2 heterodimers form one-to-one contacts between the E2 protein and the nucleocapsid monomers.
Replication occurs within the cytoplasm, and virions mature by budding through the plasma membrane, where virus-encoded surface glycoproteins E2 and E1 are assimilated.
These two glycoproteins are the targets of numerous serologic reactions and tests including neutralization and hemagglutination inhibition. The alphaviruses show various degrees of antigenic cross-reactivity in these reactions and this forms the basis for the seven antigenic complexes, 30 species and many subtypes and varieties. The E2 protein is the site of most neutralizing epitopes, while the E1 protein contains more conserved, cross-reactive epitopes.
Evolution
A study of this taxon suggests that this group of viruses had a marine origin - specifically the Southern Ocean - and that they have subsequently spread to both the Old and New World.[4]
There are three subgroups in this genus: the Semliki Forest virus subgroup (Semliki Forest, O'nyong-nyong and Ross River viruses); the eastern equine encephalitis virus subgroup (eastern equine encephalitis and Venezuelan equine encephalitis viruses) and the Sindbis virus subgroup.[5] Sindbis virus, geographically restricted to the Old World, is more closely related to the eastern equine encephalitis subgroup, which are New World viruses, than it is to the Semliki Forest virus subgroup which is also found in the Old World.
Taxonomy
Group: ssRNA(+)
- Family: Togaviridae
- Genus: Alphavirus
- Aura virus
- Barmah Forest virus
- Bebaru virus
- Cabassou virus
- Chikungunya virus
- Eastern equine encephalitis virus
- Eilat virus
- Everglades virus
- Fort Morgan virus
- Getah virus
- Highlands J virus
- Madariaga virus
- Mayaro virus
- Middelburg virus
- Mosso das Pedras virus
- Mucambo virus
- Ndumu virus
- O'nyong-nyong virus
- Pixuna virus
- Rio Negro virus
- Ross River virus
- Salmon pancreas disease virus
- Semliki Forest virus
- Sindbis virus
- Southern elephant seal virus
- Tonate virus
- Trocara virus
- Una virus
- Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus
- Western equine encephalitis virus
- Whataroa virus
The seven complexes are:
- Barmah Forest virus complex
- Barmah Forest virus
- Eastern equine encephalitis complex
- Eastern equine encephalitis virus (seven antigenic types)
- Middelburg virus complex
- Middelburg virus
- Ndumu virus complex
- Ndumu virus
- Semliki Forest virus complex
- Bebaru virus
- Chikungunya virus
- Mayaro virus
- Subtype: Una virus
- O’Nyong Nyong virus
- Subtype: Igbo-Ora virus
- Ross River virus
- Subtype: Bebaru virus
- Subtype: Getah virus
- Subtype: Sagiyama virus
- Semliki Forest virus
- Subtype: Me Tri virus
- Venezuelan equine encephalitis complex
- Cabassou virus
- Everglades virus
- Mosso das Pedras virus
- Mucambo virus
- Paramana virus
- Pixuna virus
- Rio Negro virus
- Trocara virus
- Subtype: Bijou Bridge virus
- Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus
- Western equine encephalitis complex
- Aura virus
- Babanki virus
- Kyzylagach virus
- Sindbis virus
- Ockelbo virus
- Whataroa virus
- Recombinants within this complex
- Buggy Creek virus
- Fort Morgan virus
- Highlands J virus
- Western equine encephalitis virus
- Unclassified
- Salmon pancreatic disease virus
- Sleeping Disease virus
- Southern elephant seal virus
- Tonate virus
Notes
Barmah Forest virus is related to the Semliki Forest virus. Middelburg virus, although classified as a separate complex, may be a member of the Semliki Forest virus group.
It seems likely that the genus evolved in the Old World from an insect-borne plant virus.[7]
Sindbis virus may have originated in South America.[8] The equine encephalitis viruses and Sindbis viruses are related.
The Old World and New World viruses appears to have diverged between 2000 and 3000 years ago.[9] Divergence between the Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus and the eastern equine virus appears to have been ~1400 years ago.[10]
The fish infecting clade appears to be basal to the other species.
The southern elephant seal virus appears to be related to the Sinbis clade.
Pathogenesis and immune response
| Virus | Human Disease | Vertebrate Reservoir | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barmah Forest virus | Fever, malaise, rash, joint pain, muscle tenderness | Humans | Australia |
| Chikungunya virus | Rash, arthritis | Primates, humans | Africa, Latin America, India, SE Asia |
| Mayaro virus | Rash, arthritis | Primates, humans | South America |
| O'nyong'nyong virus | Rash, arthritis | Primates, Humans | Africa |
| Ross River virus | Rash, arthritis | Mammals, humans | Australia, South Pacific |
| Semliki Forest virus | Rash, arthritis | Birds | Africa |
| Sindbis virus | Rash, arthritis | Birds | Europe, Africa, Australia |
| Una virus | Rash, arthritis | Primates, humans | South America |
| Eastern equine encephalitis virus | Encephalitis | Birds | Americas |
| Tonate virus | Encephalitis | Humans | South America |
| Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus | Encephalitis | Rodents, horses | Americas |
| Western equine encephalitis virus | Encephalitis | Birds, mammals | North America |
There are many alphaviruses distributed around the world with the ability to cause human disease. Infectious arthritis, encephalitis, rashes and fever are the most commonly observed symptoms. Larger mammals such as humans and horses are usually dead-end hosts or play a minor role in viral transmission; however, in the case of Venezuelan equine encephalitis the virus is mainly amplified in horses. In most other cases the virus is maintained in nature in mosquitoes, rodents and birds.
Alphavirus infections are spread by insect vectors such as mosquitoes. Once a human is bitten by the infected mosquito, the virus can gain entry into the bloodstream, causing viremia. The alphavirus can also get into the CNS where it is able to grow and multiply within the neurones. This can lead to encephalitis, which can be fatal.
When an individual is infected with this particular virus, its immune system can play a role in clearing away the virus particles. Alphaviruses are able to cause the production of interferons. Antibodies and T cells are also involved. The neutralizing antibodies also play an important role to prevent further infection and spread.
Diagnosis, prevention, and control
Diagnoses is based on clinical samples from which the virus can be easily isolated and identified. There are no alphavirus vaccines currently available. Vector control with repellents, protective clothing, breeding site destruction, and spraying are the preventive measures of choice.
Research
Alphaviruses are of interest to gene therapy researchers, in particular the Ross River virus, Sindbis virus, Semliki Forest virus, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus have all been used to develop viral vectors for gene delivery. Of particular interest are the chimeric viruses that may be formed with alphaviral envelopes and retroviral capsids. Such chimeras are termed pseudotyped viruses. Alphaviral envelope pseudotypes of retroviruses or lentiviruses are able to integrate the genes that they carry into the expansive range of potential host cells that are recognized and infected by the alphaviral envelope proteins E2 and E1. The stable integration of viral genes is mediated by the retroviral interiors of these vectors. There are limitations to the use of alphaviruses in the field of gene therapy due to their lack of targeting, however, through the introduction of variable antibody domains in a non-conserved loop in the structure of E2, specific populations of cells have been targeted. Furthermore, the use of whole alphaviruses for gene therapy is of limited efficacy both because several internal alphaviral proteins are involved in the induction of apoptosis upon infection and also because the alphaviral capsid mediates only the transient introduction of mRNA into host cells. Neither of these limitations extend to alphaviral envelope pseudotypes of retroviruses or lentiviruses. However, the expression of Sindbis virus envelopes may lead to apoptosis, and their introduction into host cells upon infection by Sindbis virus envelope pseudotyped retroviruses may also lead to cell death. The toxicity of Sindbis viral envelopes may be the cause of the very low production titers realized from packaging cells constructed to produce Sindbis pseudotypes. Another branch of research involving alphaviruses is in vaccination. Alphaviruses are apt to be engineered to create replicon vectors which efficiently induce humoral and T-cell immune responses. They could therefore be used to vaccinate against viral, bacterial, protozoan, and tumor antigens.
See also
Sources
- http://virology-online.com/viruses/Arboviruses2.htm
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ICTVdb/ICTVdB/73010000.htm
- Alphavirus vectors: from protein production to gene therapy, C Smerdou & P Liljestrom, Gene Therapy and Regulation Vol 1 No 1 2000 pp. 33–63
- Alphavirus vectors and vaccination, J O Rayner et al., Reviews in Medical Virology vol 12 issue 5 pp 279–296
- http://ep.physoc.org/cgi/content/full/90/1/45
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=mmed.chapter.2894
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=mmed.section.2918
References
- ↑ Vénien-Bryan C, Fuller SD (February 1994). "The organization of the spike complex of Semliki Forest virus". J. Mol. Biol. 236 (2): 572–83. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1166. PMID 8107141.
- ↑ Lescar J, Roussel A, Wien MW, Navaza J, Fuller SD, Wengler G, Wengler G, Rey FA (April 2001). "The Fusion glycoprotein shell of Semliki Forest virus: an icosahedral assembly primed for fusogenic activation at endosomal pH". Cell. 105 (1): 137–48. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00303-8. PMID 11301009.
- ↑ Shin G, Yost SA, Miller MT, Elrod EJ, Grakoui A, Marcotrigiano J (2012) Structural and functional insights into alphavirus polyprotein processing and pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA
- ↑ Forrester NL, Palacios G, Tesh RB, Savji N, Guzman H, Sherman M, Weaver SC, Lipkin WI (December 2011). "Genome scale phylogeny of the Alphavirus genus suggests a marine origin". J Virol. 86 (5): 2729–38. doi:10.1128/JVI.05591-11. PMID 22190718.
- ↑ Levinson RS, Strauss JH, Strauss EG (1990). "Complete sequence of the genomic RNA of O'nyong-nyong virus and its use in the construction of alphavirus phylogenetic trees". Virology. 175 (1): 110–123. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(90)90191-s.
- ↑ ICTV. "Virus Taxonomy: 2014 Release". Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ↑ Powers AM, Brault AC, Shirako Y, Strauss EG, Kang W, Strauss JH, Weaver SC (November 2001). "Evolutionary relationships and systematics of the alphaviruses". J. Virol. 75 (21): 10118–31. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.21.10118-10131.2001. PMC 114586
 . PMID 11581380.
. PMID 11581380. - ↑ Lundström JO, Pfeffer M (November 2010). "Phylogeographic structure and evolutionary history of Sindbis virus". Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 10 (9): 889–907. doi:10.1089/vbz.2009.0069. PMID 20420530.
- ↑ Weaver SC, Hagenbaugh A, Bellew LA, Netesov SV, Volchkov VE, Chang GJ, Clarke DK, Gousset L, Scott TW, Trent DW (November 1993). "A comparison of the nucleotide sequences of eastern and western equine encephalomyelitis viruses with those of other alphaviruses and related RNA viruses". Virology. 197 (1): 375–90. doi:10.1006/viro.1993.1599. PMID 8105605.
- ↑ Weaver SC, Rico-Hesse R, Scott TW (1992). "Genetic diversity and slow rates of evolution in New World alphaviruses". Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 176: 99–117. PMID 1318187.
External links
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR000936
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR002533
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR002548