Siege of Algeciras (1278–79)
| Battle of Algeciras | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Reconquista | |||||||
_02.jpg) Alfonso X of Castile "El Sabio, King of Castile. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Spain |
.svg.png) |
| Timeline |
|
|
The Siege of Algeciras was the first of many sieges on the city by Christian forces in the lengthy period of Spanish Reconquista. The siege, ordered by King Alfonso X of Castile also known as "el Sabio", was a fruitless military campaign initiated by the Kingdom of Castile with the objective of removing the Moroccans from Algeciras. The siege on Algeciras, then known to the Muslims as Al-Jazira Al-Khadra, was strategically important because Algeciras had been at the time the main fortress and landing place for African reinforcement troops in the Iberian Peninsula. Castile, which had a powerful armada of ships anchored in the Bay of Gibraltar to blockade such reinforcement, had a few days previously to the siege, seen that fleet obliterated by the Muslim admiral, Abu Yusuf Yaqub at the Naval Battle of Algeciras.
Context
Since the middle of the 13th century, the Marinid Dynasty was emerging as a new power in Morocco, ruled by Abu Yusuf Yaqub ibn Abd Al-Haqq. The Marinids had established contact with the Muslims of Al-Andalus and offered soldiers to the King Muhammad II de Granada in his bitter struggle against the Reconquista of the Christian kingdoms to the north. On April 12, 1275, a massive Moroccan army disembarked in Algeciras and commenced marching towards the cities of Sevilla, Jaén and Córdoba.[1][2] From Castile, Ferdinand de la Cerda, who circumstantially governed the kingdom in the absence of his father, Alfonso X, found himself being interviewed by the pope in Beaucaire,[3] could do no more than contain the invasions.
Nuño González de Lara, who controlled the frontier of Córdoba, left from the city and gave battle against the Moroccans, dying in the action, but also forced the Muslims to withdraw from their advance.[2] Due to the constantly threatened nature of the Castilian borderlands, the infante Fernando left Burgos in August to gather an army but became deathly ill and died a little while later at Ciudad Real.[4] His brother, the infante Sancho, who would later become Sancho IV eventually marched to Córdoba to finally counter the Marinid threat.[5] After strengthening their positions in the area, Sancho marched to Sevilla from where he planned to command future operations and troop movements in the campaign. The son of King James I of Aragon, also named Sancho, the Archbishop of Toledo, went to join the fight in Jaén, but not wanting to wait for Lope Díaz de Haro, Lord of Biscay, died in combat shortly thereafter. His body was beheaded and his right hand cut off. The next day, the Lord of Biscay, together with a young Alonso Pérez de Guzmán, defeated a coalition of African-Andalusian forces and obliged them to withdraw.[6]
Under these circumstances, the Muslim forces were not able to advance further into Castilian territory. In 1276, they signed a two-year truce with the Kingdom of Castile.[7] Nevertheless, the Marinids under Yusuf did not return to Africa and maintained control in force of Algeciras and Tarifa, having a large troop presence in both cities.[8] In the meantime, the Castilians busied themselves with issues of succession to the crown. Alfonso X decided to pass the privilege on to his son Sancho, even though he was under considerable pressure from the nobility and from his wife, Violante, that he pass the crown on to the children of the dead heir, Fernando.[9]
The siege
It was under this set of compromising circumstances that Alfonso X decided to lay siege to the city of Algeciras, understanding that while the city remained under Moroccan control, it continually posed the threat of a new invasion of the Kingdom of Castile. Al-Jazira Al-Khadra, the name the Muslims had given to Algeciras, had been the first city founded by the Muslim conquerors when they first landed on the Iberian Peninsula in the year 711. The contemporary city stretched to the north of the Río de la Miel and possessed a complex defensive system of walls and entrances, probably being designed by the Almohads who had improved upon the original fortifications in the 8th Century.[10] The Castilian king sent another one of his sons in March 1278, infante Pedro de Castilla y Aragón to rally his troops in Sevilla along with Sancho.[11] As soon as the armies were joined, they marched for Algeciras. The vanguard of the column was commanded by Alfonso Fernández de Castilla, illegitimate son of Alfonso X.[12]
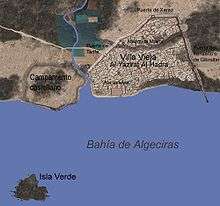
On August 5, 1278, the Castilian troops arrived at the outskirts of Algeciras.[13] The army that besieged the city consisted of about 30,000 men as indicated by the chronicles of the time. A fleet of 24 ships and 80 galleys was also in place in Bay of Gibraltar in order to prevent the supply of the city from the nearby Gibraltar. That same fleet was completely annihilated in the Naval Battle of Algeciras.[14] The fleet was commanded by Pedro Martínez de Fe and was accompanied by other important figures of the king's court, including Gonzalo Marante y Guillén de Sasanaque. The flotilla was also made up of a majority of the members of the Order of Santa María de España, a military-religious order which concentrated in naval warfare and which was later integrated into the Order of Santiago.[15] The ground forces meanwhile completely surrounded the city, digging trenches and using various types of contemporary siege weapons on the battlements and gates of the city, concentrating on perceived weak points. The fleet established its base on Isla Verde. The first months of the siege were relatively constant. Raiding parties would leave the city to attack the Christian soldiers whilst ballistas would fire at the besiegers from inside the city. In February 1279, Alfonso X arrived to the siege and took charge of the operations.[16] After many months, the siege remained stagnant. The casualties inflicted from the skirmishes continued to cause heavy losses, mainly in the Castilian camp.[17] At the same time, the Muslim forces were equally unable to dislodge the siege.
Throughout April 1279, after the king returned to Castile, the Christian camp began to feel the effects of a lack of food and supplies. This was in part due to the loss of their fleet at the naval battle. The problem was exacerbated due to the large number of besieging troops and the fact that enough supplies were not being sent from Sevilla. It would not be found out for many months that much of the tax money collected in Castile with the objective of financing the siege was being diverted by the infante Pedro to entice his mother Violante to return to Castile.[18] That autumn was especially hot and before long, the water sources that sustained the troops began to deteriorate, causing an outbreak of plague in the Christian camp.[12] Amongst the sick soldiers, the worst off were often members of the fleet who were forced to remain for weeks on their ships without proper food or supplies. By July 1279, many of the troops from the ships abandoned the fleet and joined their counterparts on the ground in the hopes of better care. Many of the boats remained anchored off Isla Verde for this reason and by the time of the battle later that month, the fleet was easily destroyed by the Muslim galleys.[17]
Arrival of the Muslim fleet
Throughout the blockade, Algeciras was able to maintain communication with Gibraltar by means of messenger pigeon, informing them of the awful conditions endured by the besiegers.[19] After hearing news of this, the Moroccan king gathered 14 galleys in Tangier to send them to Algeciras.[20] In June, Abu Yusuf Yaqub had intended to cross with his fleet onto the Iberian Peninsula, but insurrections in Nefís forced him to change his plans. On July 19, the Muslim galleys were prepared and launched under the command of the King's son, Abu Yaqub Yusuf an-Nasr.[21] By nightfall they had reached the outskirts of the Bay of Gibraltar and on July 20 the Muslim fleet attacked the now almost empty Castilian ships anchored at Isla Verde. The Castilian fleet was quickly defeated and their boats captured. All prisoners were decapitated except the officers who were taken hostage. For the second time in as many years, the entire Castilian fleet was lost.[20]
The Castilian ground army, surprised by the rapid destruction of their navy, were helpless to stop the Muslims as their ships sailed into the city and their soldiers disembarked at the shipyard. The Muslim army then hastily exited the city gates and gave battle to the Christian besiegers.[22] The infante Pedro, who was at the time in charge of the siege, fled the battle, leaving his captains to become captured and losing all siege weapons to the enemy.[23]
Aftermath
Alfonso X was forced to sign a new truce with the Marinids later in 1279.[24] After the battle, the King of Morocco built the Villa Nueva de Algeciras in the places where the siege works once stood so that future besiegers would not be able to use the same advantageous positions again.[25]
References
- ↑ Rodríguez, Manuel (1788). Retratos de los reyes de España, desde Atanarico hasta nuestro católico monarca Carlos III. Con los sumarios de sus vidas. Lorenzo de San Martín. p. 69. External link in
|title=(help) - 1 2 Lafuente, Modesto (1861). Historia general de España. Establecimiento tipográfico de Francisco de Paula Mellado. p. 290. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Álvarez de la Fuente, José (1773). Sucesión Real de España. Imprenta i librería de D. Manuel Martín. p. 208. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Cortada, Juan (1841). Historia de España: Desde los tiempos más remotos hasta 1839. Imprenta de A. Brusi. p. 559. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Lafuente, Modesto (1861). Historia general de España. Establecimiento tipográfico de Francisco de Paula Mellado. p. 291. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ de Mariana, Juan (1854). Obras del Padre Juan de Mariana. Editor M. Rivadeneyra. p. 401. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Gómez Ranera, Alejandro (1838). Breve compendio de la historia de España desde su origen hasta el reinado del señor Fernando VII. Imprenta de Fuentenebro. p. 93. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Suárez Fernández, Luis (1983). Historia de España Antigua y media. Ediciones Rialp. p. 175. ISBN 8432118826. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Lafuente, Modesto (1861). Historia general de España. Establecimiento tipográfico de Francisco de Paula Mellado. p. 302. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Jiménez-Camino Álvarez; Rafael y Tomassetti Guerra; José María (2005). ""Allende el río..." sobre la ubicación de las villas de Algeciras en la Edad Media" (1). Boletín de arqueología yazirí. pp.435-457.
- ↑ V.V.A.A. (1885). Memorial histórico español: Colección de documentos, opúsculos y antigüedades. Real Academia Española de Historia. p. 587. External link in
|title=(help) - 1 2 Lafuente, Modesto (1861). Historia general de España. Establecimiento tipográfico de Francisco de Paula Mellado. p. 303. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Ortiz de la Vega, Manuel (1858). Anales de España. Imprenta Cervantes. p. 162. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Conde, José Antonio (1844). Historia de la dominación de los Árabes en España: Sacada de varios manuscritos y memorias arábigas. Imprenta de Juan Oliveres. p. 364. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Ortiz de Zúñiga, Diego (1795). Anales eclesiásticos y seculares de la muy noble y muy leal ciudad de Sevilla. Imprenta Real. p. 296. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ V.V.A.A. (1885). Memorial histórico español: Colección de documentos, opúsculos y antigüedades. Real Academia Española de Historia. p. 588. External link in
|title=(help) - 1 2 Conde, José Antonio (1844). Historia de la dominación de los Árabes en España: Sacada de varios manuscritos y memorias arábigas. Imprenta de Juan Oliveres. p. 211. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Lafuente, Modesto (1861). Historia general de España. Establecimiento tipográfico de Francisco de Paula Mellado. p. 304. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ V.V.A.A. (1857). Memorial histórico español. Real Academia de la Historia.
- 1 2 Lafuente, Modesto (1861). Historia general de España. Establecimiento tipográfico de Francisco de Paula Mellado. p. 304.
- ↑ V.V.A.A. (1885). Memorial histórico español: Colección de documentos, opúsculos y antigüedades. Real Academia Española de Historia.
- ↑ Conde, José Antonio (1844). Historia de la dominación de los Árabes en España: Sacada de varios manuscritos y memorias arábigas. Imprenta de Juan Oliveres.
- ↑ Ortiz de la Vega, Manuel (1858). Anales de España. Imprenta Cervantes.
- ↑ Ortiz de la Vega, Manuel (1858). Anales de España. Imprenta Cervantes. p. 164. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Ortiz de Zúñiga, Diego (1795). Anales eclesiásticos y seculares de la muy noble y muy leal ciudad de Sevilla. Imprenta Real. p. 297. External link in
|title=(help)
Bibliography
- V.V.A.A. (1857). Memorial histórico español: Colección de documentos, opúsculos y antigüedades que publica la Real Academia de la historia. Real Academia de la Historia. External link in
|title=(help) - Lafuente y Zamalloa, Modesto (1861). Historia general de España. Establecimiento tipográfico de Francisco de P. Mellado. External link in
|title=(help) - Conde, José Antonio (1844). Historia de la dominación de los Arabes en Espana: Sacada de varios manuscritos y memorias arábigas. Imprenta de Juan Oliveres. External link in
|title=(help) - V.V.A.A. (1885). Memorial histórico español: Colección de documentos, opúsculos y antigüedades. Real Academia Española de Historia. External link in
|title=(help)
