Transport in Pakistan

Transportation in Pakistan (Urdu: پاکِستان نقل و حمل) is extensive and varied and serving a population of over 191 million people. Construction of new airports, roads, and railway lines have led to an employment boost in the country. Much of Pakistan's rail network railway was built before 1947, mainly during the British Raj. In recent years, new national highways have been built, with the addition of motorways which have accelerated trade and logistics within the country. Airports and seaports have been built in the last 30 years with the addition of foreign and domestic funding.
Local urban transport
In urban areas there are several means of transport available, catering to a wide range of budgets.
Rapid Transit
The government of Pakistan has planned to build a monorail system in its federal capital, Islamabad. Monorail is also planned for New Avenue in Gulberg, Lahore
- Metro rail
The Lahore Metro or Lahore Rapid Mass Transit System (LRMTS) (Urdu: لاہور میٹرو) is an under construction rapid transit system (metro train system) for Lahore, the second largest city of Pakistan. First proposed in 1991, funding was not secured, and in 2012 it was abandoned by the Punjab government in favour of the more cost–effective Lahore Metro Bus System which opened in February 2013. However, the Punjab Government decided to restart development on the Lahore Metro as a $1.6 billion project with Chinese assistance. The Orange Line, which will be 27.1-kilometre (16.8 mi) long (25.4 kilometres (15.8 mi) of which will be elevated),[1] will be the first line of the project and is under construction.[2]
- Without segregated lanes
- TransLahore: It is a BRT system in Lahore. Lahore Transport Company was established in 1984 to ease the traffic conditions of Lahore and improve bus services. LTC got all the transport responsibilities of traveling in Lahore in December 2001. A BRTS fleet of 650 Buses was introduced. It was named as TransLahore. However, the BRTS did not have dedicated lanes and had to share roads with regular traffic with no right of way privileges. This resulted in a system that was a BRTS only in name.
- With segregated lanes
- Lahore: Metrobus (Lahore) Bus Service was inaugurated on Feb 10, 2013 by CM Punjab Shehbaz Sharif.[3] It consist of 27-kilometres long road track for the Metro Bus Service, from Gajumata to Shahadra, out of this track 8.5 km is elevated. It has 27 bus stations and e-ticketing and Intelligent Transportation System are part of the MBS.
- Islamabad-Rawalpindi: Rawalpindi-Islamabad Metrobus Service is an operational bus rapid transit system which connects key areas in city of Rawalpindi and the national capital city of Islamabad. It is 24 kilometres (15 mi) long, and has 24 stations. The project was inaugurated on 4 June 2015 by Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif.[4]
- Under construction
- Multan Metrobus is under construction in the city of Multan. The 18.2 kilometres (11.3 mi) long BRT system will connect main commercial areas of the city.
- Planned
- Karachi Metrobus is planned for city of Karachi. It will consist of 5 corridors and will have total length of about 109 kilometres (68 mi), of which the Green and Red Linea are about to go into a construction phase.
The corridors include:
- Surjani Town to Jama Cloth Market (21.1 km)
- Model Colony to Regal Chowk (24.4 km)
- Landhi to Luck Star Hotel (20.4 km)
- Baldia to Shershah via Hub River Road (9.7 km)
- Hwaksbay to Gulbai via Mauripur (11.8 km)
- Orangi to Board Office (3.9 km).
- Peshawar Metrobus is a bus rapid transit system for the city of Peshawar. The project is under the consideration of PTI led Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. PMTS will be a bus rapid transit system.Which will be initially constructed on one red line having length of 18.4 kilometer from Chamkani to Hayatabad area of Peshawar.
- Faisalabad: Faisalabad Metrobus is a planned, single line BRT System, similar to Lahore Bus Rapid Transit System. Metro line will connect Faisalabad International Airport to City Bus Terminal, passing through main hubs of the city. Construction is expected to start at the end of 2015.
| City | System | Began oper. | Status | Number of stations [Note 1] |
Network length (km) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lahore | TransLahore | 1980 | Complete | 112 | 160 | |
| Lahore | Lahore Metrobus | 2013 | Complete | 27 | 27 | |
| Islamabad | Rawalpindi-Islamabad Metrobus | 2015 | Complete | 24 | 22.5 | |
| Rawalpindi | Rawalpindi-Islamabad Metrobus | 2015 | Complete | 24 | 22.5 | |
| Multan | Multan Metrobus | 2016 | Under construction | 18 | 18.2 | |
| Karachi | Karachi Metrobus | 2018 | Under construction | 90 | 109 | |
| Faisalabad | Faisalabad Metrobus | 2017 | Planned | 28 | 30 | |
| Peshawar | Peshawar Metrobus | 2019 | Planned | 18 | 26 |
Buses
Within cities, buses provide a significant role in commuting a large number of travellers from one city to another. Recently, large CNG busses have been put onto the streets of various cities, primarily Karachi and Lahore, and recently Islamabad, as the minivans which were originally used were beginning to cause large traffic problems. Private yellow and white minivans have services throughout cities in Pakistan and get commuters from one point of the city to the other at a low cost. Since 2000, however, the government has taken a comprehensive initiative to modernize the existing bus fleets and minimally impact the environment. This public-private enterprise would gradually introduce 8,000 CNG buses throughout the country and 800 buses in Karachi. This venture will ensure high standards of efficiency and cleanliness.[5]
Urban Railway
The Karachi Circular Railway, which opened in the early 1940s, is the earliest functioning Mass Transit System in Pakistan. In 1976, Karachi was slated to begin work on an underground metro system, but plans have been put on hold since.
In Lahore, Lahore Central Railway Station is the main railway station. Shahdara Bagh, Badami Bagh, Mughalpura, Shahdara Town, Lahore Cantonment, Wagah, Walton Cantonment, Kot Lakhpat, Kahna Nau, Jia Bagga and Raiwind are other busy railway stations located in Lahore. These urban railway stations of the city are served by commuter trains of Lahore. A large number of commuters use these station to get access to the city of Lahore.
Auto rickshaws



Auto rickshaws are a popular method of travelling in cities and are found in almost every city and town in Pakistan. The fare is usually negotiable before commencing a journey; however, due to the level of pollution contributed by auto-rickshaws, the government has recently begun banning older ones and replacing them with CNG auto rickshaws, which tend to be less noisy, form less pollutants and are much bigger and more comfortable. The Punjab government decided in 2005 to replace two-stroke three-wheelers with CNG-fitted four-stroke rickshaws in Lahore, Multan, Faisalabad, Rawalpindi and Gujranwala. Three manufacturers were ordered to produce 60,000 four-stroke vehicles, but they reportedly supplied 2,000 to the government which are now plying on city roads. Similar ordinances are now being considered in other provinces of Pakistan.
A new form of transport in Pakistan is the Qing-Qi (pronounced "ching-chee"), which is a cross between a motorcycle and auto-rickshaw. It runs just like a motorcycle but has three wheels instead of two and can carries a much heavier load. It is an urban transport vehicle and is used mostly for short distances.
Taxis
Another very common sight seen mainly at hotels and airports are yellow taxis. Drivers charge according to a meter located on the dashboard of the car, but fares can be negotiated if there is no meter. The cab drivers are reliable and will take passengers to any destination required.
There are also numerous privately run services that use cars and minibuses of various types throughout Pakistan, providing a reliable and quick means of transport. Recently, the Radio Cab was introduced in Pakistan, which allows riders to call a toll-free number to get in touch with the closest taxi stand. This service is currently offered in Islamabad, Rawalpindi, Karachi, Peshawar and Lahore. Services for Hyderabad and Faisalabad are now being made.
Cars
Over the years, the number of cars on Pakistani roads has tripled. Traffic jams are a common scene in major cities across Pakistan. The most popular cars on Pakistani roads are Suzuki Mehran, Suzuki Cultus, Suzuki Alto, Suzuki Bolan, Daihatsu Coure, Hyundai Santro, Honda Civic, Honda City, Honda Accord, Toyota Corolla and Toyota Vitz.
In late 2005, Suzuki introduced the APV (All-Purpose Vehicle), the first luxury family van in Pakistan. Utility vehicles (SUVs or 4x4s) are also a familiar sight in Pakistan. This type of car is very multi-functional as it allows long distance and off-road travel, within cities as well as city-to-city travel. Luxury SUVs are owned by the elite in urban cities and by large landowners in the villages and rural areas, thus making them a fairly common sight in Pakistan. The most popular models are the Toyota Land Cruiser, Toyota Prado, Land Rover Range Rover, several Mercedes, BMW and Audis. Adam Revo, Pakistan's first manufactured car, was developed to meet the needs of low income families.
Future cars
To meet future needs, students and teachers from National University of Science and Technology developed Pakistan's first ever hybrid gasoline car Devrim II, an inspiration from Turkish model Devrim.[6] Before that, students from Naval College Karachi and Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute also made a successful hybrid car, but Devrim II is the most effective one. The current team leader of the Pak-Wheelers said,[7]
"Initial design was giving a mileage of around 450 kilometres to a litre but we are trying to improve that number to more than 700 km/litre after switching to a hybrid model."— Faizan Zafar, Tribune interview
Traditional
In the small towns and farms, many people decide to walk great distances to either get to work or to walk to their nearest grocery store to get their daily shopping. The donkey cart, locally known as the Rehrri, is still visible every where in Pakistan, as poor people use this form of transport to shift cargo from one part of the city to the next. Their cargo ranges from fruits and vegetables, to textiles or machinery that factories require in industrial cities. The horse and carriage, locally known as Taanga, is mainly used for casual travelling around the city. There is one driver, with either one or two horses at the front. This method is now usually used by tourists in the spring and summer that love to see the cities in an open environment.
Camel carts are also seen from time to time, mostly in the hotter parts of Pakistan including Sindh, Punjab and Balochistan where farmers transport larger cargo that donkey carts cannot handle.
Bicycles are used by either the poorer segment of the society or for leisure. This method is still very widely used as its very economical and simple.
Bus
- Inter city
Bus service in urban areas and between cities is well established with services run by both public and private sectors. Bus services like Raja Bus Service (Azeem Bhatty), Waraich Buses, Daewoo Express, Rehber Travel, Bilal Deawoo, Faisal Movers, Kohistan, Khan Brothers, Skyways and Niazi Express have set up modern intercity service which connects to most cities in Pakistan and runs 24 hours a day. Intercity buses tend to be more modern and well kept.
- International
International bus services are also well established in Pakistan and connect to various countries:
- Quetta-Zahidan, Iran
- Quetta-Mashad, Iran
- Gwadar-Zahidan, Iran
- Karachi-Quetta-Zahidan-Tehran, Iran (proposed)
- Peshawar-Jalalabad, Afghanistan
- Peshawar-Kabul, Afghanistan
- Islamabad-Dushanbe, Tajikistan (proposed)
- Islamabad-Kashghar, China (proposed)
- Gilgit-Kashgar see Karakoram Highway
- Lahore-Delhi, India
- Muzaffarabad-Srinagar, India
Rail
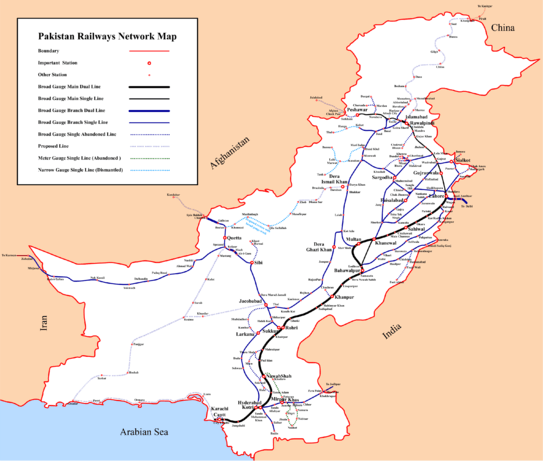

Domestic
Rail services in Pakistan are provided by the state-run Pakistan Railways, under the supervision of the Ministry of Railways. Pakistan Railways provides an important mode of transportation in Pakistan, catering to the large-scale movement of people and freight. The railway network comprises 8,163 km[8] of which 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) forms 7,718 km, including 293 km of electrified track. 1,000 mm (3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) metre gauge tracks form the remaining 445 km. Passenger earnings comprise 50% of the total revenue. During 1999–2000 this amounted to Rs. 4.8 billion. Pakistan Railways carry 65 million passengers annually and daily operate 228 mail, express and passenger trains. Pakistan Railways also operate special trains for various occasions. The Freight Business Unit with 12000 personnel operates over 200 freight stations on the railway network. The FBU serves the Port of Karachi and Port Qasim as well as in various other stations along the network and generates revenue from the movement of agricultural, industrial and imported products such as wheat, coal, fertilizer, cement, and sugar. About 39% of the revenue is generated from the transportation of petroleum, 19% from imported wheat, fertilizer and rock phosphate. The remaining 42% is earned from domestic traffic. The freight rates structure is based on market trends in road transport which is the main competitor to rail transport.
High speed rail
Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif said that a high-speed rail network will be built which will connect Peshawar to Karachi via all major cities of Pakistan during his visit to China in June 2016.. Government is making plans for this project.
Mass transit and Urban Railway
The Karachi Circular Railway, which opened in the early 1940s, is the only functioning Mass Transit System in Pakistan as of date. In 1976, Karachi was slated to begin work on an underground metro system, but plans have been put on hold since. The Lahore Metro Bus System is another rapid mass transit system which was tested by CM of Punjab Shahbaz Sharif on December 25, 2012. It began operation on February 11, 2013. Lahore Metro would be the first mass transit system of it type in Pakistan. Peshawar Metro is also planned. On 22 May 2014,[9] Pakistan and China signed a $1.6 billion agreement for a metro train project in Lahore.[10] The Government decided to build the Orange Line of Lahore Metro. The work on the project will start in 2014 and will be completed within 27 months.The total length of the project will be 27.1 km and its 25.4 km track will be elevated. 1.7 km track will be underground.
In Lahore, Lahore Central Railway Station is the main railway station. Shahdara Bagh, Badami Bagh, Mughalpura, Shahdara Town, Lahore Cantonment, Wagah, Walton Cantonment, Kot Lakhpat, Kahna Nau, Jia Bagga and Raiwind are other busy railway stations located in Lahore. These urban railway stations of the city are served by commuter trains of Lahore. A large number of commuters use these station to get access to the city of Lahore.
International routes
![]() Iran -
A 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) railway line runs from Zahedan to Quetta, and a 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge line is finished from Zahedan to Kerman in central Iran, linking with the rest of the Iranian rail network. On May 18, 2007, a MOU for rail cooperation was signed by Pakistan and Iran under which the line will be completed by December 2008. Now that the rail systems are linked up at Zahedan, there is a break-of-gauge between the Islamic Republic of Iran Railways 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge tracks and Pakistan Railway's Indian gauge tracks.[11]
Iran -
A 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) railway line runs from Zahedan to Quetta, and a 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge line is finished from Zahedan to Kerman in central Iran, linking with the rest of the Iranian rail network. On May 18, 2007, a MOU for rail cooperation was signed by Pakistan and Iran under which the line will be completed by December 2008. Now that the rail systems are linked up at Zahedan, there is a break-of-gauge between the Islamic Republic of Iran Railways 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge tracks and Pakistan Railway's Indian gauge tracks.[11]
![]() Afghanistan -
Currently there is no rail link to Afghanistan since no railway network is present in that country, however Pakistan Rail has proposed to help build an Afghan Rail Network in three phases. The first phase will stretch from the Chaman to Spin Boldak in Afghanistan. The second phase will extend line to Kandahar and the third phase will eventually connect to Herat. From there, the line will be extended to Khushka, Turkmenistan. The final phase would link 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) with Central Asian 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in) Russian gauge. It is not clear where the break-of-gauge station will be.[12] The proposed line will also be connected the port town of Gwadar via Dalbadin and Taftan, thus connecting the port town to Central Asia.
Afghanistan -
Currently there is no rail link to Afghanistan since no railway network is present in that country, however Pakistan Rail has proposed to help build an Afghan Rail Network in three phases. The first phase will stretch from the Chaman to Spin Boldak in Afghanistan. The second phase will extend line to Kandahar and the third phase will eventually connect to Herat. From there, the line will be extended to Khushka, Turkmenistan. The final phase would link 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) with Central Asian 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in) Russian gauge. It is not clear where the break-of-gauge station will be.[12] The proposed line will also be connected the port town of Gwadar via Dalbadin and Taftan, thus connecting the port town to Central Asia.
![]() China -
There is no link with China however, on 28 February 2007 contracts were awarded for feasibility studies on a proposed line from Havelian via the Khunjerab Pass at 4730 m above sea level, to the Chinese railhead at Kashgar, a distance of about 750 km.[13]
China -
There is no link with China however, on 28 February 2007 contracts were awarded for feasibility studies on a proposed line from Havelian via the Khunjerab Pass at 4730 m above sea level, to the Chinese railhead at Kashgar, a distance of about 750 km.[13]
![]() Turkey -
An Istanbul-Tehran-Islamabad passenger rail service was proposed recently.[14] Meanwhile, a container train service was launched by the former Prime Minister of Pakistan Yousuf Raza Gilani between Islamabad and Istanbul on 14 August 2009. The first train carried 20 containers with a capacity of around 750 t (738 long tons; 827 short tons) [15] and will travel 6,500 km (4,000 mi) from Islamabad, through Tehran, Iran and on to Istanbul in two weeks' time.[16] According to the Minister for Railways Ghulam Ahmad Bilour, after the trial of the container train service, a passenger train will be launched.[17] There are also hopes the route will eventually provide a link to Europe and Central Asia, and carry passengers.[18]
Turkey -
An Istanbul-Tehran-Islamabad passenger rail service was proposed recently.[14] Meanwhile, a container train service was launched by the former Prime Minister of Pakistan Yousuf Raza Gilani between Islamabad and Istanbul on 14 August 2009. The first train carried 20 containers with a capacity of around 750 t (738 long tons; 827 short tons) [15] and will travel 6,500 km (4,000 mi) from Islamabad, through Tehran, Iran and on to Istanbul in two weeks' time.[16] According to the Minister for Railways Ghulam Ahmad Bilour, after the trial of the container train service, a passenger train will be launched.[17] There are also hopes the route will eventually provide a link to Europe and Central Asia, and carry passengers.[18]
![]() India -
Thar Express to Karachi and the more famous Samjhauta Express international train from Lahore, Pakistan to Amritsar (Attari) and Delhi, India. The weekly Thar Express also runs between Karachi and Bhagat Ki Kothi (near Jodhpur, Rajasthan).
India -
Thar Express to Karachi and the more famous Samjhauta Express international train from Lahore, Pakistan to Amritsar (Attari) and Delhi, India. The weekly Thar Express also runs between Karachi and Bhagat Ki Kothi (near Jodhpur, Rajasthan).
![]() Turkmenistan -
Via Afghanistan (proposed) – avoiding 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge (or narrow gauge) intervening.[19]
Turkmenistan -
Via Afghanistan (proposed) – avoiding 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge (or narrow gauge) intervening.[19]
Miscellaneous
In Ghangha Pur, a historic, 2 ft (610 mm) narrow gauge[20] horse-drawn tramway exists. It first opened in 1898, closed in 1998, and re-opened in 2010.[21]
Road
National highways
During the 1990s, Pakistan began an ongoing project to rebuild all national highways throughout the country specifically to important financial, cargo and textile centers. The National Highway Authority or NHA is responsible for the maintenance of all national highways in Pakistan.
- The Makran Coastal Highway follows the coast of Sindh and Balochistan provinces, linking Karachi and Gwadar. Journey time has been reduced to six or seven hours with the construction of the new Coastal Highway. The highway was built as part of an overall plan to improve transport facilities in southern Balochistan.
- The Karakoram Highway is the highest paved international road in the world. It connects China and Pakistan across the Karakoram mountain range, through the Khunjerab Pass.

- The Grand Trunk Road (commonly abbreviated to GT Road) is one of South Asia's oldest and longest major roads. For several centuries, it has linked the eastern and western regions of the South Asia, running from Bengal, across north India, into Peshawar in Pakistan.
- The Silk Road is an extensive interconnected network of trade routes across the Asian continent connecting East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean world, including North Africa and Europe. It passes through the midsection of Pakistan through cities: Peshawar, Taxila and Multan.
Motorways
The construction of motorways began in the early 1990s with the idea building a world class road network and to reduce the load off the heavily used national highways throughout the country. The M2 was the first motorway completed in 1998, linking the cities of Islamabad and Lahore. In the past 5 years, many new motorways have opened up including the M1, M3 whereas M4 is near to complete which connects city of Faislabad to Multan covering major cities in between Gojra, Toba Tek Singh, Jhang, Shorkot, Pir Mahal and Khanewal.
- Total: 257,683 km
- Paved: 152,033 km (including 339 km of expressways)
- Unpaved: 105,650 km (2001)
- Vehicles on road: 4.2 million vehicles 250,000 commercial vehicles (2004 estimate)
Provincial Highways
- Provincial Highways of Azad Kashmir
- Provincial Highways of Balochistan
- Provincial Highways of Gilgit-Baltistan
- Provincial Highways of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
- Provincial Highways of Punjab
- Provincial Highways of Sindh
Air transport
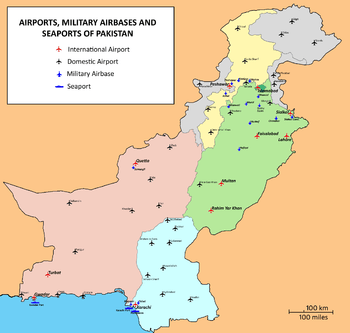
Pakistan has 148 airports.[8] The major airports are:
- Jinnah International Airport (Karachi)
- Allama Iqbal International Airport (Lahore)
- Benazir Bhutto International Airport (Rawalpindi)
- Peshawar International Airport (Peshawar)
- Quetta International Airport (Quetta)
- Faisalabad International Airport (Faisalabad)
- Multan International Airport (Multan)
- Sialkot International Airport (Sialkot)
- Dera Ghazi Khan International Airport (D.G.Khan)
- Gwadar International Airport (Gwadar)
- Shaikh Zayed International Airport (Rahim Yar Khan)
New Islamabad International Airport is also under construction in Rawalpindi District and Attock District South-West of Islamabad.
There are also several smaller airports which have flights to and from the Gulf because of the large Pakistani diaspora working in the region. There are 91 airports with paved runways of which 14 have runways longer than 3,047 meters. The remaining 48 airports have unpaved runways including one airport with a runway longer than 3,047 meters. Pakistan also has eighteen heliports.[8]
Waterways
The waterway network in Pakistan is in its infancy with Karachi being the only major city situated next to the Arabian Sea. Still plans are being proposed for the development of the waterways in the country along the Indus River and through the Punjab as it would boost employment opportunities and the economic and social development of Pakistan. See a list of dry ports and sea ports in Pakistan.
- Port of Gwadar – Gwadar, Balochistan
- Port of Karachi – Karachi (City Centre), Sindh
- Port Qasim – East Karachi, Sindh
- Port of Pasni – Pasni, Balochistan
Pipelines
- Length of pipelines for crude oil is 2,011 km (1,250 mi).
- Length of Petroleum products pipeline is 787 km (489 mi).
- Length of Natural gas pipelines is 10,402 km (6,464 mi).
The above information was calculated in 2009.[8]
Bridges
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is an under-construction development program to connect Gwadar Port in southern Pakistan to China's northwestern autonomous region of Xinjiang via highways, railway's[22] and pipelines to transport oil and gas. Chinese Premier Li Keqiang was among the first advocates of the project, since then Chinese President Xi Jinping, formar Pakistani President Asif Ali Zardari and Pakistan Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif have become strong supporters of the project.[23] When the corridor is constructed it will serve as a primary gateway for trade between China and Middle East and Africa, in particular oil from the Middle East could be offloaded at Gwadar, which is located just outside the mouth of the Persian Gulf, and transported to China through the Baluchistan province in Pakistan. Such a link would vastly cut the 12,000-kilometre route that Mideast oil supplies must now take to reach Chinese ports.[24]
The project received a major boost when control of Gwadar was transferred to China's state-owned China Overseas Ports Holding in February 2013. Built by Chinese workers and opened in 2007, Gwadar is undergoing a major expansion to turn it into a full-fledged, deep-water commercial port. On 19 February 2014, South China Morning Post reported that Pakistan and China have signed agreements for constructing an international airport at Gwadar, for upgrading a section of the 1,300-kilometre Karakorum Highway connecting to Islamabad and of a fibre-optic cable to be laid from the Chinese border to the Pakistani city of Rawalpindi.[25] [26] According to the The Diplomat with the development of the corridor, Central Asia, traditionally an economically closed region owing to its geography and lack of infrastructure, will have greater access to the sea and to the global trade network.[27] Pak-China Economic Corridor Secretariat was inaugurated in Islamabad on August 27, 2013.[28]
Gallery
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Transport in Pakistan. |
- Airlines of Pakistan
- Buses in Pakistan
- Auto rickshaw
- Customised buses and trucks in Pakistan
- Pakistan Civil Aviation Authority
- Karakoram Highway
- Khyber Pass
- Lahore Railway Station
- Makran Coastal Highway
- Mobile World Magazine
- Motorways of Pakistan
- National Highways of Pakistan
- Port of Karachi
- Pakistan International Airlines
- List of bus routes in Lahore
- Road signs in Pakistan
References
- ↑ Stations connected by transfers are counted as one station, unless otherwise noted.
- ↑ "City to lose 620 trees for Orange Line train".
- ↑ http://www.hcs.com.pk/index.php/projects/projects-completed.html
- ↑ "Lahore Metro Bus service inaugurated". The News International. 10 February 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ↑ "Shahbaz to inaugurate work on Metro Bus Service on Feb 28". Dawn. 28 February 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
- ↑
- ↑ National University of Sciences and Technology, Pakistan Students Design Pakistan's First-ever Hybrid Car
- ↑ Objectives of Pak-Wheelers
- 1 2 3 4 The Central Intelligence Agency. "World Factbook – Pakistan". Retrieved 2007-06-28.
- ↑ http://pakobserver.net/detailnews.asp?id=242308
- ↑ http://www.thenews.com.pk/Todays-News-13-30491-First-Pakistani-metro-train-to-run-in-Lahore
- ↑ Railway Gazette International
- ↑ "Govt considers railway links with central Asia".
- ↑ Associated Press of Pakistan. "PR signs deal with foreign firm for pre-feasibility study of Pakistan-China rail link". Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-06-28.
- ↑ http://www.thaishipper.com/Content/Content.asp?ID=26715
- ↑ "First container train service from Islamabad to Turkey begins Today". Pakistan Times. 2009-08-15. Retrieved 2009-08-15.
- ↑ "Leading News Resource of Pakistan". Daily Times. Retrieved 2009-08-15.
- ↑ "Pakistan | PM launches trial phase of Pak-Turkey train service". Dawn.Com. Retrieved 2009-08-15.
- ↑ "Pakistan–Turkey rail trial starts". BBC News. 2009-08-14. Retrieved 2009-08-16.
- ↑ Dr John Stubbs (2007-01-01). "Closing the gap from Bam to Zahedan". Railway Gazette International.
- ↑ Zeitschrift Blickpunkt Straßenbahn (Tram Focus Magazine) – Trams of the World 2013
- ↑ All Things Pakistan – Ghora Tram: Historic Horse Tram Returns to Gangapur, 9 March 2010
- ↑ Pak-China Economic Corridor to get high-speed railway track
- ↑ China, Pakistan Flesh Out New ‘Economic Corridor’
- ↑ Pak-China ties: Gawadar port one part of a larger plan
- ↑ China and Pakistan pave way for ‘economic corridor’
- ↑ China Pakistan
- ↑ The Pakistan-China Corridor: A new project will give Pakistan the tools of globalization. Will it use them?
- ↑ Pak-China Economic Corridor Secretariat inaugurated in Islamabad
External links
- Sindh Transport Department official website
- Pakistan Railways official website
- Karachi Port Trust website
- Daewoo Bus Service
- Pakistan International Airlines website
- Pakistan National Highway Authority website
- Decorated Vehicles at Pakistanphotos.co.uk
- Pakistani railways map at the United Nations
- Transport map of Pakistan at Relief Web
- Buy Online Used Cars For Your Own Transportation
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.






.jpg)







