Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
| Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic | ||||||||||||||
| Узбекская Советская Социалистическая Республика Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Motto Butun dunyo proletarlari, birlashingiz! Бутун дунё пролетарлари, бирлашингиз! "Workers of the world, unite!" | ||||||||||||||
| Anthem Anthem of the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic | ||||||||||||||
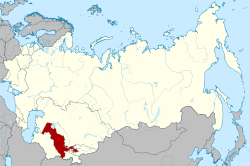 Location of the Uzbek SSR within the Soviet Union. | ||||||||||||||
| Capital | Samarkand (1924–1930) Tashkent (1930–1991) | |||||||||||||
| Languages | Uzbek, Russian | |||||||||||||
| Government | Soviet Socialist Republic | |||||||||||||
| First Secretary | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1925–1927 (first) | Vladimir Ivanovich Ivanov | ||||||||||||
| • | 1989–1991 (last) | Islam Karimov | ||||||||||||
| Head of government | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1924–1937 (first) | Fayzulla Khodzhayev | ||||||||||||
| • | 1990–1990 (last) | Shukrullo Mirsaidov | ||||||||||||
| Legislature | Supreme Soviet | |||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||
| • | Established | 27 October 1924 | ||||||||||||
| • | State sovereignty declared | 20 June 1990 | ||||||||||||
| • | Renamed Republic of Uzbekistan/Independence | 31 August 1991 | ||||||||||||
| • | Completed | 25 December 1991 | ||||||||||||
| • | New Constitution | 8 December 1992 | ||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1989 | 447,400 km² (172,742 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1989 est. | 19,906,000 | ||||||||||||
| Density | 44.5 /km² (115.2 /sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| Calling code | +7 36/37/436 | |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Today part of | | |||||||||||||
| | ||||||||||||||
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (Uzbek SSR; Uzbek: Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Sovet Sotsialistik Respublikasi'; Russian: Узбекская Советская Социалистическая Республика, Uzbekskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika), also referred to as Soviet Uzbekistan or Uzbekistan, was one of the republics of the Soviet Union. It was created in 1924. It was governed by the Uzbek branch of the Soviet Communist Party, the only legal political party, from 1925 until 1990. From 1990 to 1991, it was the sovereign part of the Soviet Union with its own legislation.
Beginning 20 June 1990, Uzbek SSR adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty within its borders. Islam Karimov became the republic's inaugural president.
On 31 August 1991, the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic was renamed to the Republic of Uzbekistan and declared independence three months before the Soviet Union's dissolution on 26 December 1991. The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic officially ceased to exist upon the adoption of the new constitution on 8 December 1992.
History
In 1925, the borders of political units in Central Asia were changed along ethnic lines determined by Vladimir Lenin’s Commissar for Nationalities, Joseph Stalin. The Turkestan ASSR, the Bukharan People's Republic, and the Khorezm People's Republic were abolished and their territories were divided into eventually five separate Soviet Socialist Republics, one of which was the Uzbek Socialist Soviet Republic (Uzbek SSR), created on 27 October 1924. The next year the Uzbek SSR became one of the republics of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Soviet Union). In 1928, the collectivization of land into state farms was initiated, which lasted until the late 1930s.
The Uzbek SSR included the Tajik ASSR until 1929, when the Tajik ASSR was upgraded to an equal status. In 1930, the Uzbek SSR capital was relocated from Samarkand to Tashkent. In 1936, the Uzbek SSR was enlarged with the addition of the Karakalpak ASSR taken from the Kazakh SSR in the last stages of the national delimitation in the Soviet Union. That same year in December, it was renamed to the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic. Further bits and pieces of territory were transferred several times between the Kazakh SSR and the Uzbek SSR after World War II.
In 1937–38, during the Great Purge, a number of alleged nationalists were executed, including Faizullah Khojaev, the first prime minister.

During World War II, many industries were relocated to the Uzbek SSR from vulnerable locations in western regions of the USSR to keep them safe. Large numbers of Russians, Ukrainians and other nationalities accompanied the factories, altering the demographics of the republic. The demographics situation was further aggravated by Stalin’s relocation of some ethnic groups suspected of collaboration with the Axis powers from other parts of the USSR to the Uzbek SSR. This included large numbers of ethnic Koreans, Crimean Tatars, and Chechens.
During the Soviet period, Islam became a focal point for the antireligious drives of Communist authorities. The government closed most mosques, and religious schools became anti-religious museums. On the positive side was the virtual elimination of illiteracy, even in rural areas. Only a small percentage of the population was literate before 1917; this percentage increased to nearly 100 percent under the Soviets.
Another major development, one with future catastrophic impact, was the drive initiated in the early 1960s to substantially increase cotton production in the republic. This drive led to overzealous irrigation withdrawals of irrigation water from the Amu Darya and the subsequent Aral Sea ecological disaster.
The Communist Party was the only legal party in the Uzbek SSR until 1990. The first secretary, or head, of the Communist Party of Uzbekistan was consistently an Uzbek. Long-time leader of the Uzbek SSR was Sharof Rashidov, head of the Communist Party of Uzbekistan from 1959 to 1983. Islam Karimov, leader of the Communist Party of Uzbekistan since 1989 and subsequently head of that party's reincarnation, the People's Democratic Party (PDP), became president of the Uzbek SSR in 1990. On 20 June 1990, the Supreme Soviet adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Uzbek SSR, which took over the laws of the Soviet Union days after the Russian SFSR adopted theirs.
Independence

Uzbek SSR participated in the referendum in March 1991 as a part of the proposed Union of Sovereign States. This never came to pass after unsuccessful coup attempt events between 19-21 August 1991 in Moscow. In the aftermath, the Uzbek SSR was renamed the Republic of Uzbekistan and declared its independence on 31 August 1991, formally remaining a part of the Soviet Union until 26 December 1991. With the final collapse of the Soviet Union, the Uzbek SSR became the independent nation of Uzbekistan. The referendum was confirmed on 29 December 1991.
Subdivisions
| Eastern Bloc |
|---|
 |
|
Allied states |
|
Dissent and opposition 1953 uprisings
1956 protests
|
List of changes
- 1924-10-27 creation of Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
- 1929-10-15 Tajik Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic[1] and a region around Khujand/Khodzhent split off and become the Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic
- 1936-12-05 Karakalpak Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was joined to the Uzbek SSR
- 1963-02-16 Syr Darya Oblast (center: Gulistan) is formed. "In 1973 a large part of the oblast’s territory was transferred to the newly formed Dzhizak Oblast"[2]
- 1973-12-29: Dzhizak Oblast split from Samarkand Oblast,[3] Ru WP: Dzhizak is formed
- ca. 1981: Navoiy Oblast split from Bukhara Oblast[4]
- 1982-04-20 Ru WP Navoiy Oblast is formed
1927
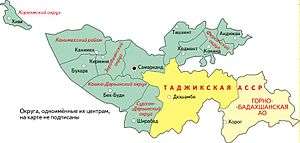
- Khorezm Okrug (cap: Khiva)
- Kanimekh Raion (cap.: Kanimekh)
- Bukhara
- Zeravshan Okrug (cap: Kermine)
- Kashka-Darin Okrug (cap: Bek-Budi)
- Samarkand
- Surkhan-Darshin Okrug (cap: Shirabad)
- Tashkent
- Khotshent
- Fergan Okrug (capital: Kokand)
- Andizhan
- Tajik ASSR
- Dushanbe
- Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Oblast (cap:Khoror)
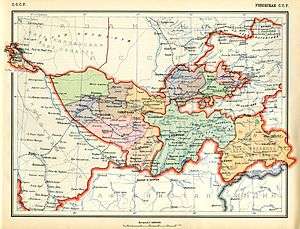
1936
Constitution of the USSR:
ARTICLE 26. The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic consists of the Bukhara, Samarkand, Tashkent, Ferghana, and Khorezm Regions, and the Kara-Kalpak Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic.[5]
1938
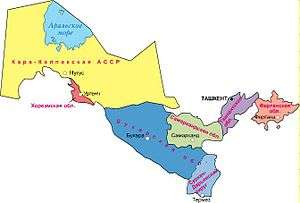
- Karakalpak Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (Nukus)
- Khorezm Oblast (cap: Urentsh)
- Bukhara Oblast
- Surkhan-Darshin Okrug (today: Surxondaryo Province)
- Samarkand Oblast (today: Samarkand Province, Jizzakh Province, Sirdaryo Province)
- Tashkent Oblast
- Fergana Oblast (capital: Fergana, today: Namangan Province, Andijan Province, Fergana Province)
1989
- Karakalpak ASSR
- Khorezm Oblast
- Bukhara Oblast
- Samarkand Oblast
- Kashkadarya Oblast
- Surkhadarya Oblast
- Jizzakh Oblast
- Syrdarya Oblast
- Tashkent Oblast
- Andijan Oblast
- Namangan Oblast
- Fergana Oblast
1991
References
- ↑ Uzbekistan Regions. Statoids.com.
- ↑ Syr Darya Oblast definition of Syr Darya Oblast in the Free Online Encyclopedia. Encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com.
- ↑ Uzbekistan Regions. Statoids.com.
- ↑ Uzbekistan Regions. Statoids.com.
- ↑ 1936 Constitution of the USSR, Part I. Departments.bucknell.edu.
External links
- Uzbekistan; Another Big Leap Forward by Afif Alimov
Coordinates: 59°25′00″N 24°45′00″E / 59.4167°N 24.7500°E



